Solana's Dark Forest Rules: Uncovering the Capital Game of Thrones behind MEV's Monopoly Profits

Reprinted from panewslab
04/23/2025·24DThe Memecoin craze has made Solana a gold sacred place for traders over the past year. Countless people chased the Meme coins that had skyrocketed and plummeted, trying to seize the opportunity with Trading Bot. But few people realize that the profit-making business that truly makes steady profits does not jump on the K-line chart, but is hidden deep in the dark forest of blockchain. This is MEV (maximum extractable value).
Compared with the publicly visible Bot income, the income of MEV is often hidden in the block construction and sorting mechanism, and the "invisible hand" that masters it is often the "invisible hand" that controls on-chain power and infrastructure. Many people don’t know that this system has a high operating threshold, extremely asymmetric information, and extremely concentrated controllers.
When you use Bot to grab the inner trading and anti-pinch, the MEV catcher controls the trading order behind the scenes and accurately captures the arbitrage space; when retail investors compete for hand speed and strategy, large institutions with pledge advantages and node authority have relied on their structural advantages to firmly sit at the top of the income pyramid.
In Solana, MEV is not just a trading opportunity, it is also an infrastructure-level power-it is controlled by a very small number of people, forming a capital game with high threshold, high monopoly and high profits. Today we will reveal the big business of Solana on MEV.
1. First of all, what is MEV?
MEV is called miners extractable value, which means that when miners package blocks, they can include, omit and sort transactions, thereby earning as much additional income as possible. Due to the Memecoin boom and DeFi active, MEVs are huge.
From a business perspective, MEVs usually include: liquidation, arbitrage and sandwich attacks.
• Liquidation: Liquidate loan positions that are on the verge of default for rewards.
When borrowers fail to maintain the mortgage rate required for loans in the lending agreement, their positions will be eligible to be liquidated. MEV searchers monitor these under-collateralized positions on the blockchain and perform liquidation by repaying some or all of the debt in exchange for part of the collateral as a reward.
• Arbitrage: Buy and sell on different DEXs at the same time and make profits by using the price spread.
The simplest arbitrage is when two DEXs have different prices for the same trading pair, the arbitrageur uses a transaction to earn the difference from it.
• Sandwich Attack: Buy before the target transaction and then sell to make a profit.
Sandwich attack is an arbitrage strategy in the DeFi market. The attacker realizes profit through three atomic bundling transactions: first, pushing the asset price up to the highest level allowed by the victim's slippage with an unprofitable preemptive transaction, then the victim's transaction is executed at a high level, further pushing the price up. Finally, the attacker sells the asset at an inflated price through a repurchase transaction (post-trading), offsetting the initial cost and obtaining net profit.
In terms of behavior, the general difference is front-run (first transaction) and back-run (post-transaction)
• Pre-Trading: Pre-Trading refers to the MEV searcher identifying another trader’s buy or sell order in the memory pool and placing the same order before that trader makes a profit from the price impact on another trade.
• Post-Trading: Post-Trading is the correspondence of a preemptive transaction, a specific MEV strategy that takes advantage of temporary price imbalances caused by another transaction, which are usually caused by improper routing. Once a user's transaction is executed, the reverse transaction searcher will balance the prices of each fund pool by trading the same asset and ensure profit.
The liquidation is back-run, most arbitrage is back-run, and the sandwich attack is front-run + back-run. For specific MEV cases, you can refer to Helius' report, which contains very detailed explanations and examples.
2. How big is the MEV business?
According to some unverified statistics, last year, trading robots made $1.1 billion, pump made $500 million, mev made $1.5 billion, amm made $1 billion, and celebrity affiliates such as Trump made $500 million, and were taken off-site by nearly $5 billion.
On the Solana network, with the rise in network activity and the arrival of the Memecoin boom in 2024, MEV revenue on Solana has also risen sharply. From Helius' report, Jito's arbitrage detection algorithm analyzes all Solana transactions, including those outside the Jito bundle, which has identified 90,445,905 successful arbitrage transactions over the past year. The average profit per arbitrage was $1.58, and the single arbitrage earnings with the highest profit was $3.7 million. These arbitrages generated $142.8 million in profits, of which $126.7 million (88.7%) were denominated in SOL.
MEV is a big business!
3. The MEV on Solana is particularly serious, the MEV king---Jito
The MEV on Solana is more intense and centralized than the MEV on ETH, which is due to the difference in the underlying design of their chain.
Solana: High performance --> Sacrifice some decentralization --> High centralization --> High power centralization
Solana is known for its high performance, with block time of only 400 milliseconds (12 seconds on Ethereum), but its design sacrifices part of the decentralization, resulting in a high concentration of power.
Since there is no memory pool on Solana, other nodes must connect with the currently generated validator node to obtain the block data and submit transactions. This design gives up the validator nodes of blocks with great power and lack of mechanism checks and balances, which leads to serious MEV problems on Solana and high returns.
In contrast, Ethereum's MEV market is more market-oriented. There is a high level of competition between MEV Searchers and Block Builders, which drives down overall MEV returns.
Jito is Solana's MEV overlord. In August 2022, Jito launched the Jito-Solana client. In the first nine months, Jito-Solana client adoption has been below 10% due to low network activity and limited MEV rewards. Starting from the end of 2023, adoption has accelerated significantly, reaching 50% by January 2024. As of the end of 2024, more than 94% of Solana validators (weighted by equity) use the Jito-Solana client, forming an absolute dominance.
How does Jito work?
The biggest difference between Jito-Solana client and official client is that it natively supports MEV extraction mechanism, and its core function is to provide Bundles services. The validator runs the client, which means joining the Jito alliance. The alliance provides a transaction priority execution channel for the outside world, and traders submit bundles through tips (Tips) to gain the advantage of transaction sorting. Therefore, the Jito client significantly improves the node's revenue capabilities compared with the official client.
- 1. Jito Bundles (Jito Bundles)
Jito Bundles allows traders to prioritize submitting and executing key transactions by bundling transactions and paying tips. This is not only suitable for MEV opportunities, but is also often used for other purposes such as acceleration, batch trading, and trading anti-pinching. The core process is as follows:
1. Trading assembly: Traders discover arbitrage opportunities and quickly build transactions.
2. Bundle submission: encapsulate the transaction into a bundle and send it to the Jito node, accompanied by a tip to increase the sorting priority. These bundles will be passed to the block leader by Jito nodes.
3. Priority execution: If a Jito verifier becomes the leader of the current Slot, these transactions will be packaged into the block first and executed in the preamble position. The benefits will be distributed to validators and Jito protocols by mechanism.
- 2. Jito 's pledge mechanism
We mentioned earlier that the more money you pledge on the Jito node, the more Tips and MEV revenue will be. Therefore, Jito nodes need to attract more SOLs to stake on them. Therefore, the Jito protocol will allow users to pledge and share the pledge income and MEV income of some nodes to these users.
To further expand the amount of its node staking, Jito launched a staking agreement, allowing ordinary users to delegate SOL to Jito nodes and share block rewards and MEV benefits proportionally. The pledger obtains profits, the node increases the probability of block production, and the trader obtains priority execution opportunities, forming a complete MEV interest closed loop
Three key characteristics of MEV: information advantages, monopoly effect, and capital barrier
1. MEV is an information war, winners take all
Competing for MEV opportunities on Solana is about millisecond-level speed and on-chain information sensitivity. Whoever can discover the arbitrage space as soon as possible and accurately enter the same/next Slot will be able to take advantage of this piece of profit. This depends on two points:
-
Fast information synchronization capability, usually requires RPC services connected to large Jito nodes;
-
Fast transactions are on the chain, priority is given to submit transactions through the Jito Bundles channel, and sufficient Tips are paid.
2. Jito 's bundle service is a monopoly service.
The key to MEV is "who is the leader". Jito If you want to provide traders with stable and reliable bundling services, you must cover as many Leader Slots as possible. This requires that its client has extremely high coverage in the network to ensure that most rounds are Jito nodes to generate blocks.
Once the critical point is reached, the network effect will be self-enhanced: the wider the adoption, the more stable the service will be, and the more difficult it will be to shake the competitors. This is why Jito quickly consolidates 94% of its client share.
3. Solana 's MEV is a capital game
Solana is a PoS chain. The more pledges, the higher the probability of becoming a leader. Leader has the right to sort blocks, so he can naturally get the most MEVs and Tips. This brings about a highly concentrated capital barrier:
-
Large nodes have many stakes, high frequency of blocks, and fast information synchronization;
-
The more sensitive the information, the stronger the arbitrage;
-
Prices of RPC services for large nodes (even services in the same computer room) have risen, becoming a scarce resource for information entrances.
Those who can earn MEV can often only pass the most capitalized nodes.
4. MEV earnings flow on Solana: Who made money?
As mentioned earlier, the MEV revenue on Solana is very considerable. So who will these benefits eventually flow to? It mainly belongs to three core stakeholders: Jito protocol itself, large high-staking nodes, and block space sales brokers.
• Jito Agreement: Taxers of Infrastructure
Over the past year, Jito has processed more than 4.3 billion transaction bundles, resulting in a total of 5.51 million SOL payments, which is worth approximately US$7.7 billion at the SOL price of $140. There is a 3-5% platform share between jito and verifiers, so in fact, the profit of jito itself is about 20-27W SOLs in the past year, that is, about 3,500W US dollars.
• High-staking nodes: On-chain privileged class
Since Solana is a PoS chain, nodes with higher pledge amounts have a higher probability of block generation. These "head validators" can not only continuously obtain base block rewards and inflation gains, but also get a large number of trading Tips from Jito Bundles. The normal node income is about 6%. When the network activity is high, the annualized income of some nodes can reach more than 20%, which is far higher than that of ordinary nodes. Its revenue sources include: inflation rewards, block rewards, Jito Tips, and some income from selling SWQoS transactions on-chain rights.
• Block space sales broker: transaction-on-chain intermediary
This type of broker plays the role of a secondary seller in block space. The operating logic is as follows:
-
They establish partnerships with high-staked nodes to purchase transactions on SWQoS at a preferential market price; (Stake-Weighted Quality of Service SWQoS allows leaders to identify and prioritize transactions from staked validators. In the case of network congestion, SWQoS ensures that transactions of high-staked validators are unlikely to be delayed or discarded)
-
Package multiple users' transactions into Jito Bundle and centrally increase Tips to get higher priority;
-
The user pays a lot more Tips than the brokers pay to validators, and brokers earn the difference;
-
At the same time, they also embed their own arbitrage transactions (such as Backrun) in the Bundle to further obtain MEV returns.
For example, you can see some of the revenue data (links) of bloXroute on DefiLlama, which shows that the Tips it receives are very considerable. However, it should be noted that this data does not cover all of its collection addresses, nor does it exclude the shares distributed to validators and order flow providers.
In general, Solana has experienced a high centralization of rights, and most of Jito's MEV returns are captured by Jito protocol, large validator nodes, and block space sales brokers.
5. Solana's client competition landscape
Currently, there are more than 1,300 validator nodes on Solana, and more than 94% of the nodes are Jito nodes. The main clients include the following categories:
• Solana node
This is the most basic node client, without any MEV optimization mechanism, and the nodes running this client have been almost marginalized because the benefits are much lower than those running Jito.
• Jito node
The Jito client is based on the official client and has added the Jito protocol and Bundles support, allowing nodes to accept bundled transactions and collect Tips from them. If users want to achieve demands such as jump-start, anti-pinching, and fast-tracking, they can submit transactions to verifiers through the Jito Bundle service and attach a tip to increase execution priorities. Since nodes running Jito client can earn additional Tips, more than 90% of the nodes on the current main network have been converted to Jito nodes, becoming the default choice.
• Paladin node
Paladin is an improved version based on Jito client, aiming to provide a fairer transaction-first mechanism, mainly solving the "sandwich attack" problem that Jito has in bundle sorting (that is, there are evil validators who insert sandwich transactions but are not punished). According to community information, the current adoption rate of Paladin client is about 15%, and since it is still recognized by the network as a Jito client, it is included in the 94% overall statistics.
• Firedancer node
Developed by Jump Crypto, Firedancer is an independent high-performance Solana client. The original intention is to improve network throughput and facilitate Jump to conduct quantitative transactions. The initial version did not support Jito protocol, so it could not access Tips revenue, and the main network adoption rate was extremely low. But as the new version begins to be compatible with the Jito protocol, validators can also earn Jito Tips revenue using Firedancer. Although the mainnet is currently deployed in fewer mainnets, most nodes on the test network have adopted Firedancer, indicating that they may gain a larger market share in the mainnet in the future. Solana Foundation also supported it.
The competition logic of these node clients:
• Jito VS Paladin: The Fairness Controversy
Due to the high concentration of the Jito protocol, it has formed a factual monopoly on MEV extraction. However, the protocol currently lacks a punishment mechanism for evil behaviors (such as validator sandwich attacks), resulting in users who use bundles still being clipped. This just gives Paladin a client opportunity, which is provided to a bidding process for a fairer transaction priority on the chain. But Paladin was originally modified on Jito-solana. If Jito improves the mechanism in the future, it may suppress Paladin's living space.
• Firedancer VS Other Clients: Performance Replacement
Firedancer's biggest advantage is its performance, which claims that TPS can reach 1 million (theoretical 1 million, the actual effect is unknown). If Solana network transaction volume continues to grow in the future, high-performance client nodes that can meet performance requirements will gain advantages and squeeze low-performance clients. Once a high-performance node starts to package larger blocks, low-performance clients may not keep up with the synchronization progress, affecting verification performance and eventually being marginalized. Therefore, when our TPS demand for Solana is higher, it will drive the entire Solana network to natural migration to high-performance clients.
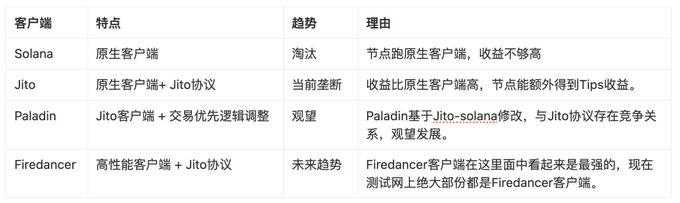
In general: Most nodes on the Solana mainnet run Jito-Solana client, and the Jito protocol has become part of the infrastructure. As the Firedancer client begins to be compatible with the Jito protocol, the main network may experience iterative upgrades in the future - from "you can make more money by running Jito" to "you can run high-performance Jito without being eliminated."
6. How can large institutions become interest traders on Solana step by
step?
Solana's architecture naturally tends to centralize power, which provides a favorable soil for large institutions to intervene and dominate the ecology. Solana Foundation, Jito, Multicoin, Jump, Helius, Coinbase, Binance, Jupiter, etc. have great governance power in Solana. There are also many institutions that are optimistic about Solana's future prospects and hope to become one of the interests traders on Solana. Taking Sol Strategies, which has frequent recent trends as an example, we can clearly see how large institutions can take step by step and become Solana's interest traders:
Step 1: Sol Stratagies has become one of the main players by acquiring nodes to expand its market share and ecological dominance.
Solana's current staking rate is as high as 65.6% (about 380 million SOLs are pledged), controlling the validator nodes means mastering the consensus mechanism and voting rights of the network. Sol Strategies acquires top nodes on a large scale and quickly enters the core of power:
• 2024.11: Cogent Crypto, a verification node operator for Solana, Sui, Monad and ARCH networks, is focusing on the SOL network for US$18 million (cash + stock).
• 2025.03: Acquisition of Solana's head verification nodes Laine and Stakewiz.com for CAD 35 million (cash + equity), the number of pledged SOLs increased to 3.3 million (valued at approximately US$388 million), and absorbed Laine founder Michael Hubbard as chief strategy officer.
Step 2: Try to promote inflation rate adjustment proposal SIMD-228 to further consolidate your power. (This proposal was not passed in the end)
SOL Strategies pushes SIMD-228 proposal to adjust the inflation mechanism, which aims to introduce dynamic inflation mechanisms to replace the current fixed deflation model. If the proposal is passed, Solana's annualized inflation rate will drop from a fixed interest rate of 4.68% to 1% or even 0%. Although the proposal was not approved in the end, the strategic intentions behind it are very clear:
• Stable SOL value: Reducing inflation can reduce the release of new SOLs, alleviate token selling pressure, and increase long-term returns of pledgers;
• Suppress small nodes and consolidate the dominance of large nodes: Reduced inflation will compress the benefits of all validators, but small nodes have weaker risk resistance and are easily eliminated, which is conducive to promoting the concentration of the network to the top validators.
Step 3: Solana's interest trading. Promote the listing of Solana ETFs, institution of Crypto assets, and become an ETF pledge provider.
Sol Strategies becomes a staking provider of 3iQ Solana Staking ETFs and promotes the listing of 3iQ Solana Staking ETFs. Try to further expand the pledge volume and compete for the dominance of blockchain governance.
Summarize:
1. MEV is a big business. Especially the MEV on Solana is particularly dramatic and has high profits.
2. Jito's MEV protocol is a monopoly agreement and has a strong head effect.
3. The rights on Solana are highly centralized, and the money of MEV is mainly captured by Jito protocol, high-staking nodes, and block space sales brokers.
4. There are now multiple clients on the Solana network. Jito-Solana client currently dominates the main network, and Firedancer client that supports the Jito protocol may become a high-performance upgrade version in the future.
5. Solana is very suitable for institutional leadership. SOL Strategies demonstrates how an institution can penetrate Solana from technology, governance to financial system and compete for blockchain governance sovereignty through mergers and acquisitions nodes, attempts to promote governance proposals, and promote ETF listings.
References:
https://www.helius.dev/blog/solana-staking-simplified-guide-to-sol-staking


 jinse
jinse