Slow fog: Cetus theft incident analysis, 1 token leverages US$230 million, SUI Foundation assists in freezing 162 million

Reprinted from chaincatcher
05/27/2025·12DOriginal title: "Slow Fog: Analysis of the stolen US$230 million event in Cetus"
Original author: Victory, Lisa, Slow Fog Technology
background
On May 22, according to community news, Cetus, a liquidity provider on SUI ecosystem, was suspected to be attacked, and the depth of the liquidity pool has dropped significantly. Several token trading pairs on Cetus fell, with an estimated loss of more than US$230 million. Cetus later issued an announcement saying: "A incident was detected in our agreement. For security reasons, the smart contract has been temporarily suspended. Currently, the team is investigating the incident. We will issue further investigation statements soon."
After the incident, the Slow Fog Security Team intervened in the analysis as soon as possible and issued a safety reminder. The following is a detailed analysis of the attack methods and capital transfer situation.

Related information
The core of this incident is that the attacker carefully constructs parameters so that the overflow occurs but can bypass detection. Finally, he can exchange a very small amount of token token to exchange for huge liquid assets. The following are the specific steps analysis:
 (Attack timing chart)
(Attack timing chart)
1. The attacker first borrowed 10,024,321.28 haSUIs through Lightning Loan, causing the pool price to plummet from 18,956,530,795,606,879,104 to 18,425,720,184762,886, with a price decline of 99.90%.

2. The attacker carefully selected a very narrow price range to open a liquidity position:
Tick Lowest Limit: 300000 (Price: 60,257,519,765,924,248,467,716,150)
Tick cap: 300200 (price: 60,863,087,478,126,617,965,993,239)
Price range width: only 1.00496621%
3. Then is the core of this attack. The attacker stated that he would add 10,365,647,984,364,446,732,462,244,378,333,008 units of huge liquidity, but due to the vulnerability, the system only charged 1 token A.

Let’s analyze why an attacker can exchange 1 token for huge liquidity. The core reason is that there is an overflow detection bypass vulnerability in checked_shlw in the get_delta_a function. This is what the attacker takes advantage of, causing severe deviations in the system when calculating how many haSUIs it actually needs to be added. Since the overflow was not detected, the system misjudged the number of required haSUI, resulting in the attacker being able to exchange a large number of liquid assets with only a very small token, thus realizing the attack.
When the system calculates how much haSUI is needed to add such huge liquidity:

The key here is that the implementation of the checked _ shlw function has serious flaws. In fact, any input value less than 0xffffffffffffffff << 192 bypasses overflow detection. However, when these values are shifted left by 64 bits, the result will exceed the representation range of u256, and the high-bit data is truncated, resulting in the result being much smaller than the theoretical value. This way, the system underestimates the required number of haSUIs in subsequent calculations.

· Error mask: 0xffffffffffffffffff << 192 = Very large value (about 2^256-2^192)
Almost all inputs are smaller than this mask, bypassing overflow detection
· The real problem: When n >= 2^192, n << 64 will exceed the u256 range and be truncated
The intermediate value liquidity * sqrt _ price _ diff = 6277101735386680763835789423207666908085499738337898853712:
· Less than the error mask, bypassing overflow detection
· However, after shifting left by 64 bits, the maximum value of u256 will be exceeded, resulting in the excess being truncated
· The final calculation result is about 1, but because it is rounded upward, quotient calculation is equal to 1

4. Finally, the attacker removes liquidity and obtains huge token returns:
· First removal: Obtain 10,024,321.28 haSUI
· Second removal: Obtain 1 haSUI
· Third removal: Obtain 10,024,321.28 haSUI

5. The attacker returned the flash loan, with a net profit of approximately 10,024,321.28 haSUI and 5,765,124.79 SUI, and the attack was completed.
Project repair situation
After the attack, Cetus released a fix patch. For specific repair codes, please refer to: https://github.com/CetusProtocol/integer-mate/pull/7/files#diff-c04eb6ebebbabb80342cd953bc63925e1c1cdc7ae1fb572f4aad240288a69409.
The fixed checked _ shlw function is as follows:

Fixed Note: Correct the wrong mask 0xffffffffffffffffffffffff << 192 Correct the correct threshold 1 << 192 Correct the judgment condition from n > mask to n >= mask Ensure that when shifting the left by 64 bits may cause overflow, the overflow flag can be detected correctly and returned.
MistTrack Analysis
According to analysis, the attacker 0xe28b50cef1d633ea43d3296a3f6b67ff0312a5f1a99f0af753c85b8b5de8ff06 made a profit of approximately US$230 million, including SUI, vSUI, USDC and other assets.

We found that the attacker had Gas Fee ready two days ago and then made a try before the attack, but failed:

After making a profit, the attacker crosses the funds such as USDC, SOL, and suiETH through cross-chain bridges such as Sui Bridge, Circle, Wormhole, and Mayan to the EVM address 0x89012a55cd6b88e407c9d4ae9b3425f55924919b:

Among them, 5.2341 WBNB cross-chain to BSC address 0x89012a55cd6b88e407c9d4ae9b3425f55924919b:

The attacker then deposited $10 million worth of assets into Suilend:

The attacker also transferred 24,022,896 SUI to the new address 0xcd8962dad278d8b50fa0f9eb0186bfa4cbdecc6d59377214c88d0286a0ac9562, which has not been transferred out yet:
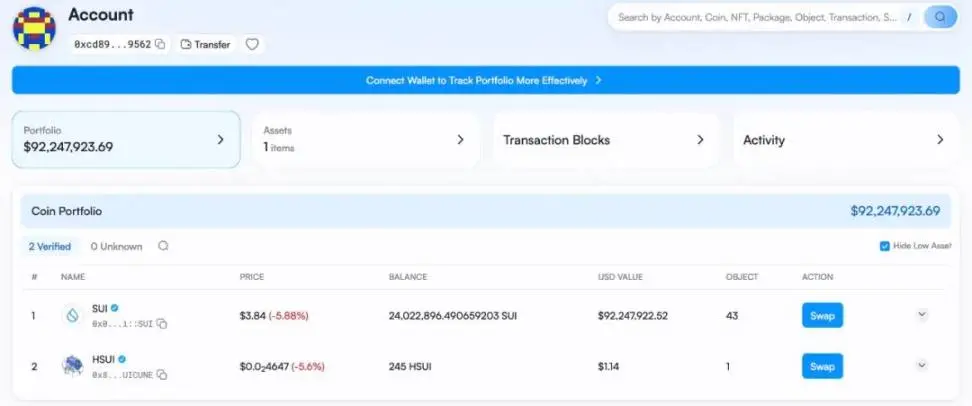
Fortunately, according to Cetus, the $162 million stolen funds on SUI have been successfully frozen under cooperation with the SUI Foundation and other ecosystem members.
 (https://x.com/CetusProtocol/status/1925567348586815622)
(https://x.com/CetusProtocol/status/1925567348586815622)
Next, we use the on-chain anti-money laundering and tracking tool MistTrack to analyze the address 0x89012a55cd6b88e407c9d4ae9b3425f55924919b on EVM. This address received 5.2319 BNB on BSC and has not been transferred out yet:

The address received 3,000 USDTs, 40.88 million USDCs, 1,771 SOLs and 8,130.4 ETHs on Ethereum. Among them, USDT, USDC and SOL are exchanged for ETH through coW Swap, Para Swap, etc.:


Then, the address transfers 20,000 ETH to address 0x0251536bfcf144b88e1afa8fe60184ffdb4caf16, and has not yet been transferred out:

The current balance of this address on Ethereum is 3,244 ETH:

MistTrack has added the above related addresses to the malicious address library. At the same time, we will continue to monitor the address balance.
Summarize
This attack demonstrates the power of a mathematical overflow vulnerability. The attacker uses precise calculations to select specific parameters, and uses the flaws of the checked _ shlw function to obtain billions of liquidity at the cost of 1 token. This is an extremely sophisticated mathematical attack, and the Slow Fog Security Team recommends developers to strictly verify the boundary conditions of all mathematical functions in smart contract development.


 jinse
jinse