Reality slaps Web3 in the face How far is we from the real "decentralization"?

Reprinted from jinse
04/30/2025·1MI have long wanted to talk about the topic of " decentralization ". It is not a new word, and it even tastes a bit "censored", but I always feel that it is the most misunderstood and underestimated word of this era.
Now, the opportunity has finally come.
In the past two weeks, Amazon and Google , the two giants in the Web2 world , have mercilessly rubbed the entire encryption industry on the ground with a fiber and a line of scripts. This is not a technical speech, not a philosophical debate, but a naked reality.
So, starting from this article, I will write a three-part series, the title is: "Decentralized Trilogy"
I will try my best to answer the following three questions:
-
How far are we from true “decentralization”? This article you are reading.
-
What is the underlying logic of "decentralization" implementation? Focus on how protocol functionalization fails centralization from the micro perspective.
-
What exactly can "decentralization" bring? Focus on the subversion of Web2 business logic by decentralization.
Don’t talk about slogans, just tell the truth; don’t talk about ideas, talk about reality first.
Let’s start with these two “realistic critical strikes”.
1. Reality Crisis
This is the first time in history that some people clearly see that an invisible "fiber breakpoint" can make 15% of the global crypto spot trading market stuck at the same time.
1.1 First strike: an optical fiber detonates the lifeline of the entire
encrypted chain

In the early morning of April 15, 2025, at 3:00 Tokyo time, Japan, AWS (Amazon Cloud Service) Tokyo area suddenly broke down. In the first 15 minutes, Binance's API response time soared 12 times, MEXC's user withdrawal requests queued for more than 180,000, and KuCoin and Gate.io's pending order failure rates soared to 47.3%.
Not only does transaction delay, but user login also timed out on a large scale. Especially in the 42nd minute of the AWS failure, DeBank wallet data showed that active transaction volumes of addresses on-chain in Asia Pacific plummeted by 58%. The assets are still on the chain, but want to move? ——Sorry, the off-chain account system has been down.
Binance's emergency announcement was very restrained:
We are aware of an issue impacting some services on the #Binance platform due to a temporary network interruption in the AWS data center.Some orders are still successful, but some are failing. If users failed, they may keep retrying.
(Translation) Some orders failed due to an AWS network outage. If you fail, please continue to try again.
MEXC directly alerts:
Abnormal candlestick charts (candle chart exception)
Failed order cancellations
Delays in asset transfers for spot trading
In that hour, the order failed, the order was stuck, and the assets were frozen. The on-chain vault was like it was blocked by an electronic door, and no one could open it. Even if the blockchain network is normal, as long as these key business logics are still entrusted to the centralized server, you are giving your life to "other people's sockets."
1.2 Second click: a line of scripts to "silence" countless crypto
entrepreneurs
8 days later, something more lethal happened.
On April 23, 2025, Google officially implemented the new advertising policy under the Crypto Asset Market Ordinance (MiCA) in the EU:

-
All crypto projects must upload license numbers issued by local financial regulatory agencies when advertising;
-
Unverified accounts will be stopped within 72 hours.
This is not a removal or blocking, and there is no warning. The Google advertising team just quietly added a line of whitelist filtering logic in the background . There was no downtime, no network blocking, and it was normal for users to click on ad links, but these ads disappeared silently from the search results .
Within three days, the advertising traffic in France, Germany and Spain changed rapidly:
-
Advertising volume related to keywords such as "buy bitcoin" and "crypto wallet" plummeted by 67% ;
-
Small and medium-sized projects such as Coinstore, Bitget, and BitMart have even evaporated by 84% of the exposure in some markets .
At the same time, giants such as Crypto.com, Revolut, Bitpanda, etc. that have obtained compliance licenses have taken advantage of the trend to harvest traffic. According to media statistics, in just one week, their number of new users registered more than 5 times higher than that of the banned projects .
Google did not unplug your network cable. It just gently pushes a button in the background and makes you "online" but "no one can see you".
1.3 Two breakdowns reveal a cruel truth
Different methods - one is physical chain break, the other is policy blockade; different performances - one is technical downtime and the other is traffic blockade; but the results are the same:
-
Assets are on the chain, people cannot move them ;
-
The logic of the agreement has not changed, and the market cannot see you ;
-
Under the shell of the system's "decentralization", all key abilities are still parasitized on the centralized platform.
This is not "a company is not lucky." This is a common disease in the entire industry. It was a collective nude run, a fantasy bubble silently exposed by "reality".
It is these two realistic scenes that make us have to ask again:
-
What is true decentralization?
-
Why is decentralization not only a technological ideal, but a minimum guarantee for business survival?
-
If we do not decentralize, what way out will we have when the next disaster comes?
Let’s explain this issue clearly now.
2. What is decentralization
The word "decentralization" sounds like some kind of technical slogan or idealistic slogan. In many people's impression, it is "no company", "no boss", "many nodes", "no servers"... but these expressions are just vague impressions, or even misunderstandings.
To understand "why must be decentralized", we must first answer a seemingly simple but few people really explain it clearly:
What is true "decentralization"?
2.1 Pseudo-decentralization
Let’s first look at three common pseudo-decentralizations:
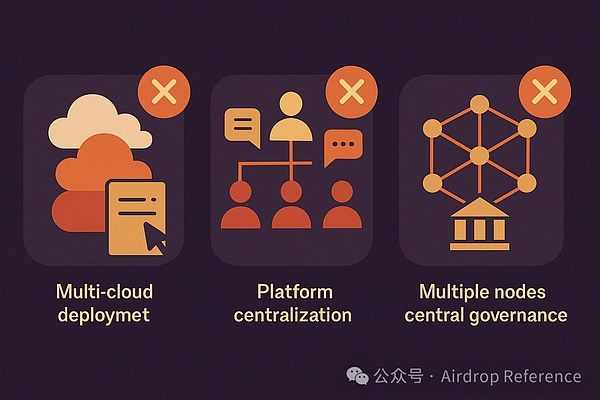
- Misconception 1: Multi-cloud deployment ≠ decentralization
Moving the server from AWS to GCP and preparing an Alibaba Cloud hot backup does not mean decentralization. This is just the redundant fault tolerance of centralized services, it is a physical distribution, not a permission distribution. Control is still concentrated in the hands of a single company, and it can still be cancelled by a "ban" or "freeze" operation.
- Misconception 2: Is DAO a decentralized organization?
If a DAO governance logic is written in Discord and Google forms, rather than in on-chain contracts, then this "DAO" does not even step on the threshold of "authorization that cannot be tampered with". Decentralization ≠ There is no leadership, but every layer of control can be replaced and verified.
- Misconception 3: If there are many nodes, it means decentralization?
If all nodes are operated by a foundation and are only distributed in different regions and IP addresses, then it is essentially a centralized cluster. This is called "false distribution, real center".
2.2 True decentralization
Decentralization is not "no center", but "everyone is center". "Decentralization" in the true sense includes three dimensions: architecture layer, process layer, and governance layer , each of which is indispensable.

2.2.1 Architecture Layer: Distributed Ledger
Public chains such as Ethereum and Bitcoin are representatives of distributed ledgers. Anyone can build nodes and synchronize block data, and all nodes jointly maintain a globally consistent copy of the ledger. This means:
-
If any node is hung up, the network will still be running normally;
-
No one can "delete" or "rewrite" the ledger record;
-
The network status can be reverified at any time.
This is the first line of defense against "physical chain breaks".
2.2.2 Process layer: No permission execution
A truly decentralized system cannot require you to "register an account, submit information, and wait for approval" to participate. For example:
-
Anyone can call a smart contract;
-
Anyone can deploy their own contract or front-end;
-
All function calls are open and transparent and can be reviewed.
For example: Uniswap is a typical "licenseless agreement". Whether you are a Wall Street trader or a novice user in Southeast Asia, as long as you know how to operate your wallet, you can directly call its contract to trade or provide liquidity without any review.
2.2.3 Governance layer: Rules are written into code
In the Web2 world, the rules are set in the background, and the administrator changes it as soon as he says. In the decentralized world of Web3, rules are written into smart contracts and are exposed on the chain. Any changes must be executed through on-chain voting. This is the real "machine cannot lie".

Taking MakerDAO (now renamed SKY) as an example, the collateral rate, interest rate, and support assets of its stablecoin USDS (formerly DAI) need to be decided through MKR token voting, and the voting records are written to the on-chain contract. Any changes are publicly verifiable and cannot be revoked afterwards.
2.3 Comparison diagram: Decentralization vs. Centralization

In a word, "decentralization" is not without control, but like sowing seeds, sowing control in every node, and everyone can verify and replace it.
2.4 The minimum standard for decentralization: Where is the passing line?
Then the question is, how do we determine whether a system is "qualified decentralized"?
Here are the generally accepted minimum standards in the industry (you can treat it as a checklist):

Otherwise, no matter how decentralized the project publicity is, it will be at most "centralized business running on the chain."
3. The real value of decentralization
In the previous section, we explained what true decentralization is from the three dimensions of structure, process and governance.
But it is not enough to just define it. Many people are not against decentralization, they are just-
"I know it's good, but I don't know how good it is."
In other words, we need to use real-world cases to illustrate the key scenarios of decentralization 's actual role .
And this question has been answered harshly once with reality.
3.1 Resilience: Structural redundancy that resists downtime
Recalling the AWS downtime (April 15, 2025):
-
Binance, MEXC, and KuCoin have both pending orders and withdrawal failures;
-
The front-end login of DeBank failed, the on-chain transfer was normal, but the UI stopped responding;
-
Within one hour, the number of interactive addresses on the APAC region on the chain decreased by 58%.
The reason behind this is not actually complicated:
Although the assets are recorded on the blockchain, the transaction matching system, user account system, and risk control audit system are all run on the centralized server. Once the server goes down, the on-chain assets are like being locked in a vault in the basement – you know it’s there, but you can’t get it.
Then the question is: if it is a decentralized system, can it withstand this disaster?
Let's look at a set of data comparisons:

The comparison can be seen:
-
The protocol running on the core business logic chain can still be called through API and the third-party front-end continue to be used normally even if the front-end is lost;
-
Projects that match off-chain and centralized control can only be "waited for cloud recovery".
A summary of one sentence:
Decentralization does not guarantee that you will not have any problems, but it ensures that you will not be completely paralyzed when there is a problem."
3.2 Review Resistance: Disabled Front-end vs Unblockable Agreement
Next, I will use an example to explain this problem thoroughly.
Back in August 2022, the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) under the U.S. Treasury Department officially announced sanctions on Tornado Cash, citing that it was "used as a money laundering tool by North Korean hackers."
The next 72 hours have almost become a "fixed-point clearance" action in global cyberspace:
-
Tornado Cash's GitHub repository was removed from the shelves;
-
The official front-end domain name
tornado.cashis blocked by DNS; -
Cloudflare withdraws TLS support and is not accessible to the front end;
-
Core developer Roman Storm was arrested by the U.S. government;
-
USDC contracts initiate a blacklisting mechanism to freeze all on-chain addresses that interact with Tornado Cash.
According to common sense, this agreement should be "cold".
But the result shocked everyone:
No line of code in Tornado Cash 's smart contract is closed or aborted.
Even if the front-end portal disappears, developers are jailed, and cloud service providers block support, the contract still runs as usual on the Ethereum blockchain . This is not based on people, but on code - the resilience and immutability of decentralized architectures.
3.2.1 The data won 't lie: the protocol is still alive, and someone is using it
Public data from Dune Analytics (@hildobby) shows:
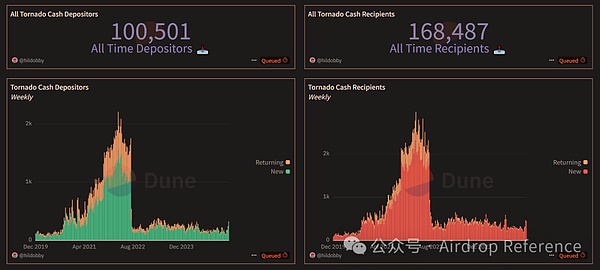
-
A total of 100,501 addresses have been deposited into Tornado Cash;
-
168,487 addresses withdraw assets from them;
-
During the peak period of 2021–2022, more than 2,000 new users were involved every week;
-
Even after the sanctions and continue to this day, hundreds of addresses continue to use the protocol every week.
in other words:
Even if the "official" is eliminated, the "protocol" still replicates, persists itself, and executes itself in a decentralized way.
The community quickly deployed more than 20 front-end images (such as
tornado.eth.limo ), and users can also interact directly through CLI, RPC
tools, ENS addresses, etc., completely bypassing the censorship and blockade
of centralized service providers.
3.2.2 The latest court ruling: Code is not an entity, development is not a crime
What is more noteworthy is that at the end of 2024, this case ushered in a key legal turning point. In a landmark ruling, the U.S. federal court made it clear:
OFAC does not have the authority to include the "open source smart contract code" itself on the sanctions list because it does not constitute an "identifiable controlled entity (Entity).
This ruling conveys a triple judicial position:
-
Smart contracts are not legal persons, companies or organizations and cannot be sanctioned as "subject";
-
Writing and publishing open source contract codes belong to "freedom of speech" protected by the First Amendment;
-
The broad blockade of decentralized protocols is equivalent to reviewing users' "tool choice" and is contrary to constitutional principles.
On March 21, 2025, based on this ruling and policy review, the US Treasury formally removed sanctions on Tornado Cash.
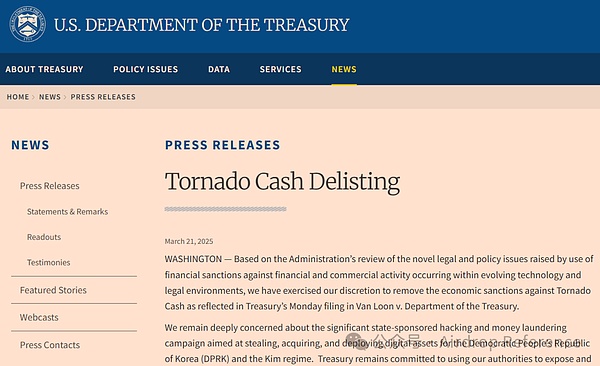
This victory is equivalent to writing a "constitutional-level disclaimer" for global crypto developers and decentralized agreements .
From then on, the boundaries between "writing code" and "doing co-conspiracy" were officially drawn.
3.2.3 Decentralization, defending the right to exist
Whether it is Tornado Cash maintaining the activity of the agreement under the pressure of review or the U.S. court's final denial of OFAC's overreach of power, it reveals a fact:
-
True anti-censorship does not rely on moral appeals, but on structural design;
-
The true "freedom" is not in the homepage button, but in contracts where the code cannot be stopped and permissions cannot be blocked.
This is the real value displayed by decentralization in extreme scenarios - not sentiment, but the technical guarantee of the "right to exist" itself.
3.3 Lower limit of trust: You can trust the system without trusting
anyone
The essence of trust is not that you believe that someone will not do evil, but that he cannot do even if he wants to do evil.
This is exactly the "lower limit of trust" implemented by decentralized systems through code constraints + data disclosure .
For example:

-
When FTX burst in 2022, the user asset deposit and withdrawal operation records were completely opaque;
-
Alameda Research can secretly embezzle user funds up to $8 billion in the background , but the users are completely unaware of it.
On Uniswap, every liquidity injection, every transaction, and every pool fee allocation can be queried in real time through the on-chain browser; in MakerDAO, any change in Stability Fee will be written to the on-chain contract through a 48-hour time lock + referendum record.
Users don't need to believe that the development team has a good character.
As long as you can trust the code and verify the data, it is enough.
3.4 Summary: Decentralization is a tool of survival, not a slogan of
faith
To sum up, decentralization is not more "idealist", but more "realistic".

You don’t need to “believe” in decentralization, you just need to feel its resilience and freedom when systemic risks break out.
4. The Philosophical Dynamics of Decentralization
"You blockchain people just don't want to be regulated."
——This is the first impression of many traditional industry people in the crypto industry.
But if we clear the surface, we will actually find that the motivation for decentralization is not an escape from supervision, but a respect for power, defense of freedom, and the ideal of co-governance .
The real source of decentralization is not Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, but the foreshadowing was laid as early as the late 1980s.
4.1 Personal freedom: The Tinder of Password Punk
Before the torrent of decentralized technology swept the world, a black and white document born in 1988 had quietly written its prophecy.
This is the Crypto Anarchist Manifesto written by Timothy C. May, which is known as the spiritual starting point of the Cypherpunk movement.

A specter is haunting the modern world, the specter of crypto anarchy.
Translation: A ghost, a ghost of crypto-anarchism, wanders in the modern world.
This is the beginning of a parody of the Communist Manifesto. He is not advocating chaos, but reminding: if technology is not allowed to serve freedom, technology will eventually serve monitoring. The declaration reads:
“Computer technology is on the verge of providing the ability for individuals and groups to communicate and interact with each other in a totally anonymous manner.”
“These developments will alter completely the nature of government regulation, the ability to tax and control economic interactions, the ability to keep information secret, and will even change the nature of trust and reputation.”
A simple translation is:
Computer technology is on the verge of providing individuals and groups with the ability to communicate and interact with each other in a completely anonymous way. These developments will completely change the nature of government regulation, the ability to tax and control economic interactions, the ability to keep information confidential, and even the nature of trust and reputation.

Crypunks represented by Timothy C. May are not idealists, they are people who are clearly aware of the boundaries, motivations and speed of corruption in government, businesses, and organizations. They know very well that corruption of power is not "whether it will happen", but "when".
So the answer they gave is:
Don’t rely on morality, but let the technology itself achieve freedom.
In a centralized system, we are always asked to "trust" the platform:
-
Trusting it will not delete your account;
-
I won't block your wallet;
-
Your data will not be recorded and sold.
But in a truly decentralized system, this trust is not needed because:
-
Your private key is kept by yourself and is not on the platform;
-
Your assets exist on the chain and cannot be tampered with;
-
Transaction logic is executed by smart contracts and does not rely on manual matching.
Just like the famous saying that is regarded as a standard by the encryption circle:
“Not your keys, not your coins.”
If you don’t master the private key, you won’t own the assets.
When you use a wallet like MetaMask for the first time, when you use a string of mnemonics to control the overall situation without registering or logging in for the first time, when you find that you can switch front-end, switch RPC, leave any platform at any time, but the assets and rights are still in hand - you will truly realize:
"Freedom" is not a slogan, but a structural right designed.
4.2 Checks and balances of power: Montesquieu-style incentive structure
French Enlightenment Thinker Montesquieu once said:
-
All powerless people are prone to abuse their power, which is an eternal experience.
-
To prevent abuse of power, power must be bound with power.

In modern society, the law, the constitution, and the separation of powers are weapons against the abuse of power; in the decentralized system, the "pled mechanism + consensus algorithm + incentive model" is an algorithm replacement to fight corruption.
Take Ethereum's PoS consensus mechanism as an example:
-
Becoming a verifier requires staking 32 ETH;
-
If you want to do evil (such as double signing, refusing to trade), you will be automatically punished (Slash) ;
-
The punishment is automatically triggered by the consensus layer, irrevocable and non-arbitrary.
This is like a "machine version of separation of powers":
-
Incentives are legislation (the rules are disclosed);
-
On-chain execution is administrative (verification transaction);
-
Node verification is judicial (automatic ruling).
Without such a design, power will inevitably become corrupted after concentration.
For example, some early DPoS public chains (such as EOS) in 2017 experienced problems such as super nodes colluding with "interest dividends" due to voting concentration and node alliances, and the verification process was completely black box operation.

In a more scattered and transparent on-chain recording system, this kind of evil behavior will be immediately detected and dealt with by the community, on-chain analysis tools, and other nodes.
This is the " programmed checks and balances " brought about by decentralization .
4.3 Collaborative Autonomy: DAO writes human-machine co-governance into
code
We know from history that the greatest form of organization of mankind is "cooperation" . But cooperation is never simple. It requires consensus, trust, governance structures and incentives.
DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) is the answer to this proposition by the crypto world. A typical DAO:
-
There is no board of directors, no CEO;
-
Each token holder can vote to participate in the decision;
-
Governance logic is written to on-chain contracts, and all operations are traceable, verifiable, and irrevocable.
Take MakerDAO as an example (now renamed SKY):
-
Its core asset is the decentralized stablecoin USDS (DAI remains);
-
Governance token MKR holders determine interest rate (Stability Fee), collateral asset type, and risk parameters;
-
Decisions are made through on-chain Snapshot voting, and the results are written to the contract;
-
No one can unilaterally "raise interest rates" or "add junk collateral".
In 2024, SKY's DAO management funds exceeded US$6 billion. A "virtual organization" without an office and without a CEO manages more assets than most mid-sized commercial banks.
This governance form of " using machine consensus instead of human credit " has greatly reduced the space for organizational friction and corruption.
More importantly, it lowers the threshold for "participating in governance". Any ordinary person with governance tokens can propose proposals, vote, and influence policies. You are no longer a bystander, but a participant in the rules.
DAO is the " institutional design capability " expressed by technology . It tells us: the human organizational model is not only companies, governments, and foundations, but also "code + community".
4.4 Philosophy: Use technology to protect the most basic civilization
bottom line
Ultimately, the philosophical value of decentralization can be summarized in the three words " freedom-check and balance-co-governance ":

We cannot prevent the existence of a centralized system, but we should ensure that we have a "centralization-free" option .
Because in many cases, this is not only a right, but also a dignity.
Conclusion: Problems after the crisis
At this point, we have completed a penetrating reality review.
From an optical fiber that went down in AWS in Tokyo to a line of scripts banned by Google's EU advertising , we can no longer naively think that the so-called "decentralized industry" means that on-chain transactions run fast and nodes are widely distributed.
The truth is, no matter how much you use DEX, DAO, and DeFi, if:
-
The match is run on a centralized server.
-
Log in with the platform account system.
-
Advertising depends on Web2 platform traffic.
-
Decisions are written in Notion and Discord.
Then, you are still in a centralized and closed system - it may be more vulnerable than you think.
Decentralization is not a belief label, but a survival issue.
-
It is not for showing off skills, but for an extra escape channel in the face of systemic risks.
-
It is not for anti-government, but for not giving all power to anyone, a button, or a backstage.
-
It is not just for geeks, but for everyone who wants to retain the right to choose and be responsible for their own assets, it is an underlying mechanism worth understanding and embracing.
But we have to admit a less sexy fact:
Can the ideal of decentralization be truly technically realized?
Can every service be "protocolized"? Can each layer of centralized infrastructure be replaced by functions? Can every business process be reconstructed on-chain? A more straightforward question:
-
How can we move from "decentralization impossible" to "decentralization can be run"?
-
From philosophy and vision to engineering and products?
These questions are the core content to be answered in the next article.

 chaincatcher
chaincatcher
 panewslab
panewslab