Global comparison of Hong Kong Web3 regulatory policies

Reprinted from jinse
06/06/2025·13DAuthor: Mask
Web3 technology is centered on blockchain and is reshaping the global financial, social and business ecosystem through innovative models such as decentralization, smart contracts and crypto assets. With the rapid development of this field, the financial risks, data security challenges and legal gaps it brings has prompted regulatory agencies in various countries to actively intervene. As key hubs for global Web3 development, the United States, the European Union, Singapore and Hong Kong have each built distinctive regulatory frameworks.
This article will deeply analyze the Web3 regulatory policies of these four major jurisdictions from the perspectives of regulatory agencies, policy frameworks, core rules and market impact, reveal their commonalities and differences, and explore the future direction of global regulatory coordination.
USA
The " law enforcement first " model under the leadership of the Securities Law
1. Multiple regulatory system and policy trends
The US regulation of Web3 shows typical " long regulation " characteristics, involving multiple federal agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) , the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) , the Financial Crime Enforcement Bureau (FinCEN) , and state regulatory agencies.
After Trump took office on January 20, 2025, he appointed Mark T. Uyeda as acting chairman of the SEC and Caroline Pham as acting chairman of the CFTC, aiming to provide a more stable and predictable policy environment for the cryptocurrency industry and realize the transition from "to achieve regulation through law enforcement" to "clear regulatory framework." .
On January 23, 2025, Trump signed the Executive Order to Strengthen the Leadership of the United States in the Field of Digital Financial Technology, aiming to promote the leadership of the United States in the fields of digital assets and financial technology and support the responsible development of the cryptocurrency industry.
The executive order proposes the establishment of the "Presidential Digital Assets Market Working Group" to explore federal regulatory measures for stablecoins and relevant solutions for national digital asset reserves, and explicitly prohibits the establishment, issuance, circulation or use of central bank digital currency (CBDC).

2. Establish strategic Bitcoin reserves
On March 6, 2025, Trump signed the executive order of "Building Strategic Bitcoin Reserves and US Digital Asset Inventory" and held the first cryptocurrency summit at the White House on March 7, indicating that his commitment to building the United States into the "global cryptocurrency capital." However, on March 7, the price of cryptocurrency continued its recent decline, and the price of Bitcoin fell rapidly, not meeting market expectations.
On January 23, the Senate Banking Committee established a Digital Assets Committee with Senator Cynthia Lummis as chair, which reflects the importance of regulation and development in the cryptocurrency field.
In May 2025, it was reported that the progress of the stablecoin bill and the digitalization process of the US dollar was approaching a turning point. The Trump team may support legal stablecoins (such as USDC) to write into national economic strategies. If implemented, stablecoins will become the "business hub" of the federal government's digital financial system, rather than a competitor to Bitcoin.
3. State-level supervision characteristics
In addition to the federal level regulatory framework, states have also developed distinctive regulatory models:
• New York State's BitLicense is the most influential crypto asset license, requiring businesses to comply with strict consumer protection and anti-money laundering compliance requirements.
• Wyoming adopts a relatively friendly regulatory attitude, recognizing cryptocurrencies as currencies through a series of laws and allowing banks to provide digital asset custody services.
Europe
Unified regulatory attempts under the MiCA framework
1. MiCA : Unified Rules for the European Crypto Asset Market
The EU has passed the Crypto Asset Market Supervision Act (MiCA) to become the " forerunner " in global Web3 regulation . This regulation, which will come into effect in 2024 , sets out comprehensive rules for crypto asset issuance and market transactions:
• Classified regulation: divide crypto assets into electronic currency tokens (EMT) , asset reference tokens (ART) and utility tokens. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are not within the scope of MiCA regulation.
• License Requirements: Companies that provide crypto asset services must register as crypto asset service providers (VASPs) to meet capital, reserves and information disclosure requirements.
• Stablecoin special provisions: Set reserve assets, capital requirements and daily liquidity restrictions on stablecoin issuers, especially limiting the use of non-Euro stablecoins in the euro zone.

2. Member States implementation and market response
- The implementation of MiCA adopts a " dual track system " transition period:
• Crypto service providers that already operate in the EU have a transition period of 12-18 months to adapt to the new rules.
• Newly entered the market must immediately comply with MiCA regulations.
2. The market reaction is polarized:
• Compliant companies welcome the legal certainty brought by unified standards, which facilitates free operation in the markets of 27 member states.
• Innovative companies are concerned that strict compliance requirements may curb flexibility, especially for DeFi projects.
1. Regulatory agencies and legal frameworks
Singapore's Web3 regulation is led by the Monetary Authority (MAS) , adopting a balanced model of " risk grading " and " sandbox trials " :
• Core Regulations: Classified supervision of digital payment tokens (DPTs) and securities tokens mainly in accordance with the Payment Services Act (PSA) and the Securities and Futures Act (SFA) .
• Regulatory Authority: MAS is responsible for licensing and comprehensive supervision, and the Accounting and Enterprise Regulatory Authority (ACRA) is responsible for enterprise registration compliance.

- License system and compliance requirements
Singapore implements classified license management for crypto services:
• DPT service license: Applicable to wallet services, exchanges and custodians, requiring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) , fund security and minimum capital regulations.
• Capital Market Service License: Strict supervision of SFA is applicable to securities token issuance and trading .
MAS has set up a moderately loose exemption period for start-ups, allowing limited business to be conducted before the requirements are fully met. This progressive regulatory approach has attracted well-known companies such as Circle and Paxos to settle.
3. Regulatory dynamics and market impact
1. From 2024 to 2025 , Singapore’s regulation showed a tightening trend:
• Stablecoin Supervision: The 2023 "Stablecoin Regulatory Framework" requires issuers to meet the requirements of 1:1 anchoring of reserves, independent audits and daily liquidity.
• New DTSP regulations: In May 2025 , MAS issued stricter regulatory guidelines for digital token service providers (DTSPs) , which will be implemented without a transition period starting from June 30, 2025 , and unlicensed services must be stopped immediately.
2. Despite stricter regulation, Singapore is still one of the most attractive Web3 centers in Asia, with its advantages:
• The legal framework is clear and predictable
• Regulators maintain constructive dialogue with the industry
• Excellent geographical location, radiating to the ASEAN market
Hongkong
Transformation from " Gray Zone " to Compliance Test Field
The Financial Secretary of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government, Chan Mo-po, made important speeches on Web3 on many occasions , reflecting Hong Kong 's positive attitude and regulatory thinking in promoting the development of Web3 :
On April 7, 2025 , at the " 2025 Hong Kong Web3 Carnival", Chan Mo-po said that Hong Kong is committed to promoting the development of the third generation of the Internet ( Web3.0 ), and plans to maintain fair competition in the market and encourage innovative development through a balanced and innovative regulatory framework.
He pointed out that blockchain technology is showing great potential, which can significantly improve transaction efficiency, reduce costs and enhance market transparency, and the development of Web3.0 , based on blockchain technology as the application basis , is also accelerating. Hong Kong has always adhered to the principle of "same business, same risks, same supervision" and is committed to establishing a suitable framework for the development of Web3.0 .
Chan Mo-po mentioned that Hong Kong is the first region in the world to establish a clear licensing system for virtual asset trading platforms ( VATPs ). The Securities and Futures Commission of Hong Kong has issued 10 VATP licenses so far ; in 2024 , Hong Kong was the first to approve virtual asset spot ETFs (i.e., exchange-traded funds), making Hong Kong the largest virtual asset ETF market in the Asia-Pacific region and building a bridge for innovation in traditional finance and cryptocurrency.
1. Evolution of regulatory framework
Web3 regulation in Hong Kong has undergone significant changes:
• Before 2022 : A relatively loose " regulatory vacuum " period has attracted a large number of crypto companies to register.
• 2022-2023 : Through the Virtual Assets Policy Declaration and the VASP license system, we will turn to the principle of " same business, same risks, same supervision " .
• From 2024 to present: Fully implement the licensing system and establish global compliance standards.
2. Core regulatory measures
1. Hong Kong adopts a multi-institutional collaborative supervision model:
• SFC : Responsible for the issuance of virtual asset trading platform (VATP) and the supervision of securities tokens.
• HKMA : Participate in the regulation of stablecoins and payment-related services.
2. Key regulatory requirements include:
• License system: All VATPs must obtain No. 1 ( Securities Trading ) and No. 7 ( Automated Trading Service ) licenses issued by the SFC .
• Asset custody: requires custody of customer assets through a wholly-owned subsidiary to obtain a TCSP license.
• Investor protection: Currently, only professional investors are allowed to participate in securities token trading, and retail investors protection is achieved through restricted access.
3. Market development and policy support
1. Hong Kong has enhanced its competitiveness through a number of measures:
• Approved virtual asset spot ETF in 2024 , becoming the largest virtual asset ETF market in the Asia-Pacific region.
• Policy Declaration 2025 : Plans to expand regulatory frameworks, which may include clearer stablecoin rules.
2. Hong Kong's advantages lies in:
• Capital and talent advantages brought by the status of an international financial center
• Potential connection opportunities with the Mainland market
• Clear regulatory expectations and legal certainty
1. Differences in regulatory philosophies
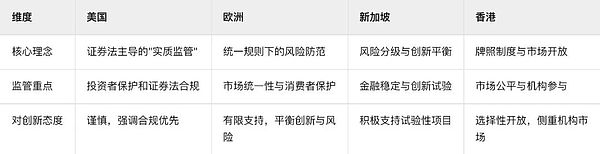
2. Comparison of regulatory in specific fields
1. Stablecoin supervision:
• U.S.: Probably relax regulation and focus on payment functions
• EU: Strict capital and reserve requirements, restrict non-Euro stablecoins
• Singapore: 1:1 anchoring requirements, independent audits and daily liquidity
• Hong Kong: 100% reserve fund custody, and the licensing system is implemented within the year
2. Securities tokens:
• United States: Securities law strictly applies, registration or exemption is required
• EU: ART tokens are subject to MiCA , and other securities tokens are subject to securities laws
• Singapore: SFA is applicable , but with small issuance waivers
• Hong Kong: Disclosure of asset ownership and smart contract risks
3. Decentralized applications:
• U.S.: High pressure regulation, strict law enforcement
• EU: MiCA retains some exemption space
• Singapore: Sandbox mechanism support trial
• Hong Kong: Regulatory framework has not been clarified and may be included in the scope of VASP
In the future, with the development of emerging issues such as real asset tokenization (RWA) and on-chain privacy, global regulatory coordination will become more important. Regulators across countries need to find a dynamic balance between protecting the financial system and maintaining technological vitality, while industry players need to develop adaptive strategies in a complex and changeable regulatory environment. The future of Web3 depends not only on technological innovation, but also on regulatory wisdom. Only by exploring feasible models within the framework of rules can this revolutionary technology realize its potential for change.


 chaincatcher
chaincatcher
