Ethereum’s growth pain: From ETF “blood loss” to on-chain weakness, can ETF staking boost the market?

Reprinted from panewslab
03/24/2025·1MAuthor: Nancy, PANews
Ethereum is experiencing a long growth pain, with prices continuing to be under pressure, on-chain activity significantly declined, and spot ETF funds continue to flow out... These signs are gradually eroding the market's confidence in its growth potential. As the US crypto regulatory environment quietly changes, many ETF issuance has recently submitted applications for Ethereum ETF pledge proposals to the US SEC. For Ethereum, which currently lacks a clear catalyst for demand, this change is also seen by the market as a key variable for Ethereum to get out of the trough in the short term.
ETF funds have suffered severe blood loss, and the ETF pledge
approval was announced as early as this month
At present, Ethereum spot ETF funds continue to lose blood, further hitting market confidence. According to SoSoValue data, since the beginning of this year, the cumulative net inflow of US Ethereum spot ETFs in January and February was about US$160 million, but the net outflow in March exceeded US$400 million, and the net outflow this year was nearly US$240 million. In contrast, although Bitcoin spot ETFs have also been outflowing significantly in the past two months, the overall net inflow this year is still exceeding US$790 million, and the scale of net outflow this month has shrunk by 74.9% compared with February.
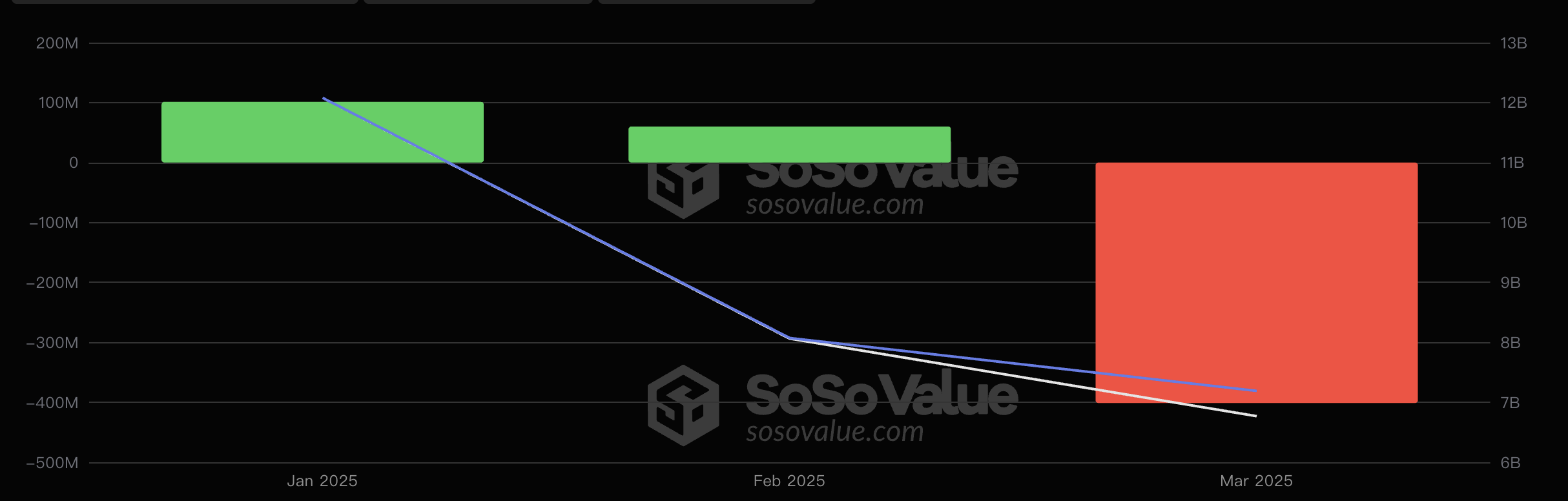
Ethereum ETF inflows this year
In this regard, Robert Mitchnick, head of BlackRock's digital assets department, believes that the approval for pledge may be a "huge leap" for Ethereum ETFs. He recently said demand for Ethereum ETFs has been mediocre since its launch in July last year, but situations could change if some regulatory issues that hinder their development can be resolved. It is widely believed that the success of Ethereum ETFs is “unprecedented” compared to the explosive growth of funds tracking Bitcoin. Although this is a "misunderstanding", the inability of these funds to obtain pledge returns may be a constraint that hinders their development. ETFs are a very attractive tool, but for today’s ETH, ETFs without staking are not perfect, and staking returns are an important part of generating return on investment in this area. This is not a particularly easy problem to solve, it is not like... the new government just gave the green light and achieved it overnight, and there are still many quite complex challenges to overcome. If these problems are solved, a leap forward will appear when you see the activities around these ETF products.
In fact, since February this year, many issuers including 21Shares, Grayscale, Fidelity, Bitwise and Franklin have successively submitted proposals to pledge Ethereum ETFs. Among them, 21Shares is the earliest institution to submit relevant applications and was officially accepted by the SEC on February 20. According to the SEC approval process, the agency must make a preliminary decision within 45 days after submitting the 19b-4 document, including whether to accept, reject or extend it. Based on February 12, the preliminary decision on the 21Shares Ethereum ETF staking application will be March 29, because the weekend may actually be postponed to March 31, the next working day, and it will be within 240 days at the latest. The final ruling is expected to be made on October 9.
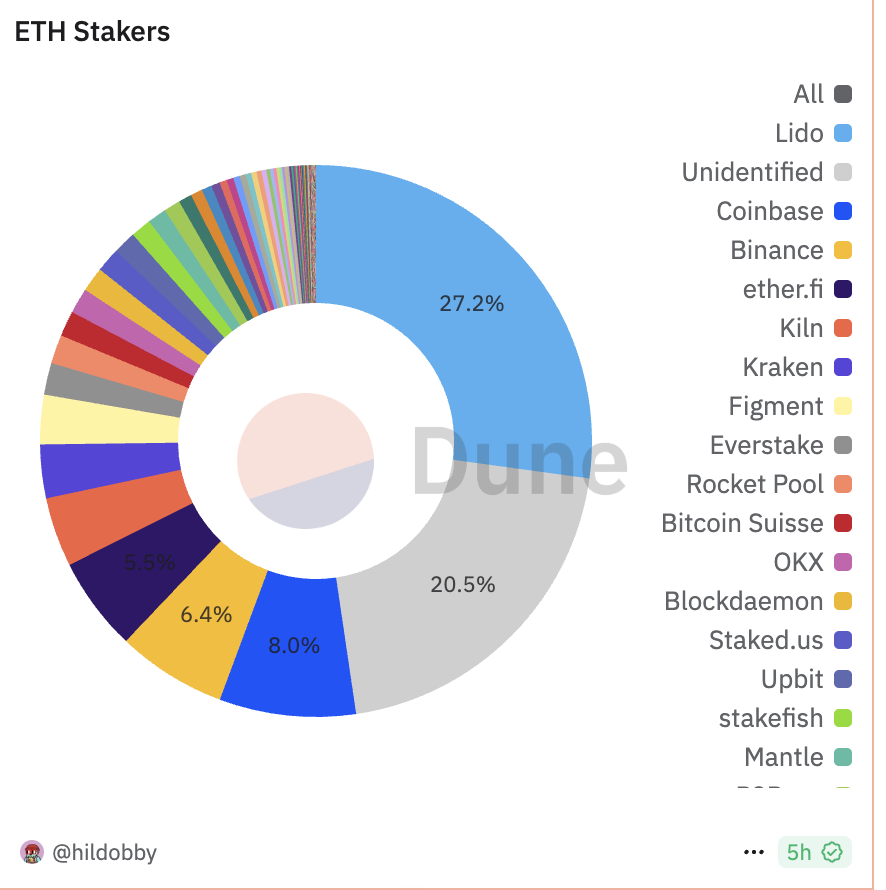
In the market's view, the introduction of staking function on Ethereum ETF is considered to have multiple potential advantages. In terms of return on investment, the current annualized rate of return on Ethereum pledge is about 3.12%. Compared with Bitcoin spot ETFs relying solely on price fluctuations, Ethereum ETFs can bring additional benefits to the ETH held through pledge. This feature is particularly attractive to institutional investors and may reverse the current situation of weak demand. In terms of price promotion, pledge locking in ETH will reduce market circulation, alleviate selling pressure, and may push ETH prices to rise. Dune data shows that as of March 24, the total pledge of Ethereum beacon chain exceeded 34.199 million ETH, and pledged ETH accounts for 27.85% of the total supply. If ETFs join the stake, this proportion will be further expanded; in terms of network security, ETFs participating in stake will increase the number of validators on the Ethereum network, increase the degree of decentralization, and alleviate the community's concerns about the risk of centralization of liquid staking protocols such as Lido. Dune data shows that as of March 24, the liquid staking protocol Lido alone accounted for 27.28% of Ethereum staking share.
However, for ease of operation and regulatory compliance, the pledge design of Ethereum spot ETFs may weaken its attractiveness to investment institutions. Taking the pledge function application document submitted by 21Shares as an example, the pledge process is managed by the custodian Coinbase, and adopts the "point-and-click staking" model, that is, the ETH held by the ETF is directly pledged through a simplified interface without transferring the assets to a third-party agreement (such as Lido or Rocket Pool), thereby reducing the security risks in asset transfer. Not only that, all the income generated by the pledge belongs to the ETF trust and is the income of the issuer, rather than directly distributed to investors. According to Dune data, compared with centralized exchanges such as Coinbase and Binance, LSD tracks such as Lido and ether.fi are still the mainstream choice for ETH staking. According to existing information, Ethereum spot ETF issuers have not explicitly allowed to share pledge proceeds directly with investors. However, with the loosening of US regulatory requirements and intensified market competition, the possibility of introducing this mechanism is not ruled out.
Not only that, Ethereum spot ETFs also face the challenge of pledge efficiency. Since the Ethereum staking entry and exit mechanism is strictly restricted (each can only allow up to 8 nodes to enter and 16 nodes to exit, and one epoch will be generated every 6.4 minutes), this also limits the flexibility of ETFs, especially when the market fluctuates violently, investors' inability to exit in time may aggravate the selling sentiment. For example, the current Ethereum spot ETF holds a total of about US$6.77 billion worth of ETH. According to the ETH price (about US$2,064), it is about 3.28 million ETH. The staking entry time is about 57.69 days and the exit time is 28.47 days. This queuing mechanism cannot meet the needs of investors, and liquid staking platforms that bypass these mechanisms are also excluded from ETF staking.
However, Pectra upgrade (EIP-7251) increases the staking limit of a single verification node from 32 ETH to 2048 ETH, greatly improving staking efficiency. This not only reduces the queue time for entering and exiting pledges, but also reduces technical barriers. But in the latest 153 Ethereum Core Developer Consensus (ACDC) conference calls, developers have decided to postpone the date of activation of the Pectra mainnet, which may be delayed until after May.
From this point of view, compared with the opening time of the staking function, issues such as income distribution and efficiency are key factors that affect the demand for Ethereum spot ETFs.
**On-chain activities continue to be sluggish, and ETF pledge is
difficult to solve the ecological dilemma**
Even if Ethereum spot ETF introduces staking function, its impact on circulation supply and market sentiment is limited, and it is difficult to fundamentally reverse the competitive pressure and growth bottlenecks faced by the Ethereum ecosystem. At present, on-chain activity continues to sluggishly, the intensified L2 diversion effect, and challenges from other high-performance public chains are all weakening Ethereum's market dominance.
From the perspective of the impact of ETF staking, as of now, Ethereum's pledge rate is about 27.78%, and the total ETH held by the U.S. Ethereum spot ETFs is 2.84%. Even if all of these ETFs participate in the pledge, the pledge rate has only been increased to about 30.62%, an increase of 2.84%. This slight change has little impact on the supply of ETH circulation and supply and is still not enough to become the decisive force driving the price upward.
In comparison, the staking rate of other PoS competitive chains is much higher than that of Ethereum, such as Sui's staking rate reached 77.13%, Aptos' staking rate reached 75.83%, Solana's 64.39%, etc. Although Ethereum has room for staking growth, the scale of funds and pledge potential of ETFs are difficult to constitute the dominant purchasing power of the market, and the symbolic significance of the pledge function is greater than the actual effect.
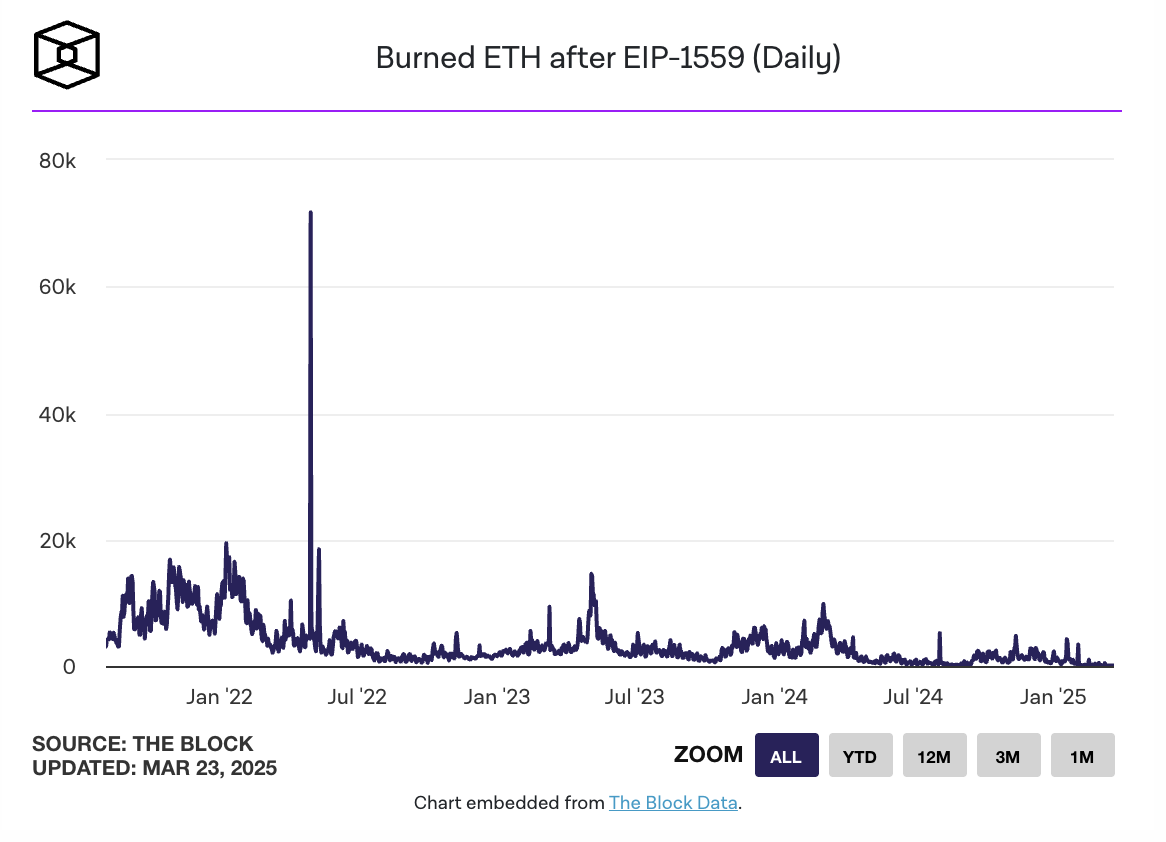
The continued decline in on-chain activity data further highlights the fatigue of the Ethereum ecosystem. According to The Block data, as of March 22, the number of ETH destroyed by the Ethereum network due to transaction fees dropped to 53.07 pieces, or about $106,000, a record low. Ultrasound.money data shows that based on the past 7 days, the annual supply growth rate of ETH is 0.76%. Not only that, the active addresses, transaction volume and transaction number on the Ethereum chain have declined simultaneously in recent weeks, indicating that the vitality of the Ethereum ecosystem is declining.
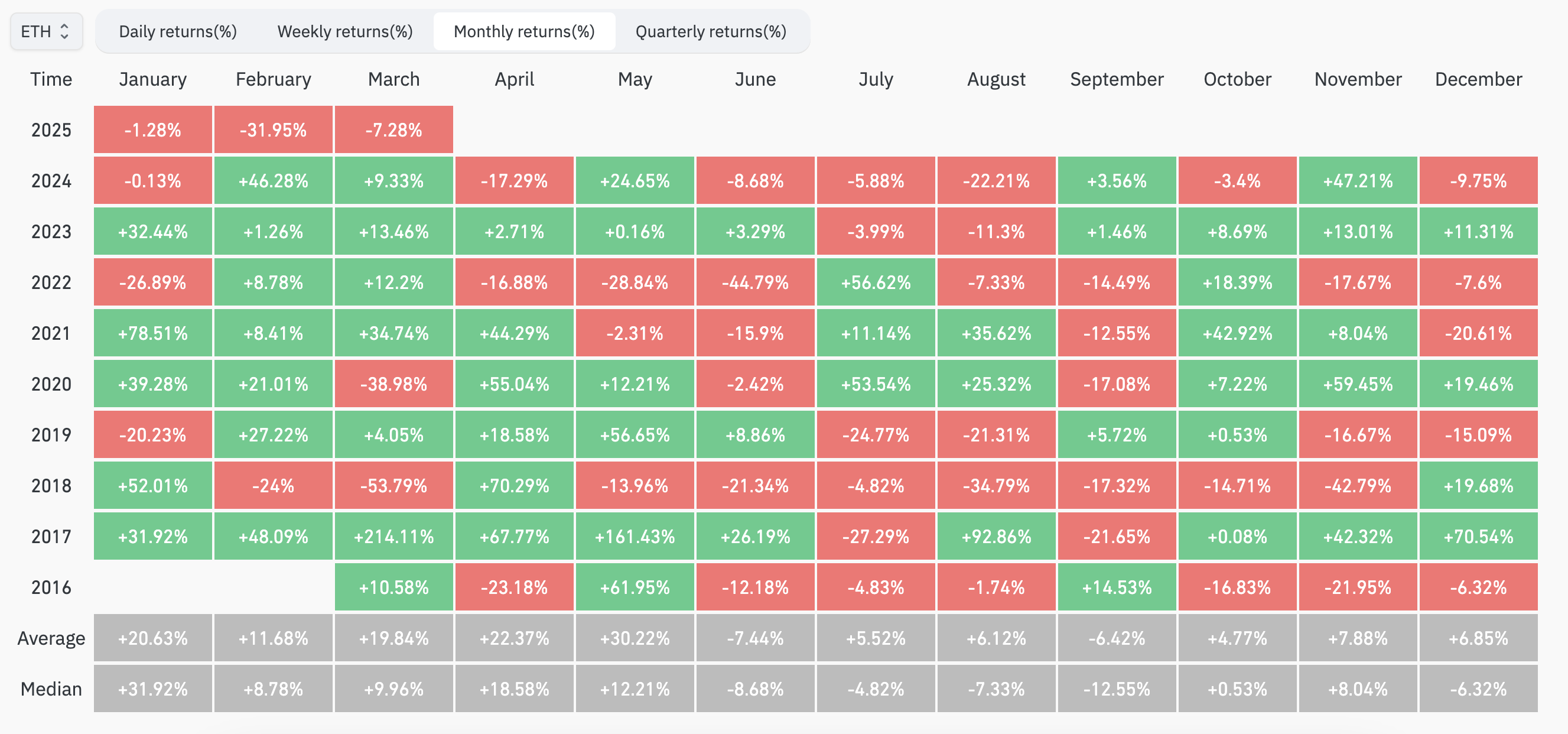
At the same time, Ethereum scored its worst performance in Q1 this year. Coinglass data shows that Ethereum experienced its worst start in recent years in the first quarter of 2025, showing negative returns for the first time: January: -1.28% (historical average return: +20.63%, median: +31.92%); February: -31.95% (historical average return: +11.68%, median: +8.78%); March: -7.28% (historical average return: +19.55%, median: +9.96%).
The dilemma faced by Ethereum stems from multiple structural problems. For example, although L2 such as Arbitrum and Optimism have significantly reduced transaction costs through Rollup technology, it also diverted the transaction volume of the main network. The proportion of these L2 transactions has exceeded that of the main network, resulting in a decrease in the main network Gas fees and ETH destruction volume. More importantly, most of the transaction fees incurred by L2 remain within its ecosystem (such as Optimism's OP token economy) rather than returning to ETH. For example, Ethereum's market share is being eroded by other public chains such as Solana due to its lack of competitiveness in high-performance application scenarios.
Standard Chartered Bank also lowered its ETH target price at the end of 2025 from $10,000 to $4,000, and put forward several key judgments: L2 expansion weakens ETH market value: L2, which was originally used to improve Ethereum's scalability (such as Coinbase's Base has caused the evaporation of US$50 billion in market value); ETH/BTC ratio is expected to continue to decline: it is expected to fall to 0.015 by the end of 2027, the lowest level since 2017; future growth may rely on RWA: If RWA tokenization develops rapidly, ETH may still maintain its 80% security market share, but the Ethereum Foundation needs to adopt more aggressive business strategies (such as taxing L2), which is lower.
In general, although Ethereum ETF staking can affect ETH supply and holder returns to a certain extent, it cannot directly solve core challenges such as ecological competition, L2 diversion or market sentiment. Ethereum still needs to seek deep breakthroughs in technology and narrative.

