AngelList on the Chain: Crypto's new era of private equity investment and financing

Reprinted from panewslab
04/27/2025·17DWhat is private equity investment and financing?
Private equity investment and financing is a broad and complex field, but simply put it in essence it is a financial transaction. In traditional private equity financing, private equity investment and financing is a financial transaction that uses fiat currency to exchange equity.
Although private equity investment and financing is just a financial transaction, it involves a lot of complex and professional work and collaboration.
From the perspective of investment, an investment usually requires four stages: fundraising, investment, post-investment management, and exit. In this process, the work of an institution or fund manager involves entity registration, investor entry and management, financial management, due diligence, as well as a large number of agreement signing, legal affairs, auditing and other work. As an investor, you need to identify investment institutions and fund managers, and review very complex fund recruitment books. From the perspective of financing, startups usually require a lot of complex work to complete financing, including entity registration, financing planning and management, equity structure management, financial management, etc.
These work often exceeds the professional competence of participants. Founders of start-ups usually do not have financing experience and relevant professional skills, and many investors are also confused by a large number of contracts (such as fund recruitment books) and complex onboarding processes. Creating and running a private equity fund is a complex project. To accomplish these tasks, they need to pay additional capital costs, time costs, labor costs, learning costs, and introduce more additional collaborations, such as hiring lawyers and financial administrators. Therefore, private equity investment and financing is a business with a very high threshold.
What is AngelList?
In the previous chapter, we mentioned that private equity investment and financing involves a lot of complex and professional work and collaboration, which not only makes it difficult to participate, but also causes problems such as high cost, low efficiency, and business boundary restrictions.
AngelList is an online tool set serving the private equity investment and financing field. Simply put, it abstracts the complex and professional work in each link of private equity investment and financing transaction into various components and programs (different components and programs can be combined into different business flows, such as investor joining), and then uses Internet technology to make it run online, so that people around the world can participate in these business flows efficiently, even with just a simple click without worrying about the professional and complex specific affairs involved. For example:
-
Investment institutions and fund managers : Investment institutions or fund managers can easily create an online operating framework through the tools provided by Angellist, such as Rolling Funds, Venture Funds, Syndicate, Scout Funds. Through these online tools, investment institutions and fund managers can easily and efficiently implement fundraising, investment and other related work. Through the fund management tools provided by Angellist, investment institutions can easily create or bind multiple bank accounts around the world and use them as fundraising and investment accounts while ensuring asset security (such as the sweep accounts function). In addition, Angellist also provides some tools to facilitate investment institutions to sign agreements, share files, notify and publicize them.
-
Investors : Investors can easily find excellent investment institutions through Angellist, and easily contact and join them through the tools provided by Angellist (investors join). When an investor joins one or more investment institutions, he can easily view and track the operation status of the investment institutions through the tools provided by Angellist.
-
Startups : Startups can quickly start and manage financing using the financing tools provided by Angelsit. At the same time, Angelsit also provides a series of management tools for start-ups, such as Cap tables, legal entity establishment, etc. In addition, startups can also use Angellist to manage funds by binding bank accounts, such as transfers, taxes, etc.
Two keywords: program, online.
Online
Before the Online Insurgency, applications were usually offline native applications, such as early financial management, text processing, etc. From a technical perspective, simply put, the business logic and data of these applications are stored in the client and do not need to rely on the network environment. Online deploys the business logic and data of the application on cloud services and interacts with users through the Internet. We can call this type of application online applications (typically a web application).
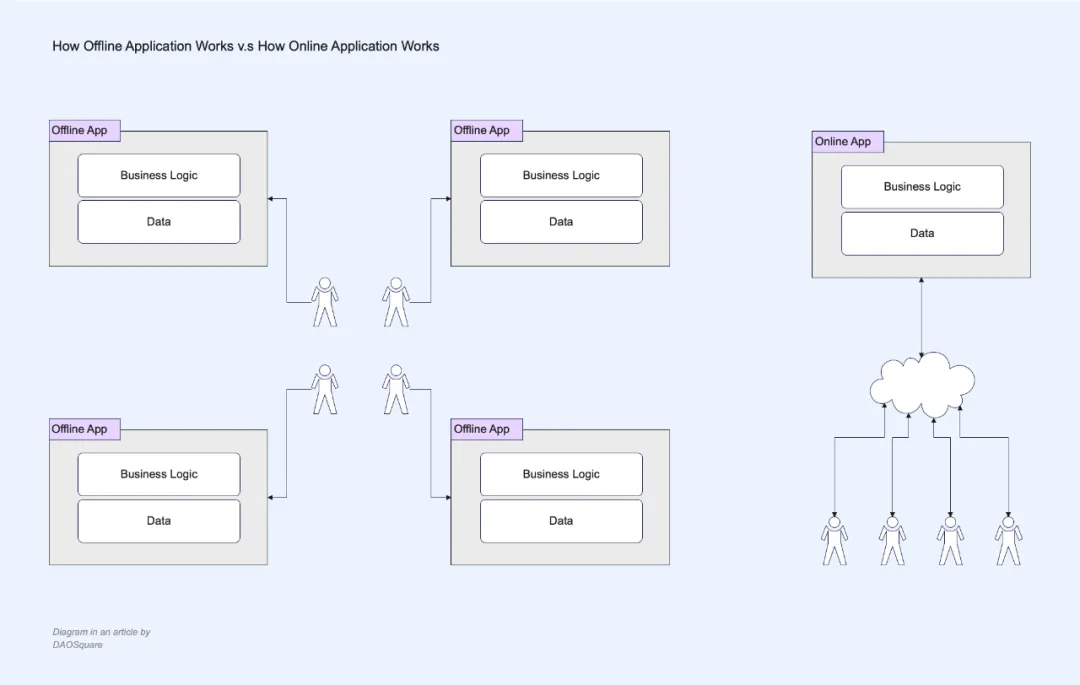
For example, before Google Docs was released in 2006, word processing applications like Word were offline native applications. If I want to invite others to edit a document together, I can only export my document as a .doc file and send it to someone else (e.g. email) who imports the file into Word to finish editing, and then exports the edited document as a .doc file again and sends it to me. I need to open everyone's manuscript one by one, summarize everyone's editing content and finally form the final version. This process often requires repeated many times, which is simply a disaster. Google Docs brings us into a whole new era, and as you see today, we can not only edit and modify, comment and discuss in real time for multiple people, but also call any supported third-party application in Google Docs, such as inserting a Google Sheet, a Youtube, etc. This is the huge change that comes with online.
The work involved in private equity investment and financing is much more complex than document collaboration. For example, a financing for a startup company, the startup company needs to prepare financing materials and contact investors through different channels, and then discuss and sign an investment agreement with all prospective investors. Next, it also needs to manage the financing funds, formulate employee option pools, manage equity allocation, etc. Before the birth of online tools represented by Angellist, these processes were completely separated, and we could only use some simple tools to do these tasks manually. As financing rounds increase, these tasks will become more and more complex. Online tools make it all simple. For example, using the financing tool (Raise) provided by Angellist, startups can complete all processes in the financing process in one-stop online, and since modules can be called before, the entire fundraising process can be highly automated. For example, when a fundraising is completed, Raise will automatically help startups update their equity structure list.
As you can see, Online has very significant advantages: improving efficiency, expanding boundaries, while reducing financial and time costs.
-
Improve efficiency : By introducing workflow Online, the efficiency of investor recruitment, investment process, startup fundraising, and legal agreement signing have been greatly improved.
-
Expanding Boundaries : Online allows us to break through the traditional social circle, investors have gained more opportunities to participate in venture capital, venture capital institutions have also raised funds from more investors, startups have connected more venture capital institutions, and venture capital institutions have also gained more investment targets.
-
Reduce costs : While improving efficiency and expanding business boundaries, Online has also greatly reduced the financial and time costs of private equity investment and financing affairs thanks to its abundant online tools. For example, Cap table management, as AngelList says:
AngelList’s equity structure list eliminates the hassle of managing the startup’s largest assets (equity). Make better decisions by leveraging unparalleled automation while maintaining compliance.
This is a paradigm shift brought to specific industries by technological changes.
New challenges brought by Crypto
There is one of the most significant differences between Crypto private equity investment and financing and traditional private equity investment and financing. The investment currencies of Crypto private equity investment and financing are usually cryptocurrencies (such as USDT, USDC, ETH, etc.). Since it is impossible to use private equity investment and financing tools like AngelList, most Crypto private equity investment and financing currently use simple management methods, such as using a multi-signature wallet to manage fundraising assets, completing fundraising and investment through manual transfer, and using traditional financial management software to record and manage funds and Portforlio. This rough operation and management model not only causes efficiency and complexity problems, but more importantly, it brings many risks.
Funding risk
Generally, after Crypto investment institutions complete fundraising, the investors' money is managed by the investment institutions (using multiple sign-up wallets or even personal wallets). The relevant personnel of the investment institutions have the right to manage the funds, while investors (such as the fund's LP) do not have substantial guarantees. Therefore, technically they can embezzle the money and even run away with it. As you can see, something like this has happened. Since the Crypto private equity investment and financing industry is still far from standardized, and the support for Crypto in most jurisdictions is still far from perfect, it is difficult to protect the rights and interests of investment institutions and investors through legal means.
Risk of default
Currently, all transaction links of Crypto investment and financing use paper contracts to constrain both parties to the transaction. For example, investment institutions raise funds from investors, investment institutions invest in startups, and startups release tokens to investment institutions, etc. This constraint method that relies on traditional trust mechanisms is effective in traditional equity private equity investment and financing, but its binding power is limited in Crypto, because the support for Crypto in most jurisdictions is far from perfect. In particular, Crypto investment and financing are usually cross-jurisdiction, and the difficulty will be further amplified.
Venture capital is in chaos
In the field of Crypto private equity investment, there are a large number of organizations and individuals called VCs that are actually cryptocurrency speculation gangs and second-hand dealers. They gain investment share of startups under the name of VC, and then exaggerate publicity through social means to push up the currency price in the short term and sell it, or sell it to other institutions and individuals at a premium after obtaining the share. Not only can such institutions not bring practical help to start-ups, but they cause many troubles, obstacles and even harm to start-ups, which is extremely unfavorable to the development of start-ups. It is usually difficult for start-ups to effectively identify these cryptocurrency speculation gangs and second-hand dealers.
The above only talks about the core interests of the various participating roles in the investment and financing field of Crypto. There are many other issues in addition, but there are undoubtedly issues related to assets that we need to pay special attention to. So in the case where traditional trust mechanisms (such as the judicial system) cannot effectively protect the rights and interests of Crypto investment and financing participants, is there a way for us to solve these risks?
New Opportunities brought by Crypto
Cryptocurrencies have brought new challenges to private equity investment and financing, but on the other hand, cryptocurrencies have also brought new opportunities to private equity investment and financing.
"What is private equity investment and financing" chapter We talked about the financial transactions in which traditional private equity investment and financing can be regarded as financial transactions that use fiat currency to exchange equity. Since the two transactions are in different accounting systems (currency and equity structures), the transaction can only be carried out asynchronously, i.e. 1) paying investments and 2) distributing equity. Therefore, in order to ensure that both parties to the transaction perform their contract, a third party, that is, a traditional trust mechanism (such as the judicial system) must be introduced to constrain both parties to the transaction. The investment currencies of Crypto private equity investment and financing are usually cryptocurrencies, and startups usually use cryptocurrencies to represent their corporate value (such as ETH, CRV, RICE, etc.).
This means that we can regard Crypto private equity investment and financing as a currency transaction, and it is a currency transaction in the same accounting system (blockchain).
Compared with traditional private equity investment and financing, this currency transaction not only makes various investment and financing links such as fundraising, investment, management, and exit simple, but also thanks to the many technical characteristics of cryptocurrencies. The transactions in these links can be achieved by restraining both parties to the transaction from a technical level to protect the rights and interests of both parties without relying on the intervention of traditional trust mechanisms such as justice, insurance, and arbitration, thereby solving the many risks mentioned above.
Let’s take a brief look at cryptocurrencies through several technical concepts (smart contracts, programmable currencies, data availability) and why it can solve the risk issues mentioned above, thus bringing new opportunities to private equity investment and financing.
Smart contracts
In the context of blockchain, a smart contract is a program deployed and stored on the blockchain to receive user instructions and execute results in accordance with programming logic (internal or external). This is like a vending machine. When the user selects 1 bottle of Coke and pays the amount set by the program (for example 1 USD), the vending machine will "spout" 1 bottle of Coke.
Unlike vending machines, smart contracts are usually irreversible and immutable once deployed to the blockchain. This means that no one can tamper with it. That is to say, it is impossible for us to modify the programming logic after this "vacancer" starts running, so that it "sprays" out 10 bottles of Coke after the user selects 1 bottle of Coke and pays 1 USD. It will always only run according to the logic of 1 USD 1 bottle of Coke. Of course you would say hacking can do it, but that 's another topic.
In addition, due to the lack of permissions in smart contracts, no one can stop users from using smart contracts.
Programmable currency
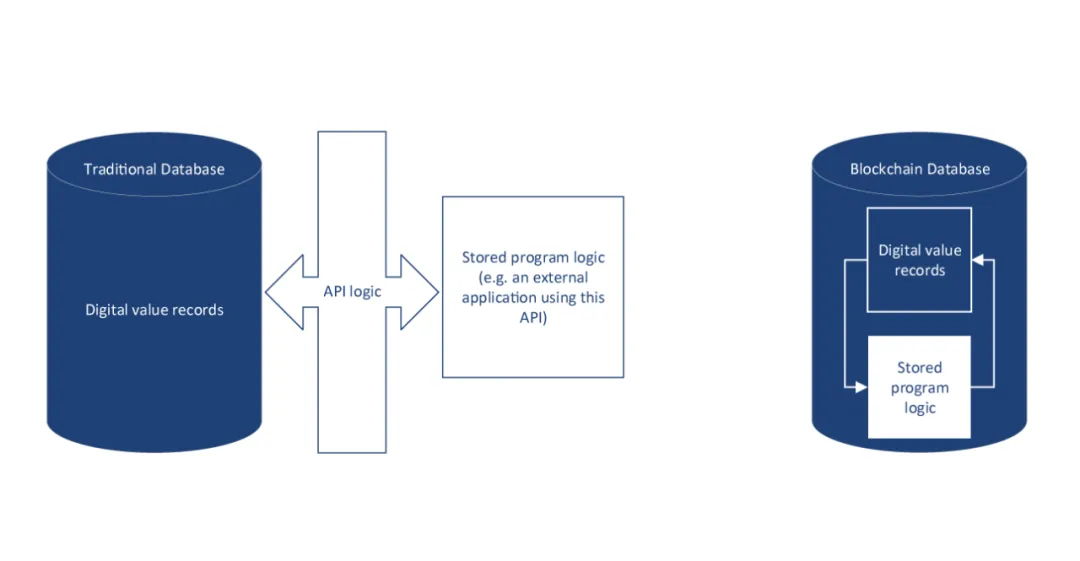
Whether it is a traditional financial system or a blockchain, it is used to digitize currency through "digital value records", and they can be called digital currencies. In traditional Internet financial systems, digital currency is a set of digital records representing tradable value stored in an online database. It allows programming logic outside the database (such as online banking APP) to adjust the digital value records in the database through APIs.
In blockchain, digital currency is a smart contract (such as ERC20) designed for monetizable value that is deployed and stored in a blockchain database. It also contains digital records representing tradable value, but its digital records are adjusted.
-
Constrained by its own programming logic . Just like the example of vending machines mentioned above.
-
And allow the programming logic of other smart contracts within the blockchain database to adjust its digital value record on the premise of conforming to its own programming logic . This is like a vending machine connected to a lucky turntable. Users can instead of selecting Coke when investing 1 USD, but authorizing the vending machine to use the lucky turntable to control which drink the vending machine "spouts". You know, there may be cokes and cars on the lucky turntable, but it may also be "thank you".
Due to its programmable properties, this digital currency running on a blockchain is also called a programmable currency, but we usually call it cryptocurrency.
Data Availability
Blockchain is not only an open network (anyone can access it and use it), but also has the characteristics of data availability. This means that we can access any user's blockchain account to verify any transactions that user has on the blockchain. So it can help us:
-
Verify the investment history of investment institutions.
-
Verify the investment preferences of investment institutions.
-
Verify the investment strategies of investment institutions (long-termism or speculativeness).
-
Monitor and track the flow of funds in investment institutions. For example, when an institution embezzles funds, take timely actions to prevent it, or assist relevant institutions (such as judicial institutions) in handling it.
As you know, in traditional finance, these are simply fantasies.
Now, let’s take a look at how these technical features can be used to solve the three types of risks mentioned above.
Funding security
For example, we can deploy a fund management contract for investment institutions on the blockchain, and the investment institutions can invite investors to deposit funds (such as USDT) into the contract to complete the fundraising. The capital control of the contract account is subject to the programming logic of the contract. Investment institutions can set up a team of managers to control funds through voting mechanisms when deploying the contract, or hand over the control of funds to all investors (investment clubs). This can technically avoid the problem of misappropriation of funds by internal investment institutions.
We can also deploy a redemption contract to enhance the security of the fund management contract. We can set a fixed redemption period, just like traditional open funds, for example once every 30 days. In this way, investors can decide every 30 days whether to continue to place funds in the investment institution or withdraw funds based on their own performance judgment of the investment institution. Alternatively, we can set the redemption period after each investment transaction is initiated, so that investors can decide whether to participate in the investment based on whether they agree with a specific investment. Due to the permissionless nature of smart contracts, investors' behavior of protecting their funds through redemption cannot be blocked by either party.
Safety of performance
Take an example of a SAFT investment agreement. We know that although we can regard Crypto private equity investment and financing as a currency transaction, it is usually not a simple transaction like Swap, which is like a simple transaction, but usually there is a Vesting Schedule, that is, the investee releases Payback currency to investors at a certain release rule at a certain time in the future after receiving the investment payment. Therefore, Vesting Schedule is usually the most important part of the SAFT investment agreement and is also the most likely part to cause defaults and disputes.
We can deploy an investment protocol contract on the blockchain and use programming logic to implement the trading rules in the SAFT protocol, including investment currencies, Payback currencies, prices, Vesting Schedule, etc. When the investment institution and the investee create an investment transaction through the smart contract (the parameters agreed upon, such as the Vesting Schedule) and "sign" the transaction, while the investment institution pays the investment, the investee's Payback currency will be entrusted to the smart contract, and the investor can independently receive the Payback token from the smart contract according to the timeline agreed in the Vesting Schedule (no one can stop him). Let's give an example:
Investor Bob used the investment agreement smart contract to create a SAFT investment transaction with entrepreneur Lisa. The transaction details are as follows:
-
Investment Currency: USDT
-
Investment Amount: 100,000
-
Investor: 0x1Bfe1F47a3566Ee904d5C592ab9268B931516B56 (Bob's wallet address)
-
Investment Fund Receiver: 0xEF72177cb6CE54f17a75c174C7032BF7703689b4 (Lisa's wallet address)
-
Payback Currency: RICE
-
Payback Amount: 100,000
-
Vesting Start: 10/01/2025
-
Vesting End: 10/01/2028
-
Claim Interval: 30 Days
When Bob and Lisa "sign" the transaction on the chain, the 100,000 USDT in Bob's wallet will be transferred to Lisa's wallet address, and the 100,000 RICE in Lisa's wallet will be transferred to the custodial contract. Starting from October 1, 2025, Bob can receive RICE from the custodial contract every 30 days, each receiving one-thirty-sixth of the total amount until October 1, 2028, with a total of 100,000 RICE available. and,
-
Bob will surely receive RICE from this smart contract starting October 1, 2025 without anyone's permission.
-
Lisa cannot prevent the implementation of the investment agreement after the successful transaction.
-
Lisa cannot retrieve RICE from the custodial contract.
-
No one can stop Bob from using the contract to claim RICE.
Venture Capital Distinguishing
Due to the openness and data availability of blockchain, we can access the investment institution's fund management accounts on the blockchain at any time and analyze their historical transactions to verify whether the investment performance and investment philosophy promoted by the institution are true. For example, Bob claims to be very optimistic about Lisa's projects and therefore holds RICE for a long time, but its transaction records show that Bob sells out immediately after each RICE is received. Then when Bob finds you and expresses his desire to invest in your project, you should be careful. Or, if Bob immediately transfers money to a group of people in batches every time he receives RICE, then there is a high probability that Bob is a second-hand dealer.
In addition, we can also summarize the investment preferences of investment institutions by analyzing these historical transactions, such as investment fields, which can also greatly save the time cost of startups in seeking investment institutions and communicating with investment institutions.
Onchain
Above we briefly introduce how to up-chain Crypto investment and financing transactions to introduce its advantages in asset security and how to give full play to the technical characteristics of blockchain data availability to help us better identify investment institutions. As you know, there are a lot of other transactions and management links in Crypto investment and financing. If we put all these transactions and management links on the chain, that is, we will build a corresponding smart contract for each transaction link, and allow these contracts to be freely combined and called each other, we can build a set of investment and financing tools on the chain, that is, Angellist on the chain.
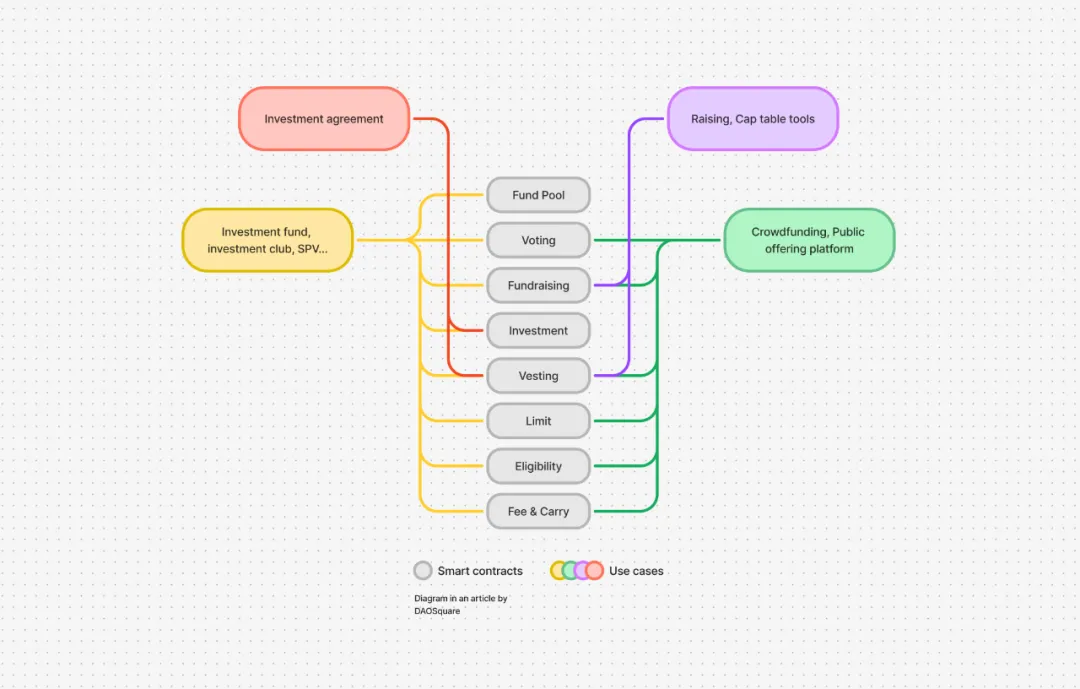
The above figure lists some basic smart contracts, such as Fundraising contracts for fundraising, Limit contracts for limiting the number of fundraising participants, Fund Pools for storing funds, voting contracts for controlling fund pools, Investment contracts for investment, Vesting contracts for freeing project tokens, Eligibility contracts for limiting fundraising participants or fund manager qualifications, Fee & Carry contracts for helping investment institutions obtain returns, etc.
We can freely combine these contracts to implement different functions, just like Lego. As shown in the figure above, we can use the combination of Investment and Vesting contracts to form a simple on-chain investment agreement. Once the investment and financing parties confirm, it will automatically trade in accordance with the agreement, and cannot be blocked and tampered with, and do not require any intervention of a third-party trust mechanism.
Startups can use a combination of Fundraising and Vesting contracts to build an on-chain enterprise management tool to manage fundraising and Cap tables.
Going further, we can use the combination of Fundraising, Vesting, Limit, Eligibility, and Voting contracts to build an on-chain crowdfunding platform or Launchpad. It will be truly decentralized, license-free, and community-based, without the asset risks brought by centralized control.
We can also use all the contracts listed above to build more complex businesses, such as running a private equity fund, investment club, SPV, etc. Through more functional modules, we can achieve more complex business needs, such as setting redemption periods and redemption fees for funds, or implementing a fund operation structure with GP + LP, etc.
These contracts not only provide us with trustless transaction guarantees, but also model the transaction process of private equity investment and financing, so that we can easily complete professional work without mastering relevant professional knowledge and skills. Therefore, it has all the advantages of Online (efficiency, boundaries, costs), and at the same time ensures the transaction security and performance of private equity investment and financing from a technical level.
This is a new paradigm transfer brought by blockchain technology to private equity investment and financing.
Today & Future
Since the birth of The DAO in 2016, a large number of developers and builders have been working on the vision of "Onchain Ventures", including Moloch, DAOhaus, TheLAO, Nouns, Juice Box, PartyDAO, Gnosis Auction, Superfluid, Syndicate, Furo, Kali, DAOSquare, etc. These builders build solutions in their respective areas of focus based on their own understanding of Onchain Ventures. Many people give up halfway, but more people continue to work hard to iterate and perfect these solutions.
As the initiator of DAOSquare, I am also honored to be the promoter and builder of this vision. DAOSquare and I are working on building an AngelList on a chain to provide a complete set of tools for Crypto private equity investment and financing, technically ensuring the asset security and performance of all parties in the transaction, and reducing the financial and time costs of all parties in the transaction while improving investment and financing efficiency and expanding business boundaries.
Like all other solutions builders, I believe that Onchain Ventures is important for the importance of Crypto private equity investment and financing and the development of Crypto as a whole, and I believe that Onchain Ventures’ future prospects, because capital will always be an important driving force for the development of the industry, both in traditional fields and in Crypto. Therefore, I believe that in the near future, with the continuous improvement and regulation of the Crypto private equity investment and financing industry, these products serving Crypto investment and financing will shine. Let's wait and see.

 jinse
jinse

 chaincatcher
chaincatcher