US$250 million in financing accelerates the upgrade of Avalanche9000. What new plans does Avalanche have in the bull market?

Reprinted from panewslab
12/17/2024·6MAuthor: Yangz, Techub News
On the evening of December 12, Avalanche announced the completion of US$250 million in financing through locked token sales. Galaxy Digital, Dragonfly and ParaFi Capital led the investment. Participants included SkyBridge, SCB Limited, Hivemind, Big Brain Holdings, Hypersphere, Lvna Capital, Republic Capital, Morgan Creek Digital, FinTech Collective, CMCC Global, Superscrypt, Cadenza, Chorus One and Tané Labs, among others 40 A number of investment companies, and the funds raised will be used to promote an upgrade called "Avalanche9000".
To be honest, the author has not heard about Avalanche9000 before. Compared with the popular Memecoin, the progress of many established public chains has been ignored in this bull market. As early as early September, Avalanche announced the launch of the Avalanche9000 upgrade (or Etna upgrade) and regarded it as the "largest upgrade" since its launch. To put it simply, Avalanche hopes to use Avalanche9000 to change its original expansion form "subnet" and build it into Avalanche L1. According to Avalanche, Avalanche9000 will allow the new Avalanche L1 to customize staking, gas tokens and governance while retaining the advantages of fast subnet finalization times and high throughput. But specifically, how will this upgrade be achieved?
As one of the original "Ethereum killers", Avalanche launched the "Subnet Road" in 2022, allowing various applications to create their own application chains. However, to become a subnet verifier, you need to verify the Avalanche main network (Primary Network) at the same time, including the contract chain (C-Chain), platform chain (P-Chain) and transaction chain (X-Chain). This is equivalent to the fact that validators must allocate at least 8 AWS vCPUs, 16 GB RAM and 1 TB storage space for network verification, in addition to a minimum pledge of 2000 AVAX.
Initially, this requirement may not be too high, but as AVAX appreciates (AVAX price is around $52 at the time of writing), the overall operating cost will become higher and higher (the minimum staking requirement can be lowered, but frequent changes may Not Avalanche's consideration). In the long run, such a high entry barrier will affect the adoption of the Avalanche ecosystem.
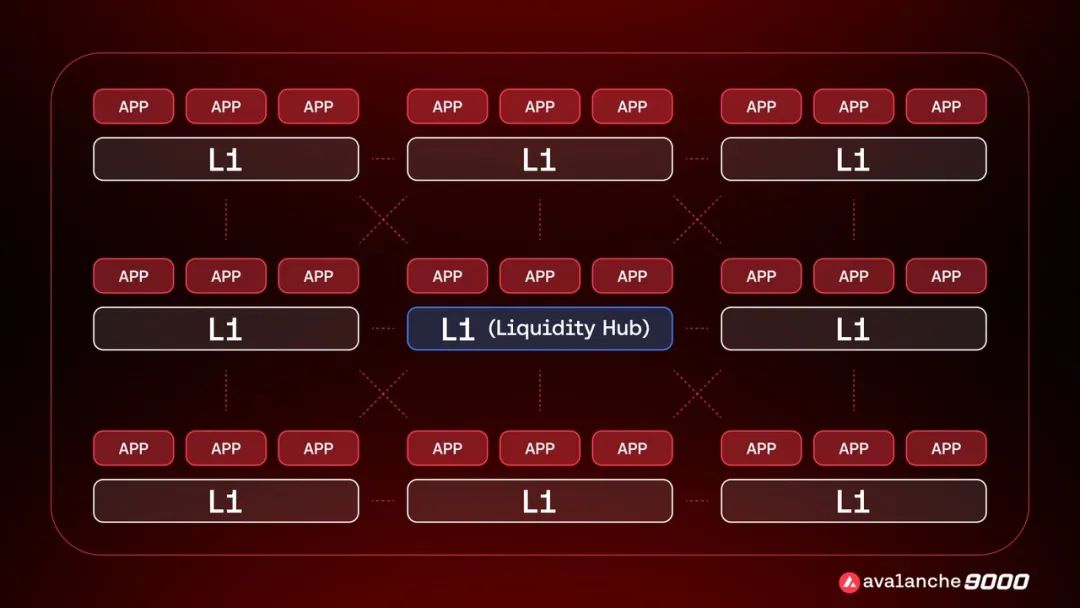
Therefore, the Avalanche Foundation launched proposal ACP-77 in April, aiming to completely reform the creation and management of subnets and give subnet creators greater flexibility.
Under the proposal, Avalanche L1 validators will no longer be required to simultaneously validate the main network. They simply synchronize with P-Chain, which tracks changes to its own set of Avalanche L1 validators and handles cross-L1 communication via AWM. In addition, Avalanche L1 can decide and implement its own verification rules and staking requirements, and P-Chain will no longer support staking reward distribution for Avalanche L1. In other words, the sovereignty of Avalanche L1 returns from P-Chain to L1 itself.
On the other hand, the proposal plans to transform P-Chain's charging mechanism from a fixed per-transaction fee to a dynamic fee that is more in line with the user-pays principle, thus ensuring the long-term economic sustainability of Avalanche after the cancellation of the 2000 AVAX staking requirement. Specifically, the dynamic charging mechanism is related to multiple factors such as the total number of Avalanche L1 validators registered on P-Chain. Fees will be adjusted based on network usage and will increase when the total number of Avalanche L1 validators exceeds target usage and vice versa.
In addition to the proposals in ACP-77, other implementation foundations of Avalanche9000 include two major interoperability protocols: Interchain Token Transfer (ICTT) and Interchain Messaging (ICM).
ICTT is a set of smart contracts deployed in multiple subnets based on the cross-chain communication protocol Teleporter and Avalanche Warp Messaging technology, allowing users to transfer tokens between subnets. Each token transferr consists of a "home" contract and at least one (possibly multiple) "remote" contracts. The "main" contract is located in the subnet where the assets are to be transferred. "Remote" contracts exist on other subnets.
ICM is designed to enable seamless communication between C-Chain and new and existing Avalanche L1. As soon as a new L1 is deployed through Avalanche, it is immediately supported and ready to interact with other L1s. Through ICM, developers can send messages from one Avlanche L1 to another by simply calling sendCrossChainMessage on the TeleporterMessenger contract. (Note: At present, the Github technical documents related to ICM have not been released yet. Interested students can refer to the relevant courses of Avalanche College.)
From September 3 to now, only more than three months have passed, but the progress of Avalanche9000 is not slow. In the month of the official announcement, the Avalanche Foundation announced the launch of two incentive programs, namely Bounty9000 with a maximum reward of US$9,000 and Retro9000, a retroactive incentive program of US$40 million, designed to reward developers who develop L1 and related tools on Avalanche. On November 26, Avalanche9000 was upgraded and launched on the Fuji test network, and the latest expected time for the main network to be launched is December 16.
Avalanche said that the Avalanche9000 upgrade will reduce Avalanche L1 deployment costs by 99.9% and reduce transaction costs on existing C-Chain by 25 times. There are currently more than 500 L1s under development, covering areas such as tokenization of real-world assets (RWA), loyalty and rewards, games, payments and institutional projects.
Avalanche9000 will undoubtedly make a significant mark on Avalanche's expansion path. However, in an environment where market sentiment is more inclined to chase risky assets without a clear technical foundation, can such technological advancements bring Avalanche back to investors' attention? In fact, not only Avalanche, but also NEAR's layout on AI, Polkadot's 2.0 plan, and the TradFi wave on Aptos, etc., have all been submerged under the torrent of Memecoin. Memecoin’s “instant burst” attribute has its own market logic, and various technological advances often take longer to settle and verify.


 jinse
jinse
 chaincatcher
chaincatcher