Underestimated high growth track: Looking for the second growth curve of oracle

Reprinted from panewslab
05/07/2025·25DTL;DR
1. Oracles are one of the cornerstones of the blockchain world. The core competitiveness of the oracle project is mainly reflected in the following four aspects: comprehensiveness and credibility of data acquisition, acquisition and value capture of exclusive data, security and decentralization of verification mechanisms, transmission efficiency and network robustness.
2. It is estimated that the overall market size of the oracle track should be between US$13.8 billion and US$23.1 billion by 2030.
3. Chainlink is the absolute leader in the oracle track, with rich data sources and extensive project cooperation; Python has advantages in transmission speed and financial data acquisition; Redstone is currently the only oracle that has two price feeding methods: Push and Pull.
4. In the future, oracles will no longer rely too much on providing price feed services for DeFi projects, and RWA is expected to become the second strong growth curve in the oracle track.
5. DePIN, AI, and DeSci businesses will have the opportunity to combine with oracle data services in the future, becoming a new driving force for oracle revenue growth, allowing the industry to grow from 2 to N.
Preface
Oracle is a service mechanism in the blockchain system, used to introduce off-chain data into smart contracts and is one of the cornerstones of the blockchain world. From the perspective of first principles, the core competitiveness of the oracle project is mainly reflected in the following four aspects: comprehensiveness and credibility of data acquisition, acquisition and value capture of exclusive data, security and decentralization of verification mechanisms, transmission efficiency and network robustness.
Figure 1: Oracle Competitiveness Model
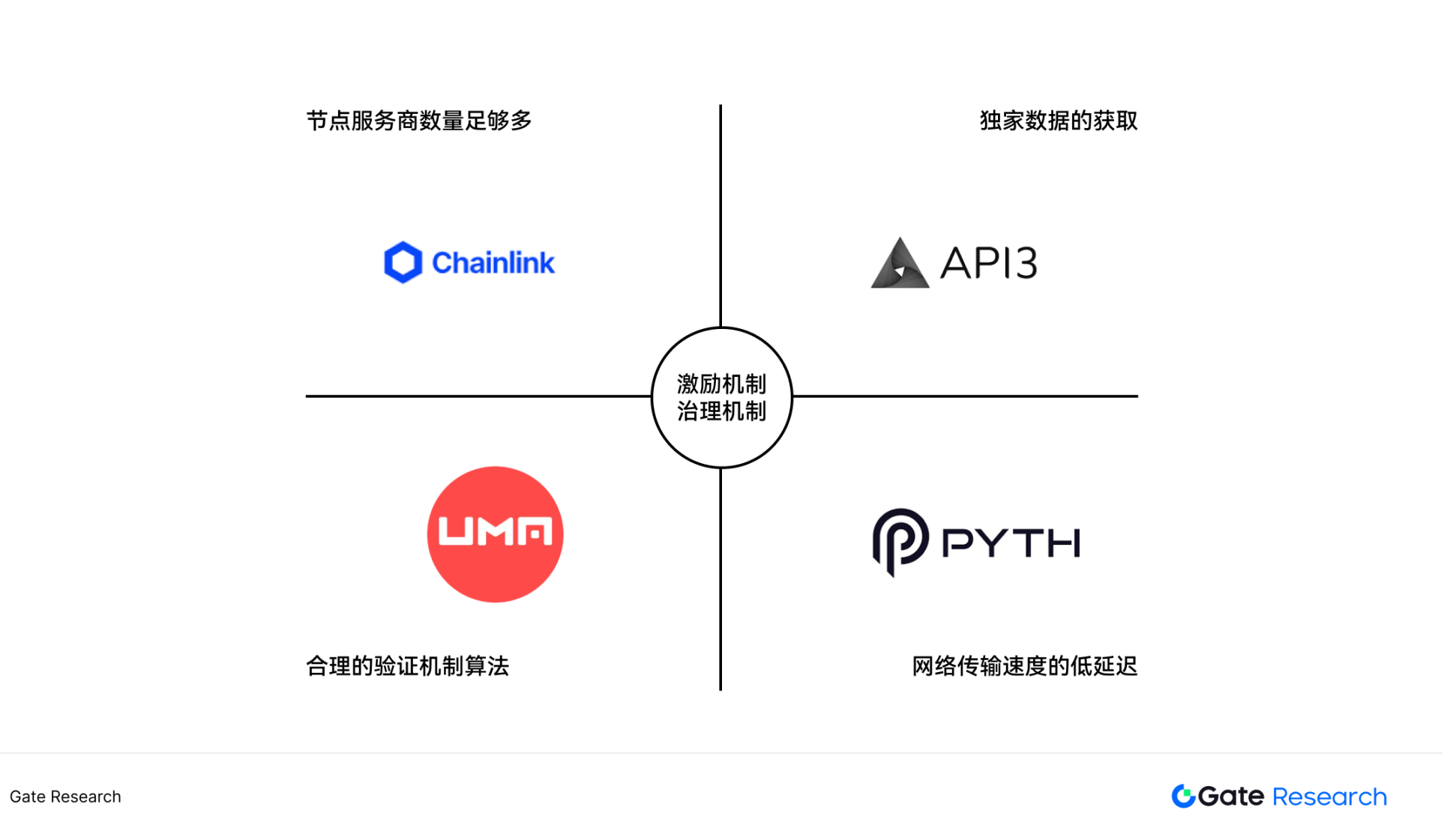
Competitiveness 1: Comprehensive and credibility of data acquisition
In short, a complete oracle platform requires having enough node service providers to provide a large amount of data for verification. Taking the Chainlink project as an example, Chainlink currently has more than 100 data suppliers, including well-known data platforms such as Arkham, Coin Metrics, and Coingecko. Multiple data providers can reduce the single point of risk of data. At the same time, these data platforms enjoy a high reputation in the industry, and the data provided has been strictly verified to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Competitiveness 2: Acquisition of exclusive data and value capture
From the perspective of the DeFi track, the data types provided by oracles are generally similar. The difference is that some highly structured indicators such as Pi Cycle, some oracles can find data suppliers, while some oracles cannot find suppliers. Exclusive data is a major growth point in the development of oracles, and more and more private data can be transmitted through oracles point-to-point.
Competitiveness 3: Security and decentralization of verification mechanisms
The verification mechanism is the core of oracle. Different projects adopt diversified aggregation algorithms (such as median, reputation weight, time-weighted average, etc.) to adapt to specific data types and scenario requirements.
Competitiveness 4: Transmission efficiency and network robustness
After solving multiple problems such as quantity, quality, and verification of data sources, the last important link is the transmission of data. Since the main application scenario of oracle is DeFi, oracle needs real-time data transmission to ensure the accuracy of transaction prices. At the same time, when encountering fluctuations in blockchain networks, the oracle must still ensure the real-time nature of data transmission.
To sum up, oracles mainly play the role of integration, verification and transmission of data. In addition to the technical dimension, the long-term development of oracle projects also depends on mechanism design, especially a reasonable token incentive mechanism, which can effectively drive node participation and ecological growth. Together these elements form the oracle's competitiveness model.
The importance of oracles to the DeFi track is self-evident. Lending agreements, pledge agreements, and derivatives exchanges all need to have a large amount of interaction with oracles to obtain real-time data on assets. Among them, the lending agreement is the most important service user of oracle data. The lending agreement needs to obtain the market price of the collateral assets in real time to calculate the collateral rate and trigger liquidation. For example, the leading lending protocols such as Aave, Compound, and Kamino have already had a high asset management scale. It is easy to have data centering risks by directly obtaining the price of a single exchange through the API. Therefore, the oracle price feeding service is generally used.
However, the application potential of oracles goes far beyond financial transaction data. Theoretically, various types of off-chain data such as real estate price data, sensor data, biomolecular data, etc. can be uploaded to the chain through oracle to trigger transactions of their corresponding assets. This indicates that there are multiple subdivision directions in the oracle track that are in potentially rapid growth stages.
In order to more comprehensively understand the oracle track, this article will analyze it from five aspects: its development history, market size, core projects, the second growth curve, and special oracle.
1. The development history of oracle
2014 and before
Augur is a decentralized forecasting market that enables users to bet digital assets on the outcome of real-world events. The demand for oracle begins to emerge. Vitalik is a consultant to the project.
2015-2016 Stage
Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin proposed the concept of oracle, emphasizing its key role as a smart contract to acquire external data. In 2015, Oraclize (now Provable) launched its first decentralized oracle service, supporting Ethereum smart contracts to obtain external data. In the same year, the main Ethereum website was launched.
2017-2018 Stage
The Chainlink project was established in 2017 and proposed the concept of a decentralized oracle network (DON) aimed at solving a single point of failure problem. Decentralized finance (DeFi) has not yet exploded, and the demand for oracles is mainly focused on simple data calls.
2019-2021 Stage
DeFi Summer arrives in 2020. As the core external data service provider of DeFi, oracle provides price feeding services for decentralized applications. Due to the outbreak of demand, oracle projects outside Chainlink such as Band Protocol and Tellor have been launched one after another, and the competitive landscape has begun to emerge.
2022-2023 Stage
The DeFi market has entered a period of adjustment, but the oracle track continues to innovate. Cross-chain interoperability and modular blockchain have become the industry trend, and oracle services have expanded to multi-chain and multi-scenarios. Chainlink launches cross-chain interoperability protocol (CCIP), which supports cross-chain data transmission and smart contract interaction. The Python Network (oracist focused on financial data) main network is online, attracting participation from many traditional financial institutions.
2024-2025 Stage
Oracle services have expanded from DeFi to games, NFT, insurance and other fields. DePIN applications are beginning to have more demands for IoT oracles. Combining AI and oracle to explore new scenarios for automated execution of smart contracts.
Figure 2: The development timeline of oracle

2. Market size of oracle track
Since there is currently a lack of authoritative forecast data specifically for the future growth of the oracle track, this article attempts to indirectly deduce the potential market size of oracle through the growth of its service object, the DeFi track.
Judging from historical data, as of the end of 2024, the total market value of the oracle project was US$10.55 billion, accounting for 11.8% of the total market value of DeFi (US$91.268 billion). Compared with the market value of oracles that once accounted for more than 25% of DeFi at the beginning of 2021, this proportion has dropped significantly. The core reason for this change is that new models such as re-staking have expanded the industry boundaries of DeFi, but compared with other inherent DeFi sub-tracks, the "necessity" of oracles is still stable.
Figure 3: 2021-2024 DeFi market value changes in oracle market value
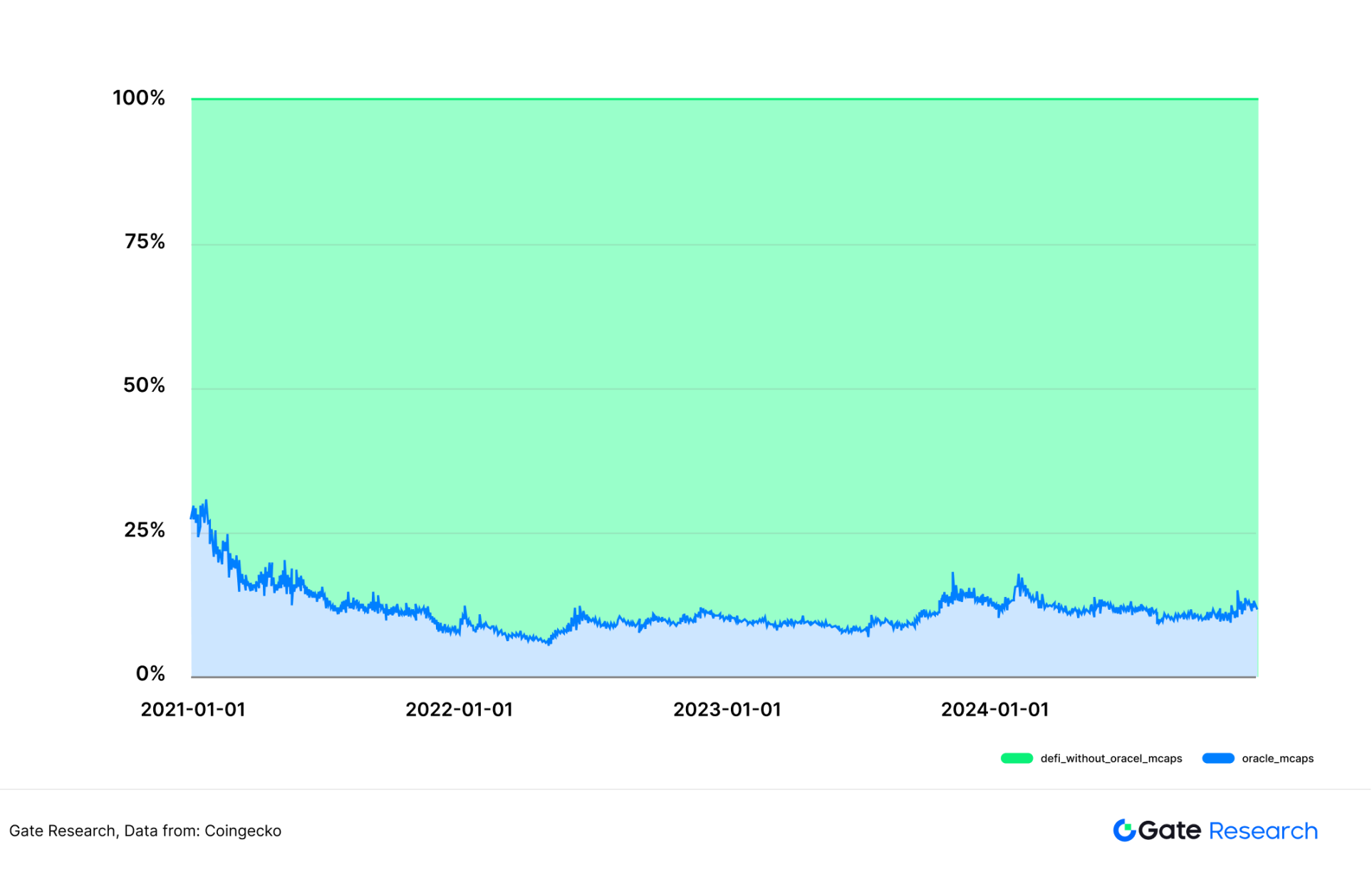
Data: Coingecko
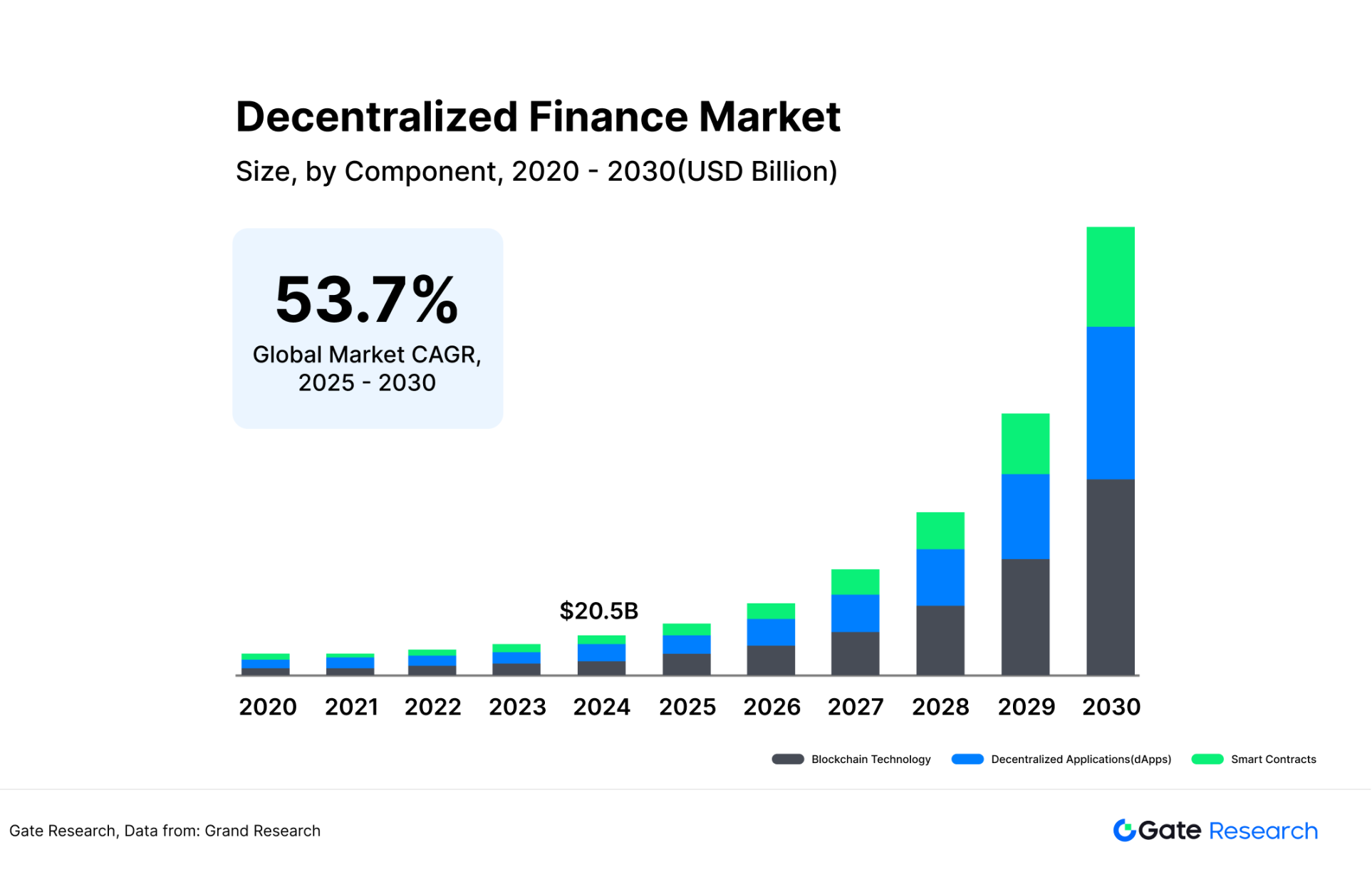
Based on Grand View Research's forecast for the DeFi market (the annual compound annual growth rate of about 53% from 2025 to 2030 will reach US$231 billion in 2030), this article introduces two hypothetical scenarios: "Stable proportion" and "Decreased proportion" to calculate the oracle market space:
●Optimistic situation: If the oracle market size can be maintained at 10% of the DeFi market size, it will reach US$23.1 billion by 2030.
●Neutral situation: The oracle market size remains at 6-8% of the DeFi market size, which will be US$13.8-18.4 billion by 2030.
This prediction model uses the method of "market value accounting for × DeFi total market value" to calculate the potential market value of oracle, which not only reflects its dependence on DeFi growth, but also takes into account the gradual slowdown in the independent growth rate of the oracle industry compared to DeFi.
Figure 4: DeFi market size predicted by Grand View Research
3. The main projects of the oracle track
The current oracle industry structure can be described as one dominant. Chainlink is the absolute leader in the track in terms of token market value and TVS (total protection value). As of March 2025, the Chainlink project's TVS was US$31 billion, accounting for 53.3% of the total TVS of the entire oracle track, and the token market value was US$9.6 billion, accounting for 76.9% of the total market value of the entire oracle track. In addition to Chainlink, Python Network, UMA, API3 and other projects also occupy a place in the oracle track with their advantages in low latency, verification mechanism, and data acquisition.
Figure 5: Market value of oracle main project tokens
Figure 6: TVS (total protection value) data, the main project of DefiLlama oracle
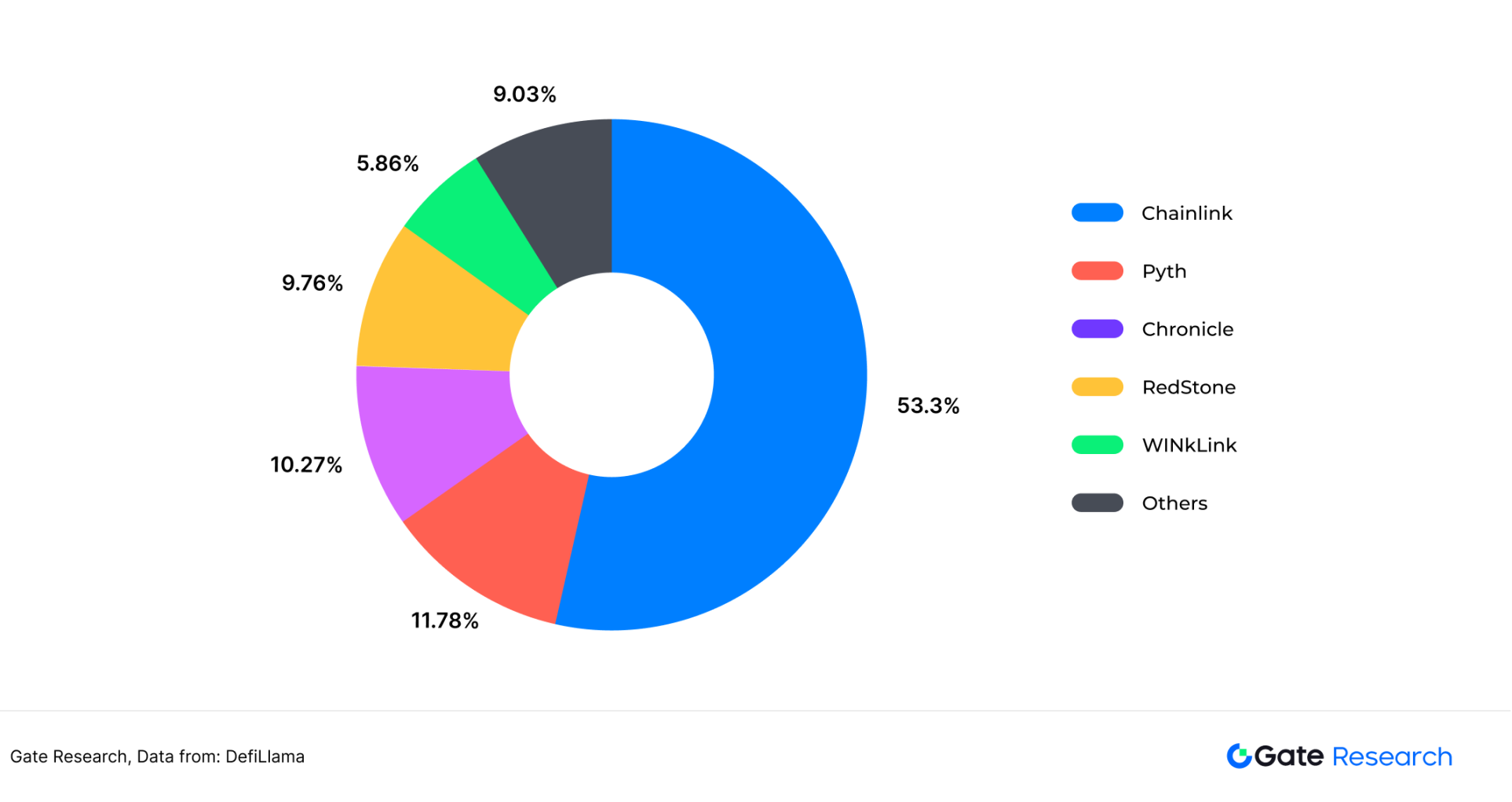
Figure 7: Comparison of main projects in oracle track
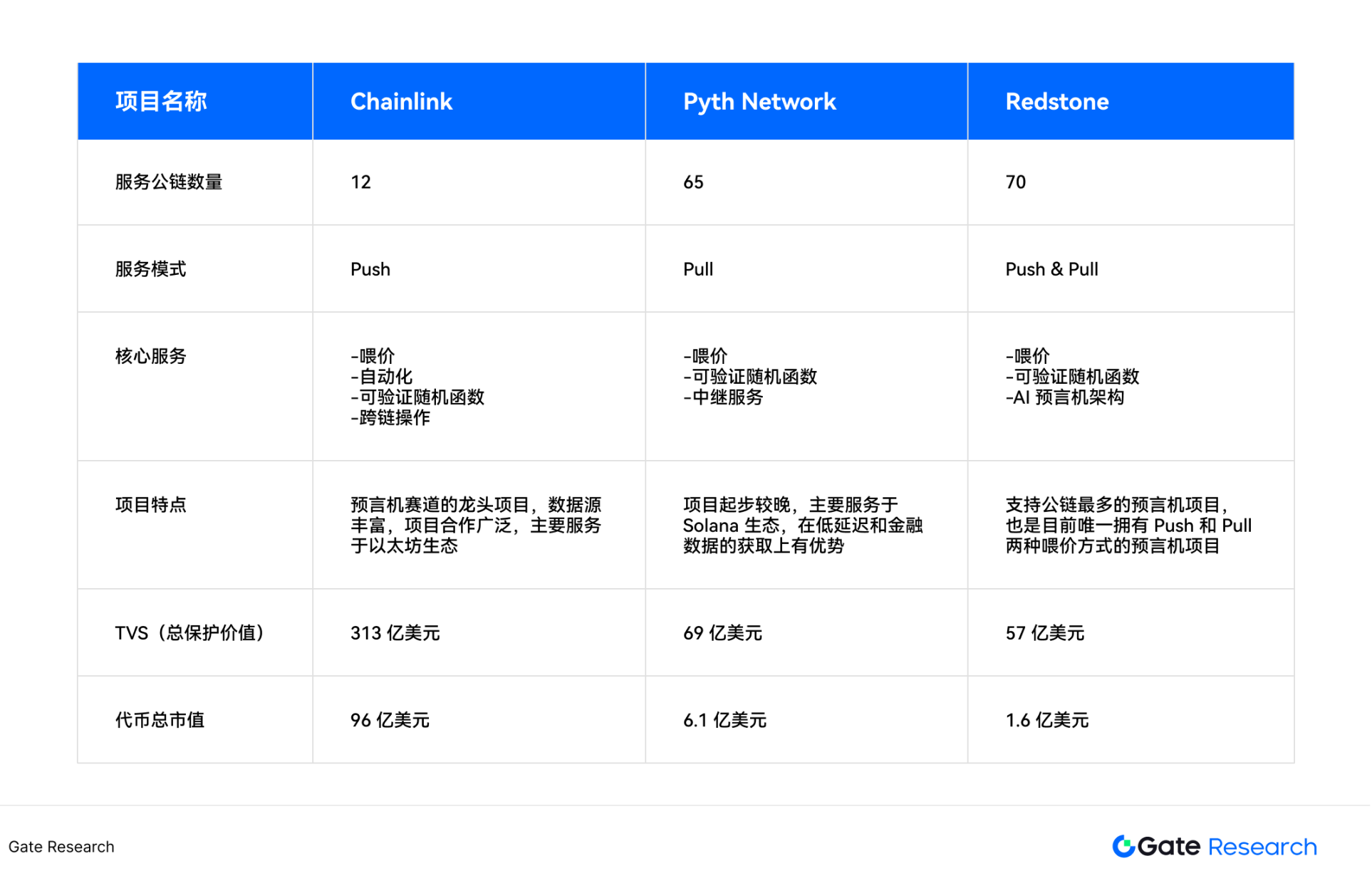
Note: The total market value data for TVL and tokens is March 2025 data
3.1 Chainlink
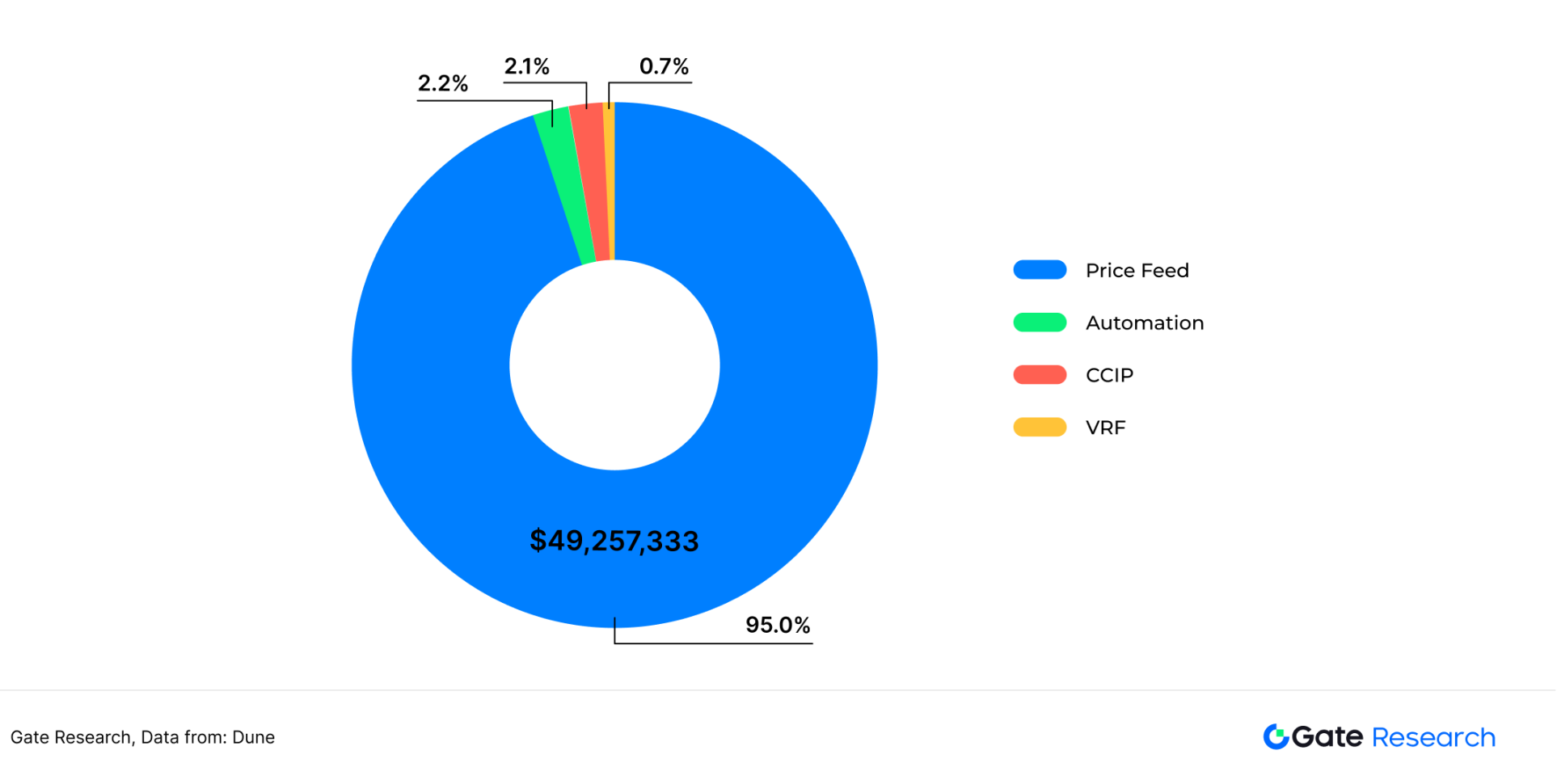
Chainlink is the absolute leader in the oracle track. The project was founded in 2017 and is one of the earliest oracle projects. Chainlink provides services such as price feed, automation, verified random functions (VRF), cross-chain operation (CCIP). In 2024, from the perspective of income composition, the revenue from price feeding services accounted for the highest proportion of project revenue, accounting for 95% of the cumulative revenue, and its main service target is DeFi agreement; the revenue from the other three types of services accounted for a total of 5%. The revenue of automation services and cross-chain services is both 2%, while the revenue of random number generation services accounts for less than 1%. 【4】
Figure 8: Revenue breakdown chart of Chainlink project in 2024
3.1.1 Chainlink price feeding service
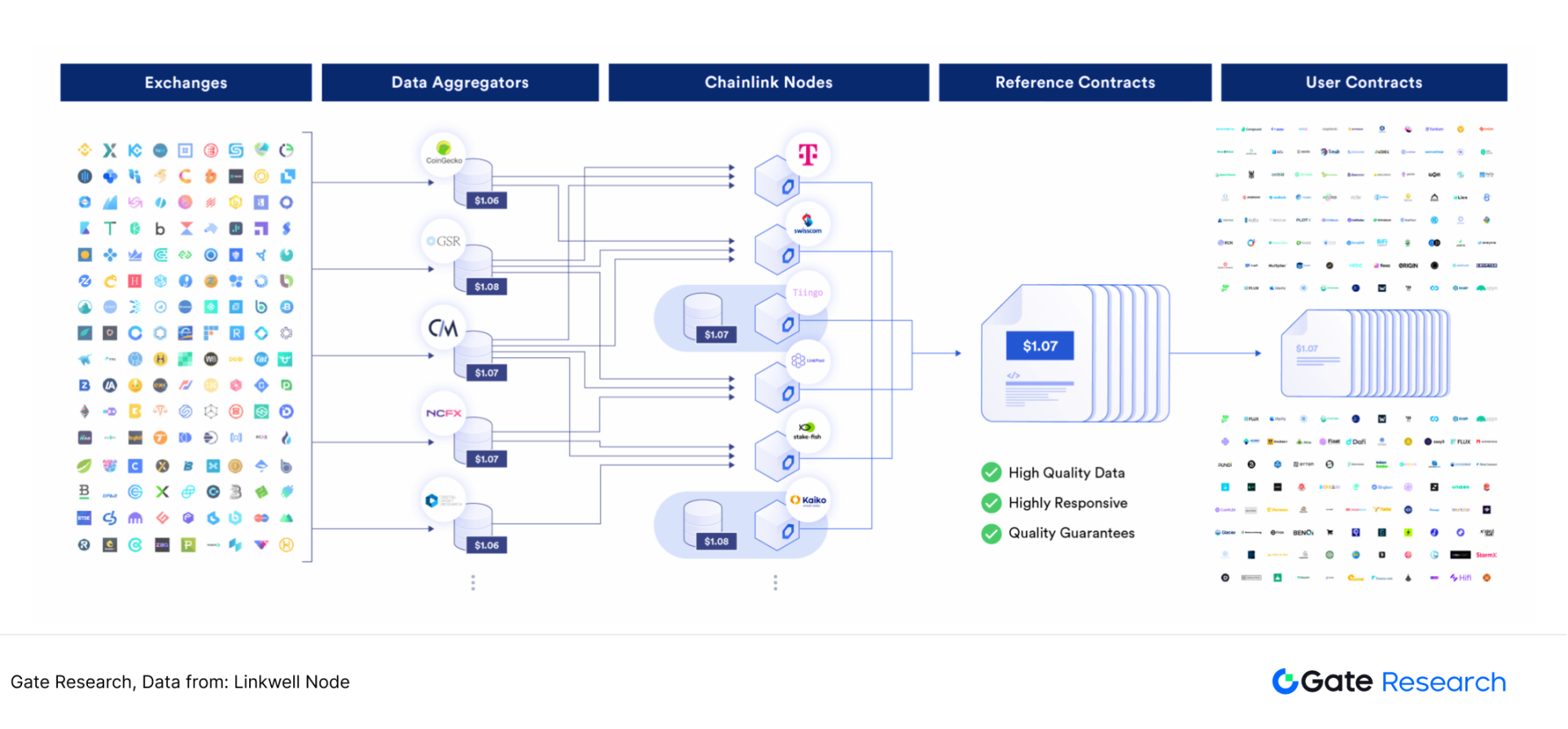
Price feeding is one of the most traditional services of oracle. As one of the earliest decentralized oracle projects, Chainlink's price feeding service does not directly obtain prices from third-party APIs, but obtains data through data nodes. Taking the Aave lending platform to obtain the ETH/USDT real-time price as an example, the user's on-chain transaction request will trigger a smart contract, which will call Chainlink's oracle service to obtain the latest price data. Chainlink oracle does not directly obtain information from a single data source, but obtains data from multiple high-quality data aggregators (such as CoinMarketCap, CoinGecko) through multiple independent nodes. The nodes locally aggregate and clean the data and submit it to the chain.
Then, Chainlink's aggregation contract will filter and weight average the data reported by all nodes again, and obtain a final on-chain price for smart contracts to call. In this process, the oracle node is composed of independent operators such as LinkPool, ChainLayer, and Mycelium. After using this price data, the Aave platform will pay the Chainlink network $LINK tokens as a service fee through a smart contract. 【5】
Figure 9: Chainlink price feed service flow chart
3.1.2 Chainlink automation
Automation is another important revenue-generating business of the Chainlink project. In 2021, Chainlink released Keeper transaction automation service. Keeper is an external account (EOA) that can trigger the execution of smart contracts based on predefined conditions under certain economic incentives. Keeper will use off-chain calculations to execute the same smart contract functions as on-chain. Once the function returns true, Keepers will initiate an on-chain transaction and call the on-chain smart contract function. In practical applications, Keeper can be used to automatically perform operations under specific event triggers, such as casting NFTs, rebalancing liquidity supply, income aggregation and loan repayment, etc. Keeper is also the most important product of the Chainlink project in the Automation 1.0 era. 【6】
Figure 10: Chainlink Keeper 's workflow
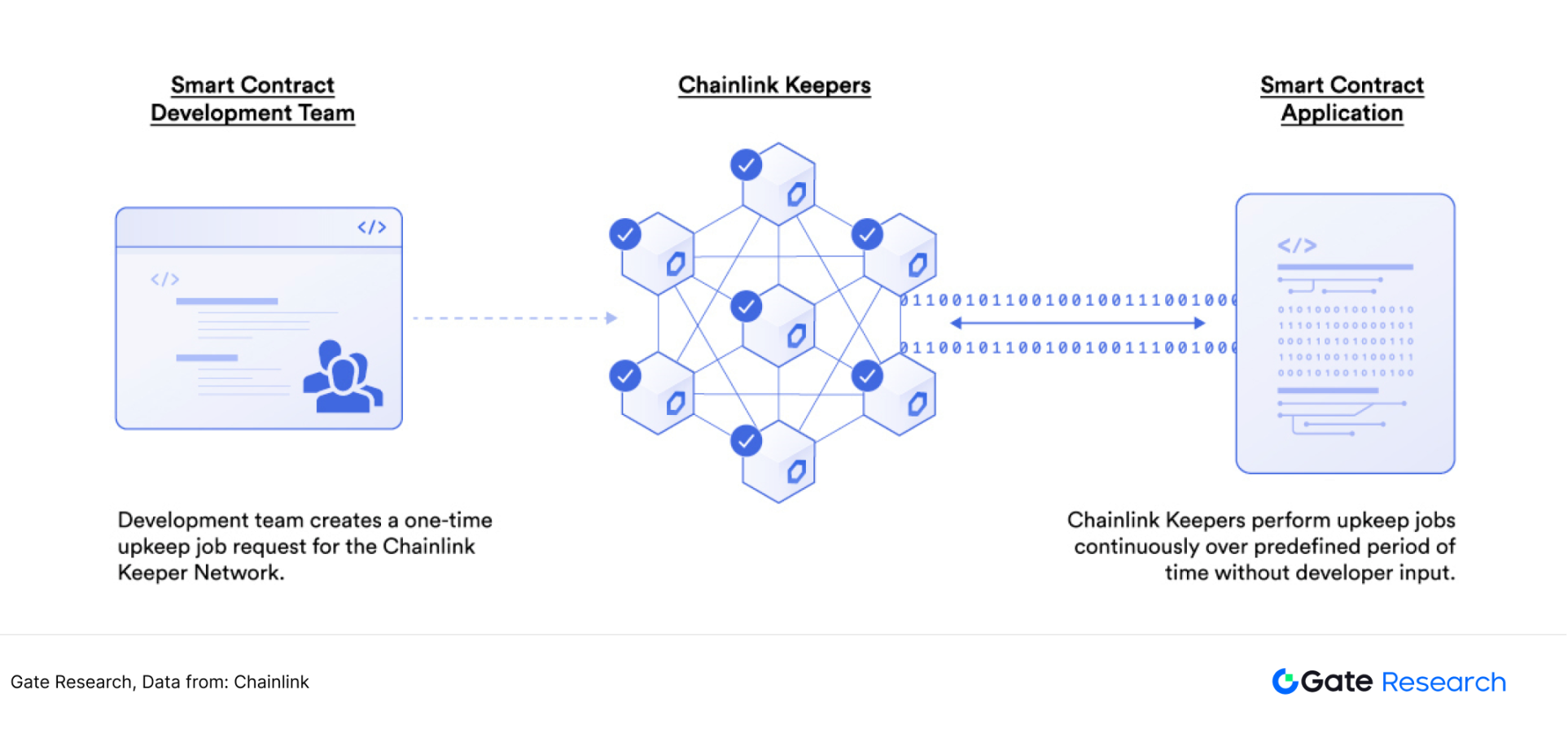
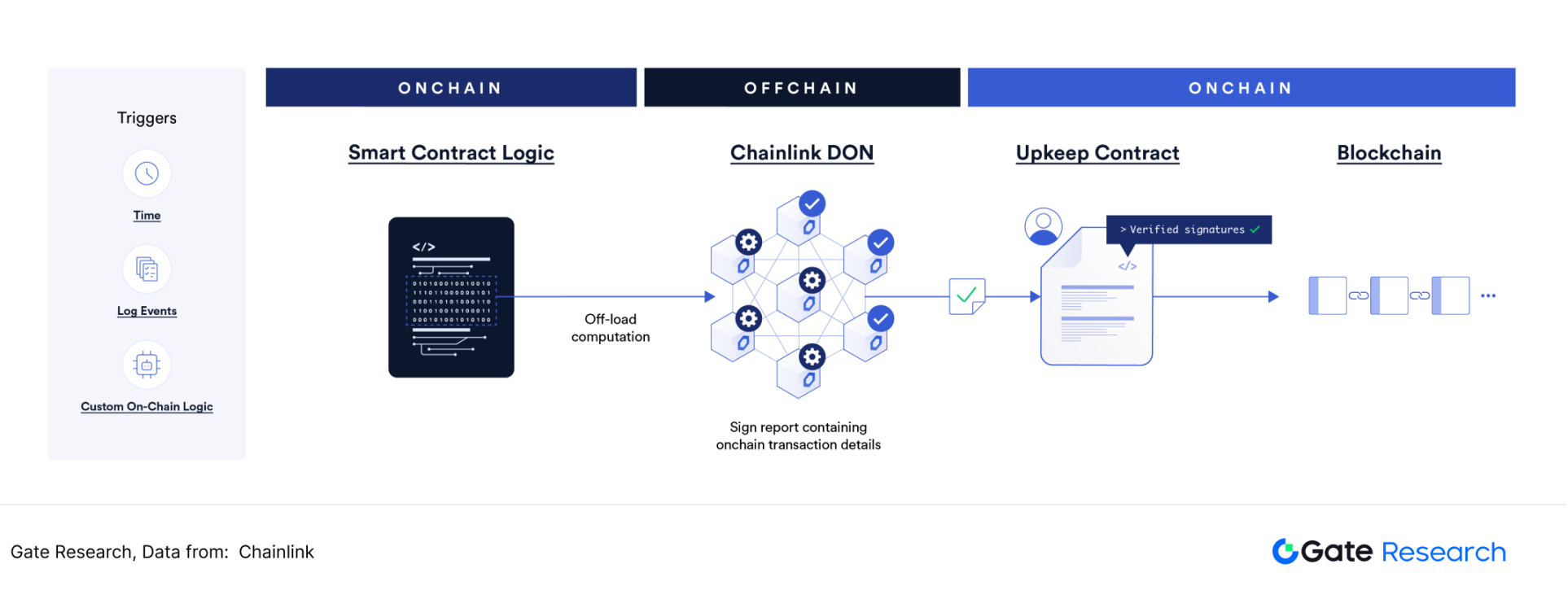
In 2024, Chainlink launched Automation 2.0. Automation 2.0 introduces cryptographic consensus in decentralized off-chain computing, transferring expensive computing verification in blockchain networks to off-chain networks. Developers are able to increase the runtime of their dApps, reduce costs, and simplify user experience. The savings of Gas fees and the improvement of computing performance will allow more developers to choose Chainlink's Automation 2.0 solution. 【7】
Figure 11: Chainlink Automation 2.0 workflow
3.1.3 Chainlink Cross-chain Protocol
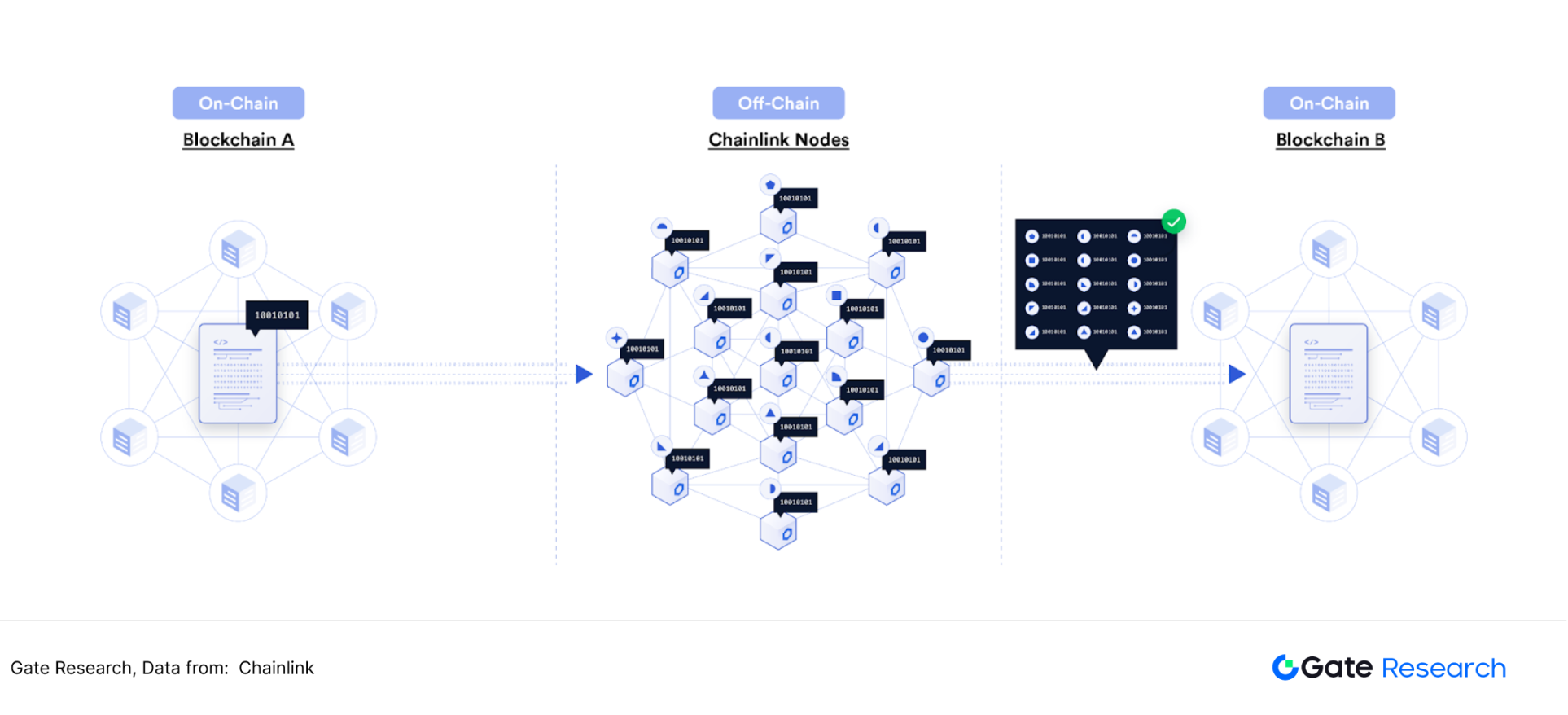
In 2021, Chainlink released the Cross-chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), which is the new open source standard for cross-chain protocols. The protocol provides smart contract developers with a universal infrastructure with computing power that can transmit data and smart contract instructions across various blockchain networks. CCIP will become the underlying protocol for various cross-chain services, including Chainlink's programmable token bridge, where users can transfer tokens safely and efficiently to any blockchain network and be scalable.
For example, a user's 1,000 USDT asset is expected to go from Sui to Solana, so the key point is that the cross-chain bridge can verify that the user actually has 1,000 USDT on the Sui chain. With its huge and decentralized node network, Chainlink network has strong advantages in cross-chain verification and data relay, which is very suitable for such cross-chain scenarios with high security requirements.
Figure 12: Flowchart of Chainlink implementing asset cross-chain
3.1.4 Chainlink verified random functions
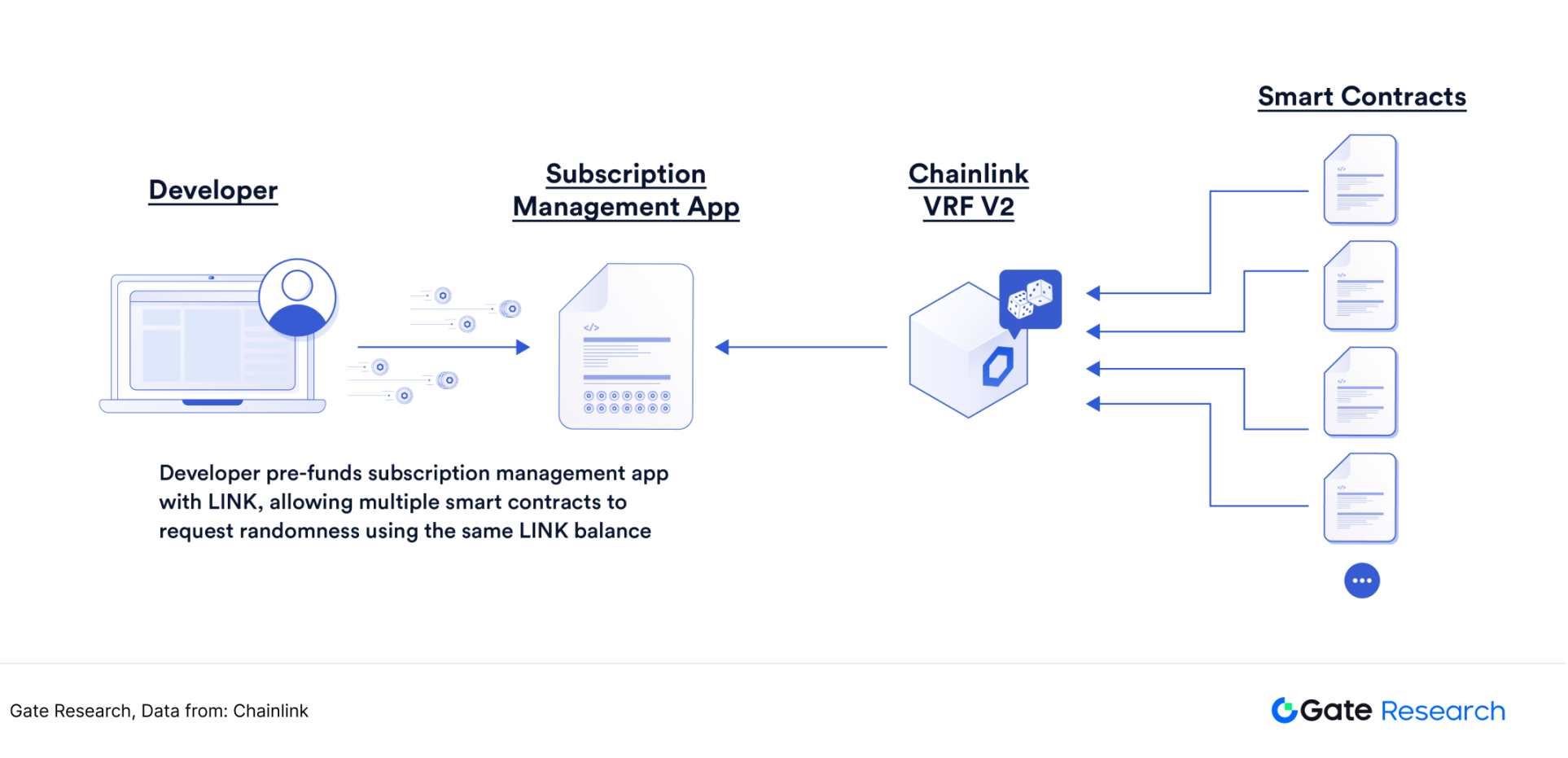
A verifiable random function is an encryption function that generates pseudo-random numbers based on data input and attaches a proof that anyone can verify. Chainlink VRF uses Goldberg's verifiable random functions (VRF). Chainlink VRF generates one or more random numbers for each random number request, and attaches an encryption proof of the random number. This proof will be published on the chain and verified on the chain. The random number will be used only after the verification is passed. Chainlink VRF has covered multiple blockchain networks including Ethereum, Polygon, BSC. In February 2022, VRF V2 was officially launched and is a new upgraded version of VRF, which has stronger performance and higher security.
Figure 13: Chainlink verifies random functions and intelligent interaction
3.1.5 Chainlink Enterprise Privacy Data Service
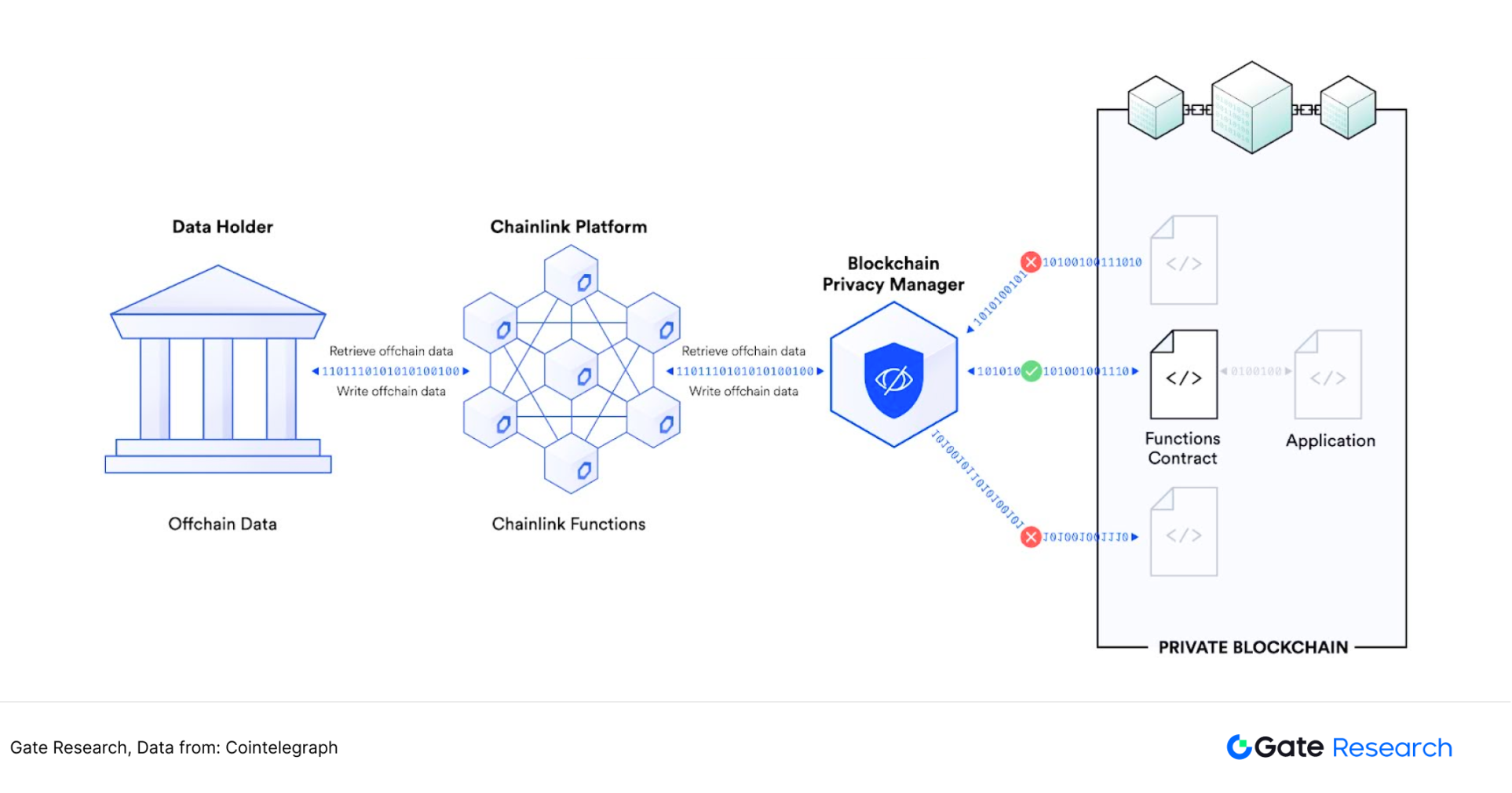
As one of the earliest oracle projects, Chainlink has not stagnated when the price feeding business has formed a relatively strong moat. There have been significant growth in automation, cross-chain protocols, verifiable random numbers, etc. In addition, there are a large number of physical enterprises that require point-to-point transmission of private data. To meet this demand, a large number of startups specialize in privacy data, including multi-party secure computing (MPC), Zero Knowledge Proof, homomorphic encryption (HE), trusted execution environment (TEE), federated learning, etc. Chainlink's powerful verification network can ensure the security and timeliness of private data transmission.
Chainlink can provide enterprises with opportunities to sell data and API services to the blockchain environment, and implement various functions such as private data on the chain, off-chain computing contract logic, and on-chain transactions of private data. In November 2024, Chainlink announced a pilot program with the Global Banking Financial Telecommunications Association (SWIFT) and Swiss banking giant UBS. The pilot project tests tokenized fund settlement between parties, including the choice of traditional financial systems to interact with the digital economy without using cryptocurrencies [8]
Figure 14: Chainlink privacy data link flow chart
3.2 Python Network
Compared with the predecessors of oracle tracks such as Chronicle, Chainlink, and WINkLink, Python Network did not complete the project launch until 2021. Oracles are a key link in the grand narrative of Solana's high-performance public chain. Not only on-chain transactions, but also narratives such as DePIN, AI, and low-latency payments all require oracles as support. Python Network is also a key project supported by the Solana Foundation. The price update frequency is fast, and it is one of the important tags of Python.
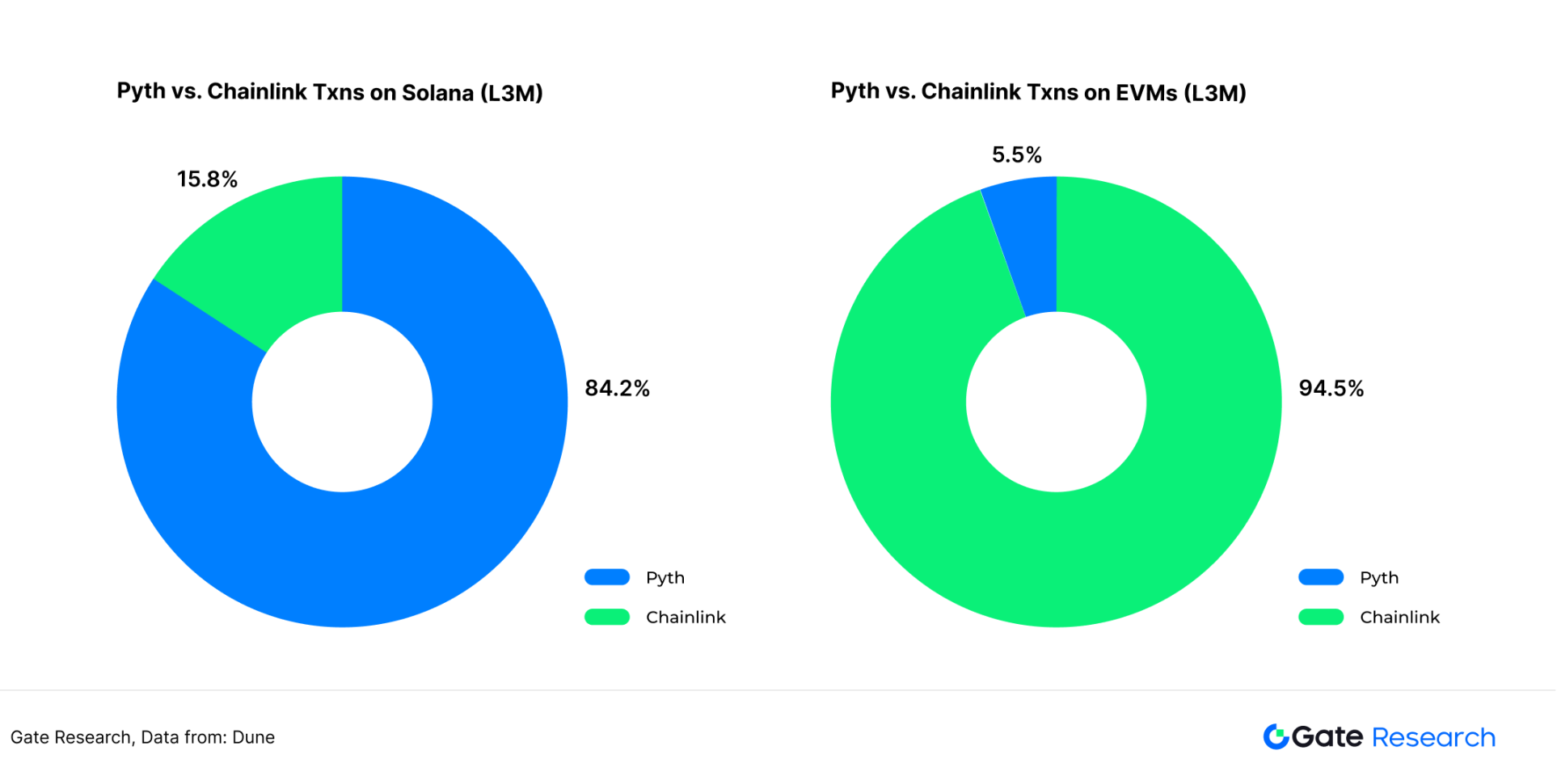
Python Network supports 65 public chains, second only to Redstone, and is one of the oracles that support the most public chains. But its main price feeding service still occurs on the Solana chain. According to Dune data analysis, Chainlink and Python have formed certain barriers to the number of interactions between Ethereum and Solana, and it is difficult for each to expand its market share in each other's public chain.
【9】
Figure 15: Number of price feeding services transactions for Python and Chainlink on Ethereum and Solana
3.2.1 Python Network Price Feeding Service
Judging from the oracle competitiveness model mentioned in the foreword, the competitiveness of Python price feeding services is mainly reflected in the low latency and exclusivity of its data. Python does not set the role of node service provider in terms of price feeding. Many financial institutions, including Wintermute and Flowdesk, are all first-tier data providers of Python. Python price feed service provides corresponding SDKs for different types of public chains such as EVM chain, Solana, and Sui. After the user has installed the SDK, he can call (import) the Python price feed service. 【10】
Figure 16: EVM chain, after installing the SDK, call the Python price feed service in the Solidity development environment
Figure 17: Solana, after installing the SDK, call the Python price feed service in the Rust development environment
Figure 18: Sui, after installing the SDK, call the Python price feed service in the Move development environment
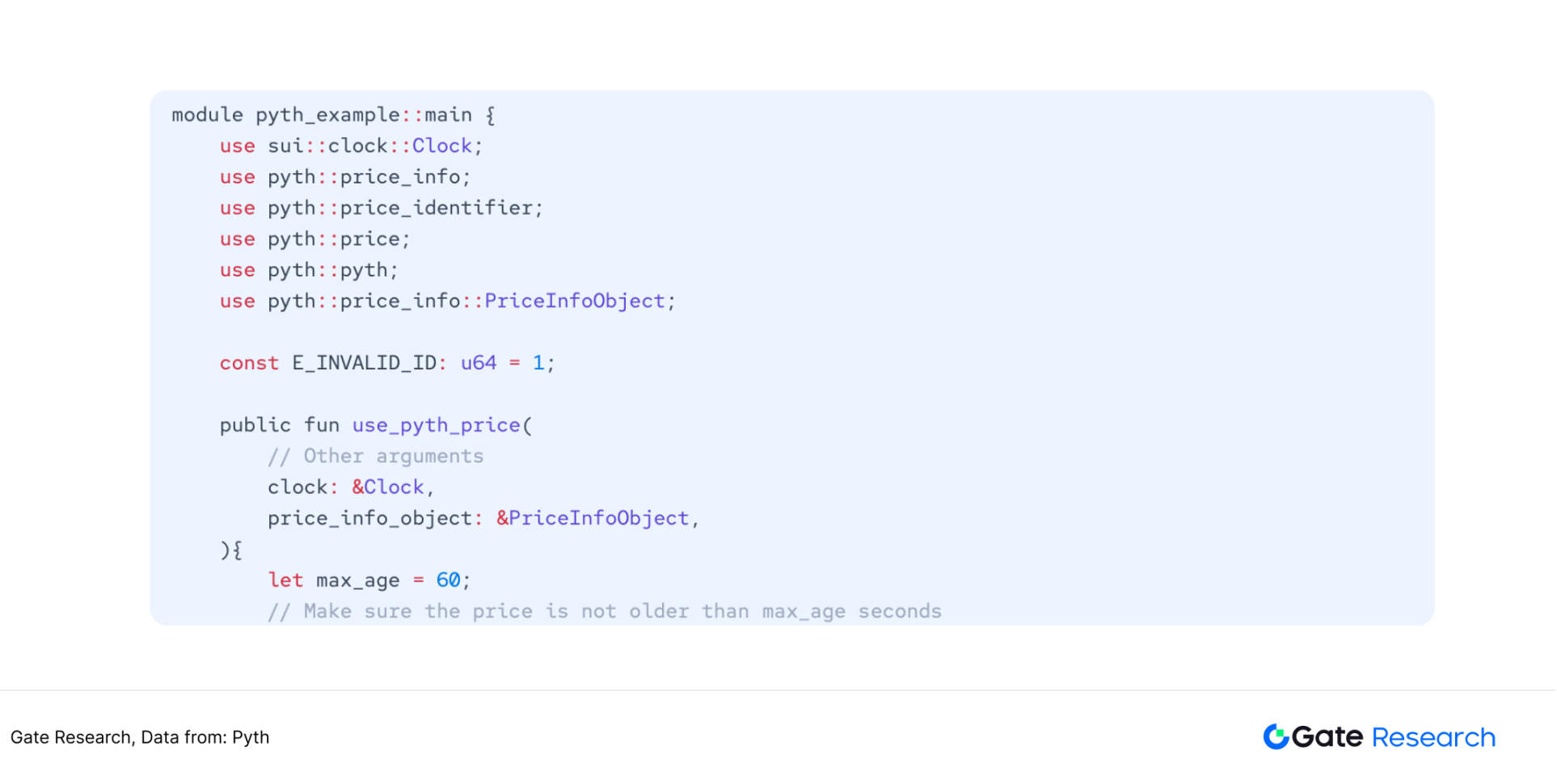
3.2.2 Python Network Random Number Generation Service
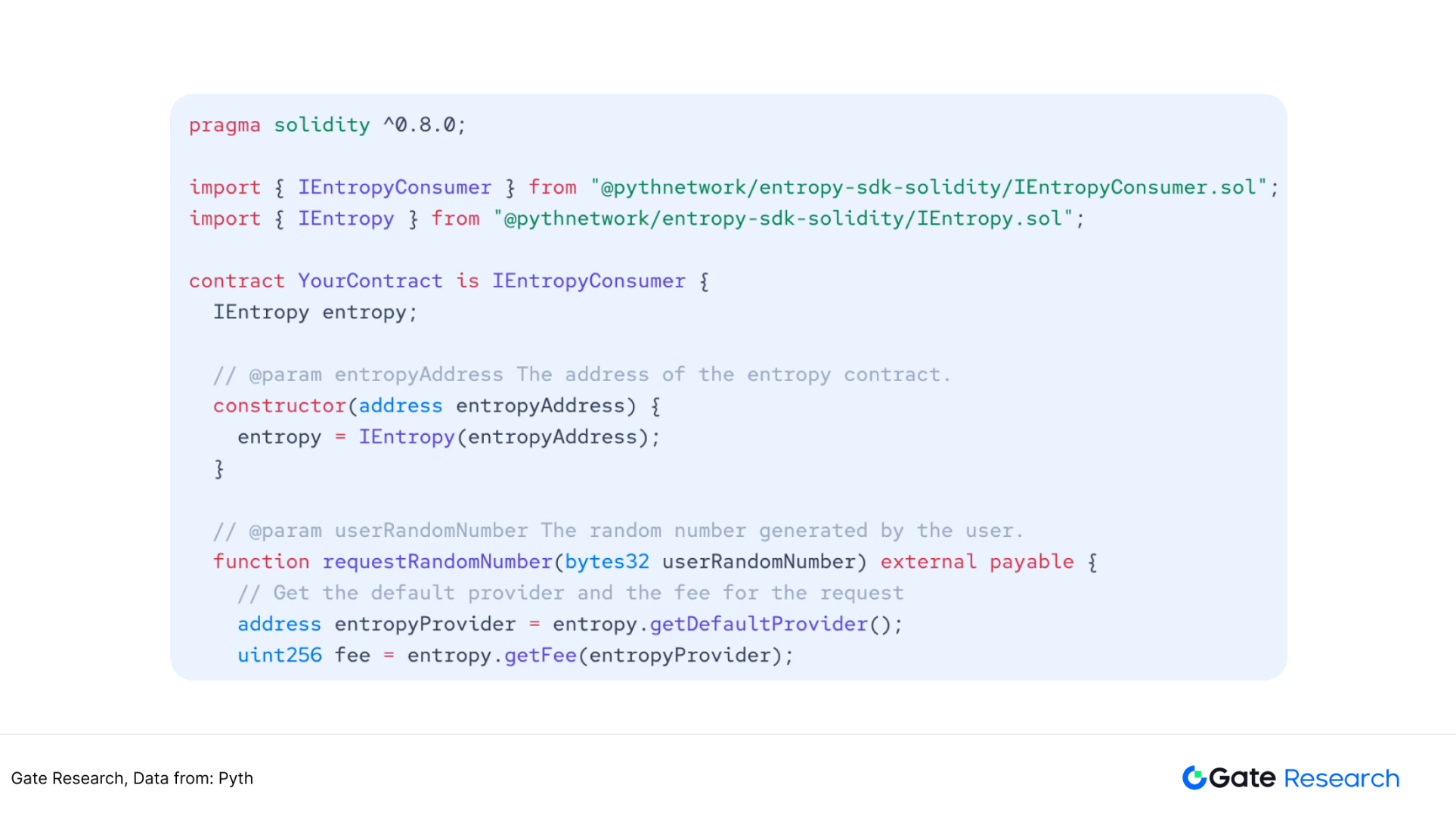
Python Entropy is a random number generation product launched by Python Network. The principle of generating random numbers is similar to Chainlink's random number generation service. Python Entropy's random number generation can be completed in just a few lines of code. Users using the service need to call the requestWithCallback method of the IEntropy contract. This method requires users to pay the fee in the form of Gas Token, and the fees on each chain are not the same. By building a callback function, let the contract obtain the random number generated by the entropy contract.
Figure 19: EVM chain, after installing the SDK, call Python Entropy in the Solidity development environment
3.2.3 Python Network Express Relay Service (Express Relay)
Fast Relay Service is the latest product launched by the Python team in July 2024, which aims to eliminate on-chain MEVs (maximum extractable value). MEV itself is a controversial topic. It specifically refers to some nodes arbitrage through transaction sorting on the chain, especially on public chains with low TPS such as Ethereum main network, arbitrage will be easier. Public chains have different attitudes towards MEVs. Some public chains choose to acquiesce, while others try to minimize the arbitrage returns of transaction sorting.
To understand the meaning of fast relay, take the Solana network as an example. Solana on-chain Memecoin transactions are transactions that require very high timeliness. A token may experience a rise or fall of more than 10% within a few seconds. Therefore, if a trader uses the Orca protocol to conduct transactions, he needs to pay a certain proportion of tips to the on-chain nodes such as Helius and Galaxy, so that the nodes can prioritize the processing of this transaction. Through fast relay, Solana network has an additional repeater for users to search and bid for priority processing of transactions. Those with higher bidding can ask nodes to prioritize the processing of this transaction. The proceeds from bidding will be given to protocol layers like Orca, rather than nodes such as Helius. The interests of the DeFi agreement are protected to the greatest extent. 【11】
Figure 20: Schematic diagram in the article "Eliminate MEV, understand the new Python Network product Express Relay"
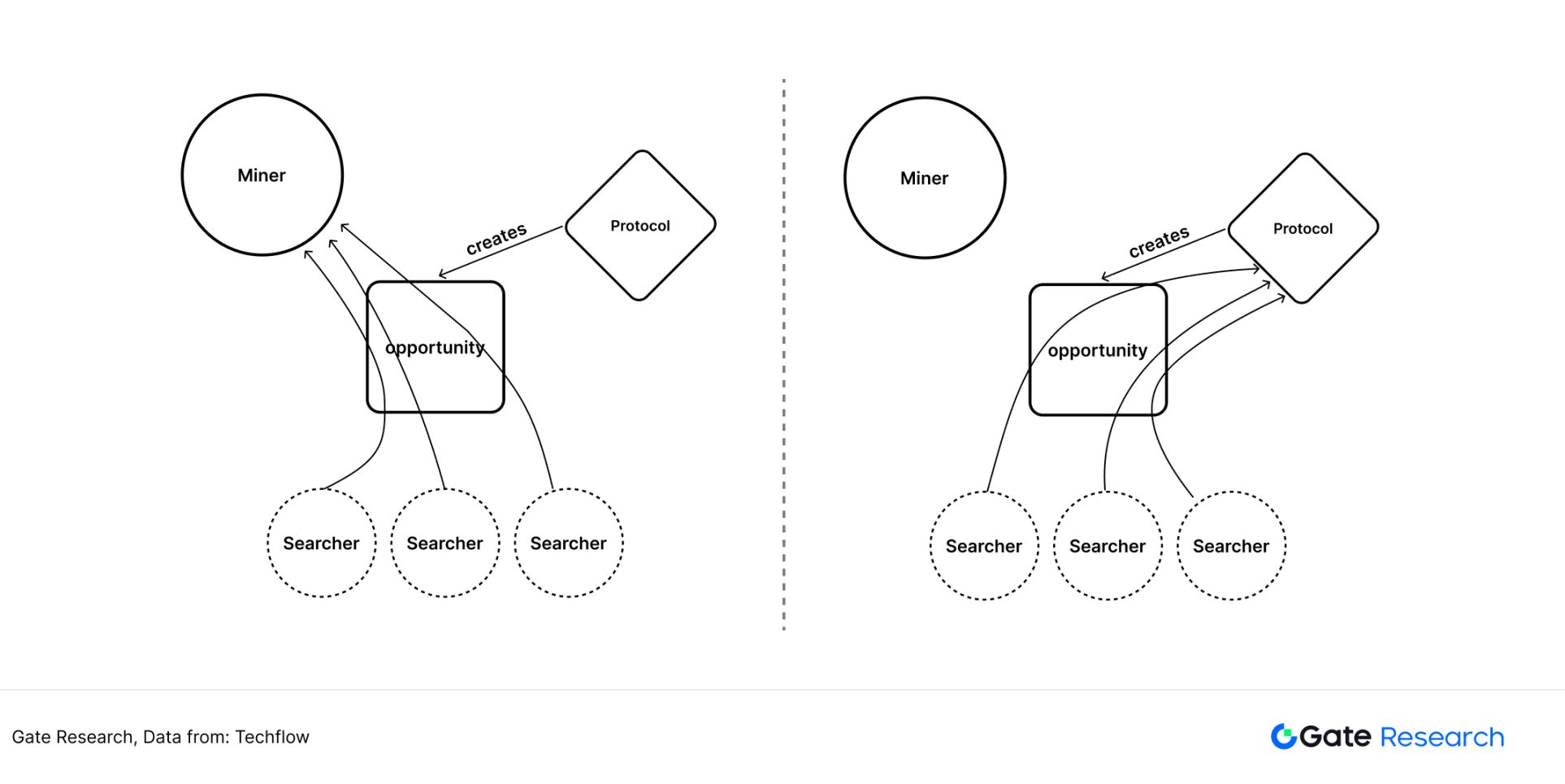
Fast relay is not just an important product launched by Python Network, it also plays a role in ensuring Solana's on-chain decentralized financial protocols such as Orca, Jupiter, and Kamino. Eliminate MEV and return the proceeds to the protocol layer. The increase in revenue will promote more DeFi developers to choose the Solana ecosystem.
3.3 Redstone
Chainlink and Python occupy a core position in the Ethereum and Solana ecosystems respectively, forming their own distinct ecological labels. But there are also some oracles on the market that do not select side stations between Ethereum and Solana, but provide services for as many public chains as possible. Redstone is a representative of this type of oracle. It has completed the integration of more than 70 public chains, which is the most integrated public chains in the oracle project.
Redstone's products include Push Model and Pull Model, as well as new areas of AI oracles. Push model and pull model are the two most commonly used methods of data acquisition by oracles. Chainlink uses push model. Data operators push data off-chain to the chain. The advantage is the speed, and the disadvantage is that the data may have errors, which requires a complete verification mechanism. Python uses a pull model, the advantage is that it is relatively flexible and can pull data when needed; the disadvantage is that the data update is unstable. Redstone is currently the only data provider that adopts both Push and Pull models. 【12】
Figure 21: Redstone service process design
3.3.1 Redstone Push Model
The push model consists of two main parts. The first part is an off-chain repeater, which is responsible for pushing data to the chain in a customized way through environment variables. The second part is an on-chain contract that stores prices and obtains prices through familiar interfaces such as Chainlink Aggregator.
Off-chain repeaters are an innovative design, and previous oracle projects did not design this processing layer. A repeater is a service that runs in a customizable way based on environment variables. It checks a defined set of conditions regularly and pushes prices when the conditions are met. The conditions that have been achieved include time conditions and price deviation conditions. This design facilitates the DApp on the chain, and only calls oracle services will be called when certain conditions are met, realizing the customization and automation of price feeding services. 【13】
Figure 22: Push model workflow
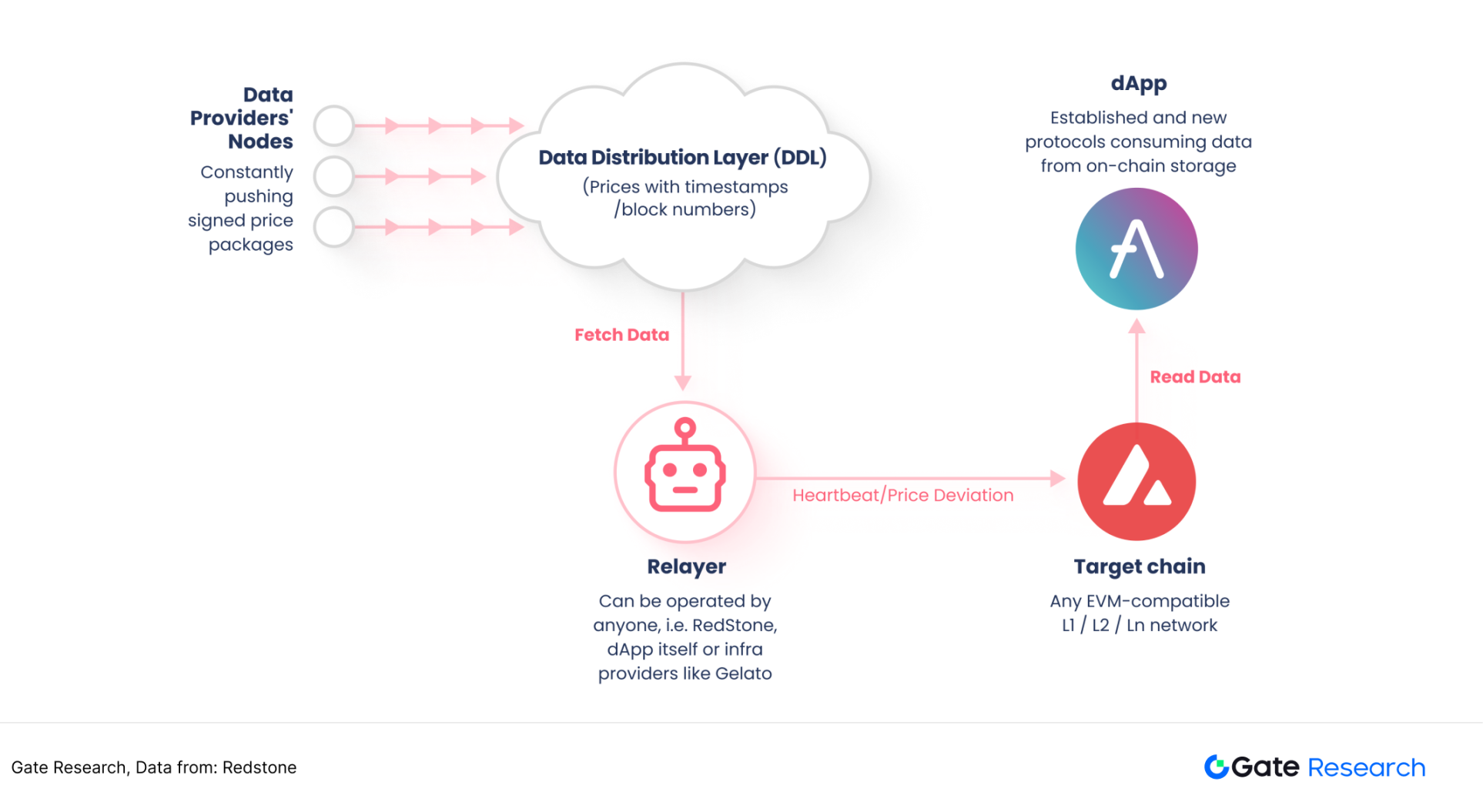
3.3.2 Redstone pull model
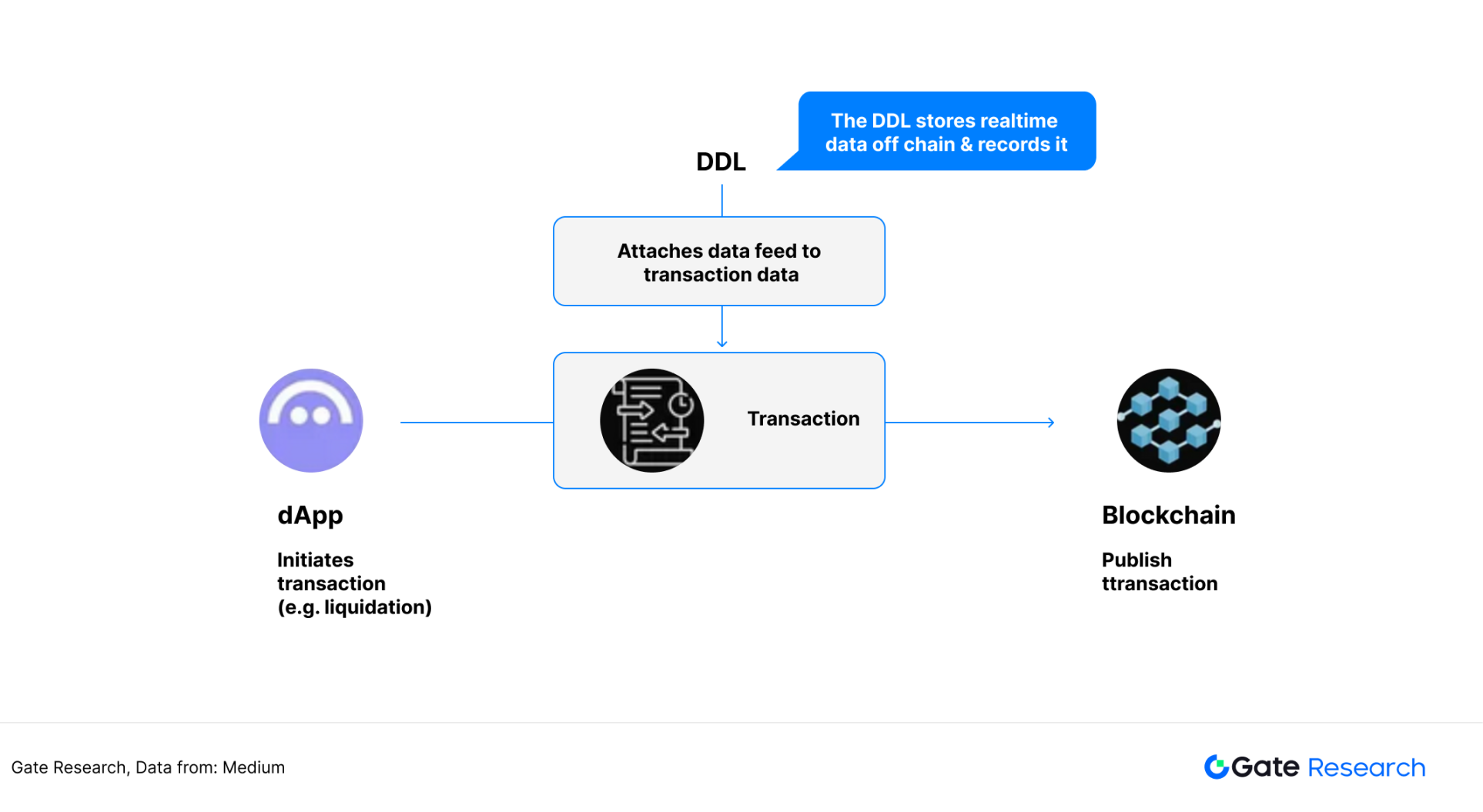
On-chain smart contracts actively call the oracle interface when data is needed to request the latest off-chain data from RedStone, rather than receiving data push in advance. RedStone's Pull model injects data directly into user transactions, maximizing gas efficiency while simplifying dApp data access. 【14】
Figure 23: Pulling model workflow
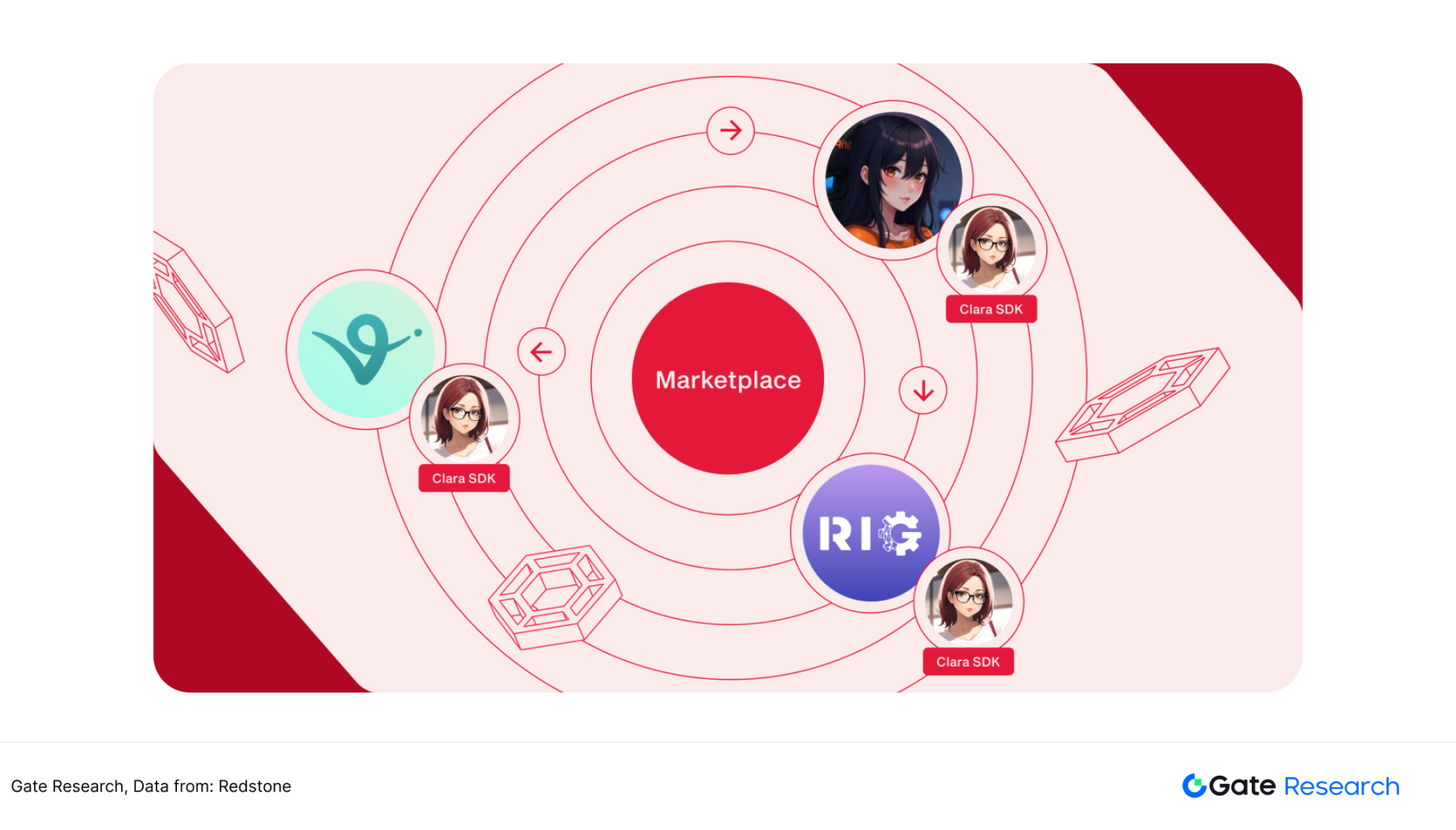
3.3.3 Redstone AI oracle architecture CLARA
CLARA is a blockchain communication layer framework launched by Redstone, aiming to enable seamless communication between agents. The CLARA proxy protocol consists of three key components. They are market modules, CLARA SDK, and framework plug-ins. The Marketing Module is responsible for coordinating the relationships between each agent and is responsible for key processes such as verification and transactions. The CLARA SDK is a developer toolkit that allows developers to easily access the CLARA network. The framework plug-in provides an interface for CLARA communication architecture to connect to the current mainstream AI Agent architecture such as Eliza, making it the communication layer of the mainstream AI Agent architecture. In the future, Redstone will also launch a number of AI-related oracle services, and its exploration in the field of AI is at the forefront of the industry. 【15】
Figure 24: CLARA can interact with multiple mainstream AI Agent architectures
4. RWA opens the second growth curve of the oracle track
As the "data bridge" of the DeFi ecosystem, oracle has deeply bound the rapid growth of the industry with its core functions such as price feeding and cross-chain clearing. However, as the DeFi market penetration rate gradually becomes saturated, the limitations of over-reliance on a single scenario are gradually emerging - protocol revenue is susceptible to market fluctuations, and technology iteration homogeneity weakens long-term value capture. Unlike DeFi that mainly provides price feeding, RWA's demand for oracles is more complex, including asset valuation and real-time tracking of physical asset status and on-chain synchronization, making it a new battlefield for the extension of oracle capabilities. Building a "second curve" in the RWA scenario is expected to open an incremental market of 100 billion US dollars with a trusted off-chain data key.
**4.1 The demand for RWA price feeding services has increased, and
oracles have become the beneficiary**
The integration of traditional finance and encryption technology is one of the biggest narratives in 2024, including Bitcoin ETFs that crypto assets actively embrace traditional channels such as IBIT, and US Treasury bonds that traditional assets actively carry on chains such as BUIDL. For cryptocurrency investors, real-world assets are a favorable tool to hedge risks on the chain. Real-time feedback on off-chain asset prices requires the oracle bridge on and off-chain, allowing investors to monitor the changes in the net value of their total assets in real time.
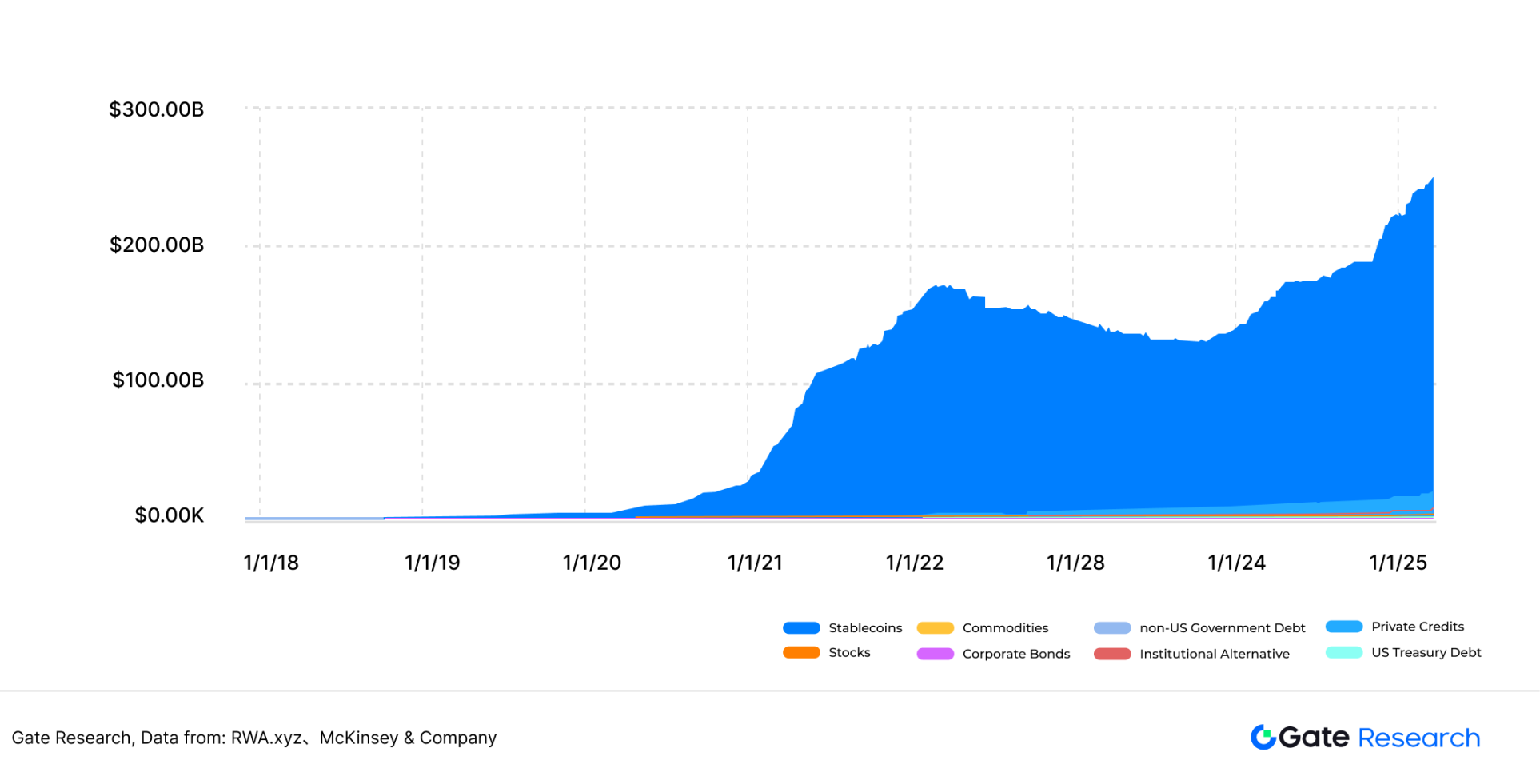
The RWA call oracle price feed service is similar to the DeFi call oracle price feed service. Since RWA really started to gradually start in 2023, the landmark event of US Treasury BUIDL on BlackRock issuance chain was in February 2024. RWA is currently in its early stages of development and still has broad room for growth in the future. Consulting firm McKinsey predicts that tokenized real-world assets will reach $2 trillion by 2030. As of March 2025, RWA.xyz platform data showed that RWA's total assets were US$247.4 billion (including stablecoins), and there is still nearly 10 times the growth potential. Oracles, as an important infrastructure for RWA, can obtain significant revenue increments. 【16】【17】
Figure 25: RWA Asset Scale Chart (Including Stablecoins)
4.2 Oracles that have served RWA projects
●Chainlink has supported Backed Finance partially tokenized RWA price feed
In July 2023, Backed Finance's bIB01, bIBTA, bCSPX and other bTokens underlying assets have supported the use of Chainlink Price Feeds, including 0-1 year US Treasury investment ETF IBO1, 1-3 year US Treasury fixed income ETF IBTA, and tokenized real-world asset (RWA) prices of ETF CSPX that tracks the S&P 500 index. Backed Finance plans to integrate Chainlink Proof of Reserve to increase transparency in Backed products.
●Redstone introduces eurozone treasury bond ETF data source for the crypto world
In August 2023, the oracle Redstone reached a cooperation with the decentralized stablecoin agreement Angle. After RedStone integrates Angle, it will provide it with the price feeding service of the eurozone Treasury bond C3M ETF at noon every day to ensure that its platform and users can access the latest and reliable data.
●Pyth Network has provided price feeding services for the RWA platform Ondo Finance
In January 2024, RWA platform Ondo Finance announced a partnership with the oracle project Python Network to expand Ondo asset price information to multiple blockchains. As of March 2025, Python has provided price feeding services on 65 public chains.
1.Distributed oracle protocol (DORA) 2.0 of Supra public chain, providing RWA price feeding services
In July 2024, the oracle protocol DORA 2.0 of Supra blockchain introduced the RWA price feed mechanism. For the first time, it uses accurate and reliable real-time price data for many traditional assets, with a final confirmation time between 600 and 900 milliseconds. As of March 2025, Supra has provided price feeding services on 36 public chains. 【18】
●Chronicle Labs launches RWA oracle "The Verified Asset Oracle"
In November 2024, the Chronicle Labs team launched the new RWA oracle, The Verified Asset Oracle. The goal is to expand Chronicle oracle services to various off-chain assets. Specific implementation method: VAO oracle will first verify the integrity and quality of these off-chain assets, and then transmit the verified data to the blockchain network. This data will be pushed directly to smart contracts or other on-chain products. According to official disclosure, VAO has reached cooperation with RWA platforms such as Plume Network, Centrifuge, Superstate, etc. to serve the real-time verification of these products and their ecological public chain assets.
To sum up, the current mainstream oracle project has been laid out in the RWA field, from Chainlink's traditional asset support to Redstone's introduction of European bonds, and then to Supra and Chronicle's expansion to financial asset modeling, there are two development paths as a whole: one is to continue DeFi logic and strengthen off-chain financial assets on the chain; the other is to explore more complex off-chain entity data modeling to provide real-time data support for high-threshold asset types. This trend shows that the oracle track is evolving from "price transfer" to "trusted data infrastructure."
4.3 Non-financial assets, high-threshold off-chain data modeling
The previously released "Article Tells Through the Core Logic and Hot Projects of RWA" states various RWA assets classified by cash flow. But for oracle-based data providers, here RWA can be divided into financial assets and non-financial assets.
The so-called financial assets are securitized assets whose fair value can be reflected in real time, such as stocks, bonds, funds, and futures. Data provision for this type of asset is relatively easy, and Bloomberg, Robinhood, and Yahoo Finance can all provide API interfaces. For oracles, transmission efficiency is the core competitiveness in financial asset data. The oracle that supports RWA data mentioned in 4.2 above mainly supports financial assets.
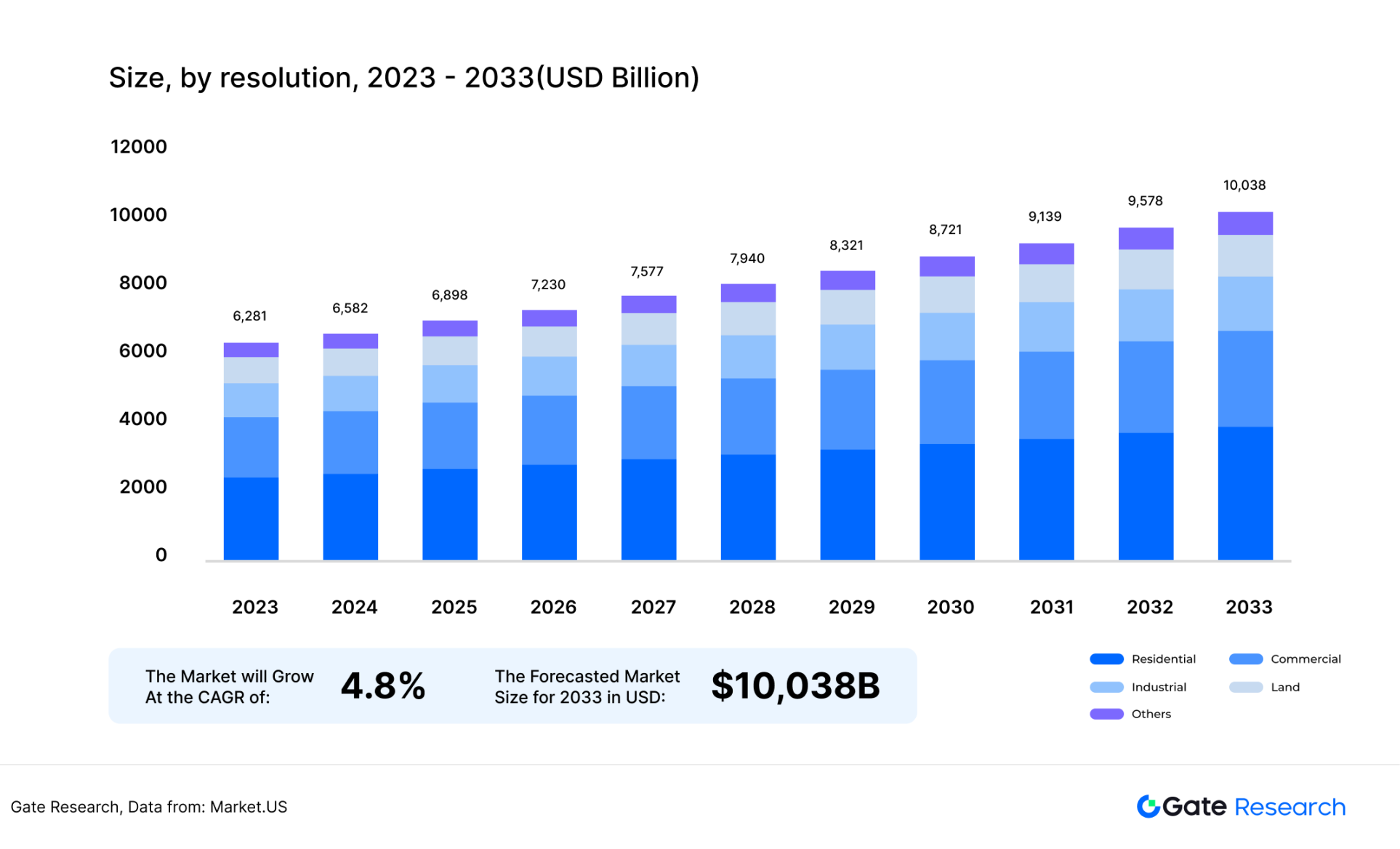
Non-financial assets refer to assets that cannot reflect prices in real time and need to reflect their prices at a certain point in time through mathematical modeling and other methods. For example, real estate, charging piles, photovoltaic components, artworks, etc. Taking charging piles and photovoltaic panels as examples, users invested in tokenized assets through on-chain funds, but these cash flow assets are greatly affected by weather, environment, and equipment management, which may affect their future cash flow distribution. Therefore, it is necessary to model the asset of this type of token and reflect the risk on the token price. According to the Market.US website forecast, the global renewable energy and real estate industries will have market sizes of US$1.4 trillion and US$6.8 trillion in 2025, respectively. Once this part of the assets is tokenized, the demand for oracle data will explode.
【19】【20】
For these non-financial assets, oracles need to provide more complex services, such as accessing data sources that reflect asset status and influencing factors (such as weather data, device operation data, etc.), and combining mathematical models to convert this information into trusted on-chain price or risk assessment, thereby supporting the valuation and management of non-financial RWA tokens. Since the valuation modeling threshold for non-financial assets is high, off-chain valuation companies need to adjust their valuation models in real time, so this type of asset has higher requirements for the transmission performance of the public chain. High-performance chains such as Solana have significant advantages in transmission performance. Based on this, the price feeding of non-financial assets may become a major growth point for Solana's on-chain oracle in the future.
In addition, with the diversification, asynchronousness and dynamic evaluation characteristics of non-financial assets becoming increasingly obvious, oracles not only assume the responsibility of "on-chain data", but also need to have the ability to "off-chain model adaptation and continuous verification". This means that future oracle projects will launch a new round of competition in terms of data depth, modeling complexity and coordination with high-performance public chains.
Figure 26: Global renewable energy market size
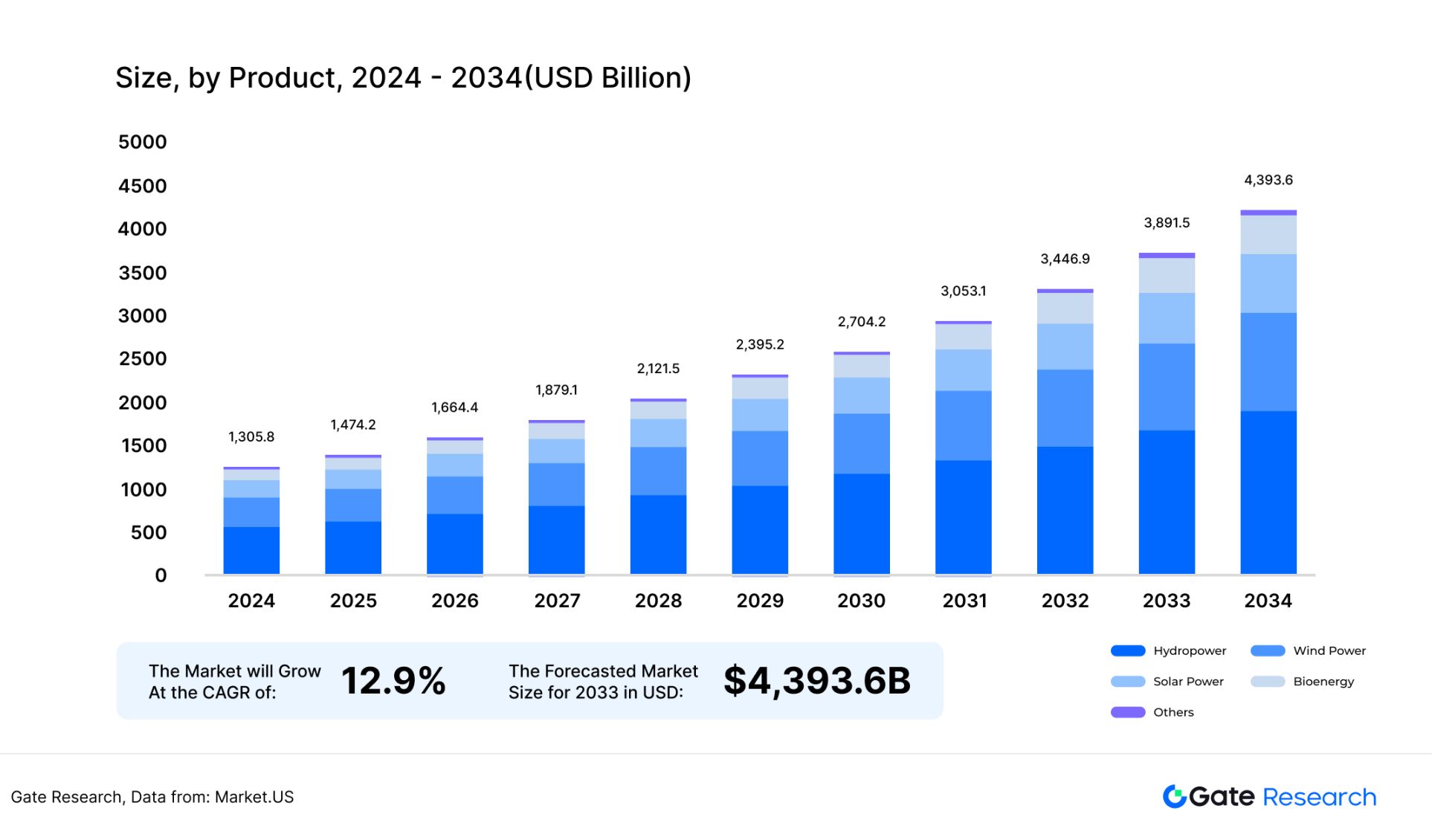
Figure 27: Global real estate market size
5. Multi-type data dedicated oracle, the industry growth curve is from 2
to N
Currently, mainstream oracles are mostly concentrated on the transmission of price data on the chain, forming a standardized service path represented by DeFi price feeding. However, with the expansion of on-chain demand, especially emerging scenarios such as RWA, DePIN, AI, and DeSci, which put forward more complex requirements on the type, format and real-time nature of off-chain data, the service capabilities of oracles are also moving from "general transmission" to "vertical processing" - building a dedicated collection, verification and upload system for specific types of data. In the future, the industry will move from "unified price feeding" to a state of parallel development of "multi-type dedicated oracle" and enter the expansion stage of "from 2 to N".
5.1 IoT data oracle, DePIN capacity expansion
The concept of DePIN has many similarities with RWA. Both are some mapping of real-world assets on the chain, but the essence of the two is that RWA focuses on investing to obtain one-time returns or continuous cash flow, while DePIN focuses on the use of storage, bandwidth, and graphics cards rather than investment. The emergence of IoT oracles allows the user of the device to monitor the device's data in real time, similar to the concept of device data networking in the industrial Internet.
In order to put the data of off-chain hardware on the chain, the concept of IoT oracle came into being. As early as 2023, aitos.io project party has proposed the oracle paradigm based on IoT data - BoAT3. BoAT3 is a PoPow (physical proof of work) paradigm, which can be understood as how much work the off-chain hardware does (such as how much weather data is collected by the thermometer), uploading the completed workload to the chain, and the workload is counted using the DU (DePIN Unit) unit. 【twenty one】
Figure 28: BoAT3 IoT oracle architecture diagram
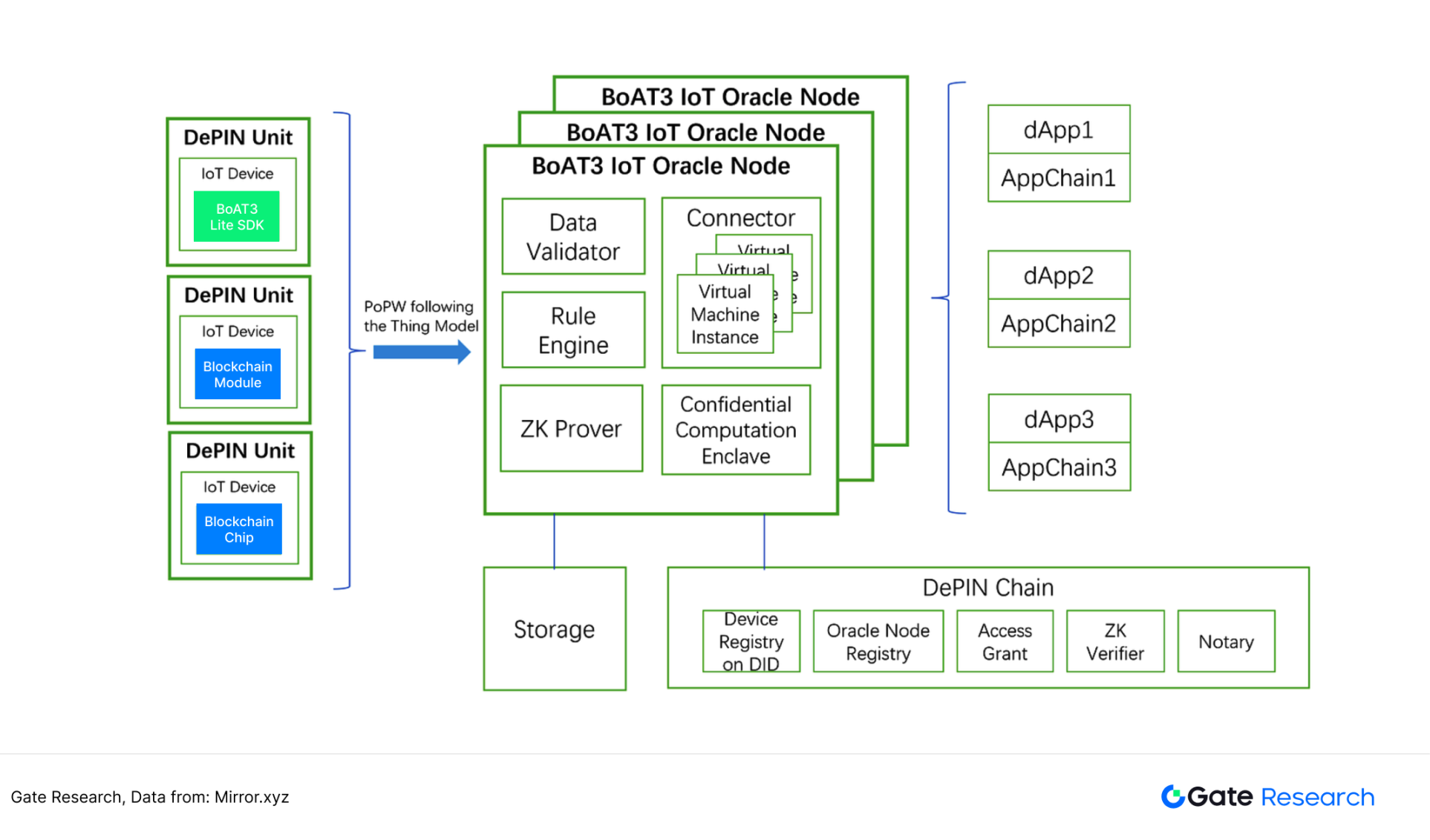
但这一架构自提出以来,并未展现出足够的影响力。笔者认为核心原因在于不同硬件对于DU 这一单位的换算机制并不明确。例如,Filecoin 的存储硬盘有1TB 的数据写入,Helium 基站热点的100GB 带宽被使用,BTC 矿机有5TH/s 的云算力投入使用,这些不同硬件的数据无法统一为相同的DU。物联网每天会产生大量非标准化的数据,例如1MB的天气数据,和1MB 的人体脉搏数据,1MB 的汽车充电数据,其价值肯定是不同的。因此,统一度量衡对于这一赛道至关重要。单位统一后,链上数据需求方可以更方便地判断链上设备完成的工作量。
目前物联网预言机尚处于发展的早期阶段,项目数量较少。部署在Solana 上的区块链预言机Echolink 是目前为数不多的为DePIN 设计的预言机,该项目已完成了约800 万硬件设备的连接。物联网数据基于PoDW(Proof of Device Work)架构。 【twenty two】
5.2 代码预言机,Bittensor 正逢其时
Bittensor 是目前AI 与区块链结合最成功的范例之一,它是一个去中心化的机器学习网络。需求方在链上发布算法问题,并悬赏让不同模型进行挖矿,解决该算法问题最好的模型将获得最多的奖励。
Bittensor 的底层逻辑和预言机有一定相似性,预言机是连接DeFi 协议与链下价格数据,而Bittensor 则是连接链上算法问题的需求方和链下的AI 模型。
拆解Bittensor 的成功案例,其上传到链上的底层数据依然是程序代码,未来可能会有专门的预言机来将链下的代码上传到链上。一个可能的场景是Uniswap、Sushiswap、GMX 这样DEX 的代码漏洞检查。以Uniswap 为例,作为去中心化交易所的龙头,Uniswap 每个季度都会推出漏洞赏金计划,让白帽客找到V2、V3、V4 合约的漏洞。
如果有上传代码的专业预言机,可以通过环境模拟与测试,找到不同白帽客修正代码的最优解,将最优代码上传给需求方Uniswap。不仅能节约Uniswap 的代码审计资源,同时也可以解决传统代码审核平台如Immunefi 和HackerOne 的中心化风险。 【twenty three】
图29:Uniswap V4 开启了高达1,550 万美元的Bug 赏金活动

5.3 生物大分子预言机,Crypto × Biotech 的基础设施
2024 年第四季度,由Vitalik 和CZ 站台的DeSci 叙事成为了加密货币行业的主要热点之一。部分获得加密货币融资的项目方,希望将资金用于生物大分子的开发。在一站式发币平台Pump.science 上已经有3 个长寿候选分子成功发币。
虽然这类代币的模因属性远大于真实科研,但如果未来有越来越多的Biotech 项目方通过链上资金渠道融资,开发生物大分子,那么相关的化合物反应数据可以帮助投资者判断一个项目是否值得投资。如果有生物大分子专用的预言机,拥有多个对于大分子临床实验结果做出评分的节点运营商,可以通过去中心化的方式,有效降低链上投资者对于生物医药行业的理解壁垒。
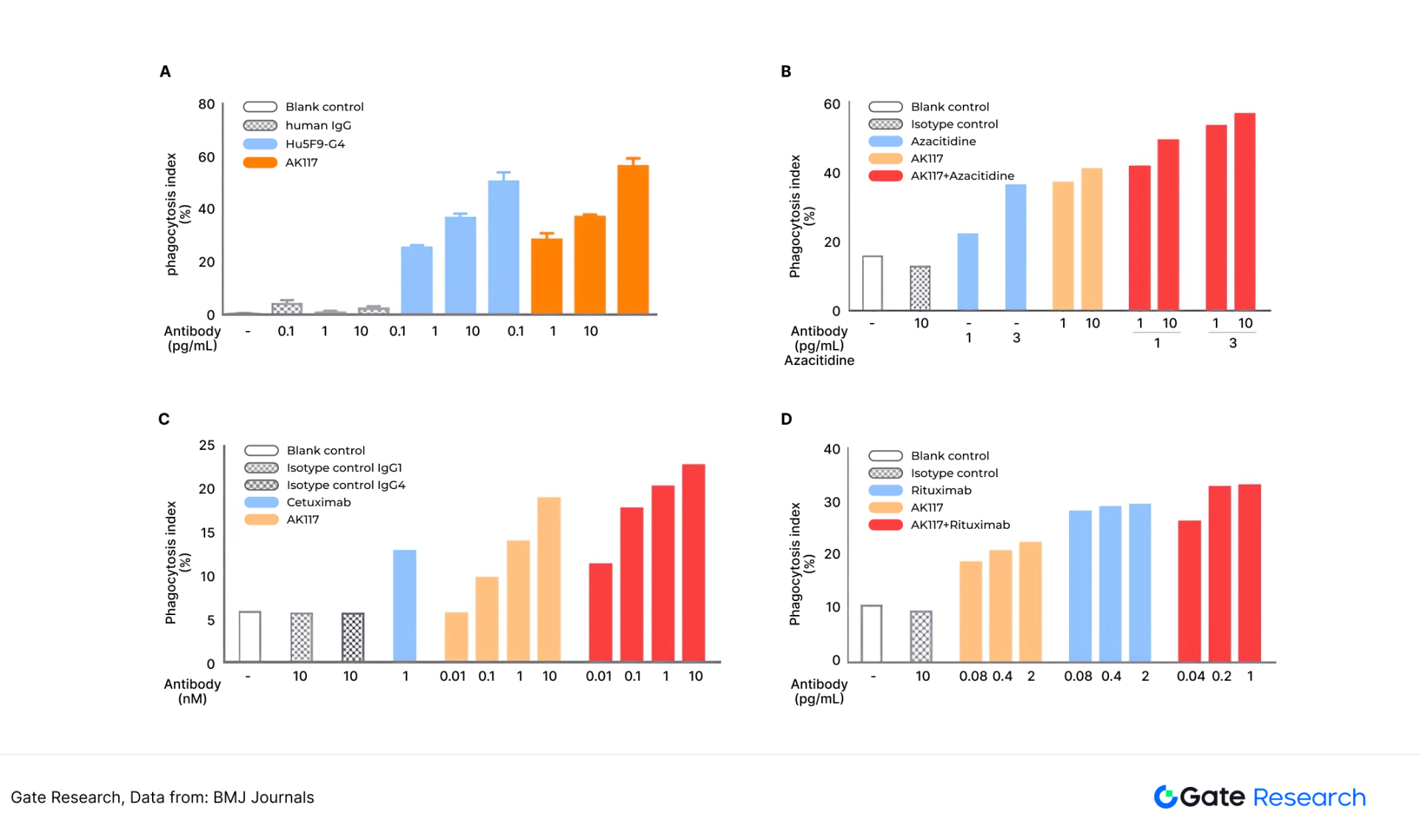
以BMJ Journals 为例,它是是全球四大顶级综合医学期刊之一,涵盖了综合医学、临床专科(如胃肠病学、风湿病学、神经科学等)、流行病学、药品研究、医学教育等领域的权威数据。这类医学期刊或数据库可以作为生物大分子预言机的数据节点,将大分子的临床表现数据上传到预言机,为大分子的代币价值提供数据支撑。 【twenty four】
图30:BMJ Journals 的临床数据展示(康方生物的AK117 分子)
综上,预言机正从服务标准化金融协议的「通用数据层」,逐步演化为支持垂直场景的「多模态基础设施」。物联网、AI 代码、生命科学等多个领域的链下数据上传需求,正在催生一批专用预言机的出现。
Conclusion
以加密货币用户目前对预言机的共识来看,预言机主要的功能是聚合并验证链下的价格数据,将其供给链上的DeFi 应用。自从2022 年以后,区块链世界与真实世界的融合越发紧密。RWA 目的是用链上资金投资链下资产(黄金、股票、房地产、能源);DePIN 的目的是将链下分散的硬件(硬盘、显卡、路由)聚合起来,降低使用硬件的成本;DeSci 的目的是将链下的科研项目(生物医药、人工智能)上链,以削弱中心化期刊的垄断地位。而以Bittensor 为代表的AI,则是将链下的AI 模型上链,以解决高难度的算法问题。
如上所述,链上对于链下数据的需求不再仅仅是BTC/USDT、ETH/USDT 这样的交易价格数据,而是需要更多真实世界的黄金价格、物联网数据、大分子数据、程序代码。对于预言机而言,处理多种模态的数据既是机遇也是挑战。机遇在于多模态数据的处理,将让预言机的收入不再过度依赖喂价,而有更多的收入增量。而挑战在于,预言机在前端数据的验证层面,以及后端的智能合约执行层面,都需要部分业务场景的重构。
在过去的三年里,加密市场的热点在Meme、DeSci、AI Agent、DePIN 之间不断切换,预言机这一重要的基础设施始终未有足够的讨论度。未来,随着链上对更多模态的数据提出需求,以及智能合约性能的提升,RWA 有望成为预言机赛道最主要的第二增长曲线,同时,垂直化的专用预言机创业项目将不断涌现。
Source of data
1. Grand Research, https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/decentralized-finance-market-report
2. Coingecko, https://www.coingecko.com/en/categories/oracle
3. Defillama, https://defillama.com/oracles
4. Dune,https://dune.com/queries/4894196/8104466
5.Linkwell Node,https://docs.linkwellnodes.io/blog/Build-A-Chainlink-Price-Feed-With-Flux-Aggregator
6. Chainlink,https://blog.chain.link/smart-contract-automation-zh/
7. Chainlink,https://blog.chain.link/chainlink-automation-2-0s-verifiable-compute-a-leap-forward-for-web3-computation-zh/
8. Cointelegraph,https://cn.cointelegraph.com/news/chainlink-introduces-chainlink-runtime-environment-framework
9. Dune, https://dune.com/agaperste/pyth-network-vs-chainlink-price-feeds
10. Pyth, https://docs.pyth.network/price-feeds/use-real-time-data
11. Techflow, https://www.techflowpost.com/article/detail_18981.html
12. X, https://x.com/0xBeyondLee/status/1880274357232214314
13. Redstone, https://docs.redstone.finance/docs/dapps/redstone-push/
14. Medium, https://medium.com/@entrepreneur6666/three-ways-to-integrate-redstone-59a519e07708
15. Redstone, https://blog.redstone.finance/2025/01/22/introducing-clara-communication-layer-for-agents-by-redstone-on-ao/
16. RWA.xyz, https://app.rwa.xyz/
17.McKinsey & Company, https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/from-ripples-to-waves-the-transformational-power-of-tokenizing-assets
18. Supra, https://supra.com/zh-CN/oracles-product/
19. Market.US, https://market.us/report/renewable-energy-market/
20. Market.US, https://market.us/report/real-estate-market/
21. Mirror.xyz, https://mirror.xyz/0x6510f5d8CC090b38BE8Bf1BBCd28d15e726395A2/IteGyM3tFgbbPLwrAimt9vwpRKe47coFcpKKll3XYaM
22. Echolink, https://echolink.network/
23. Uniswap, https://blog.uniswap.org/v4-bug-bounty
24. BMJ Journals, https://jitc.bmj.com/content/9/Suppl_2/A288



 chaincatcher
chaincatcher