Through Vield and Coinbase, see new trends in Bitcoin lending

Reprinted from panewslab
03/07/2025·2MOriginal author: Tiger Research Reports
Original translation: TechFlow
summary
- Bitcoin mortgages provide users with a way to get funds without selling cryptocurrencies, and companies such as Vield and Coinbase are leading the industry’s innovations in this area.
- Although this model has obvious advantages, it still faces major challenges such as high volatility, forced clearing and regulatory uncertainty.
- The Asian market has shown great growth potential in the field of Bitcoin lending, but the key to success lies in clear policies and regulations, widespread adoption of institutions and effective risk management.
1. Introduction
Bitcoin mortgages are an emerging financial instrument that allows cryptocurrency holders to obtain funds without selling their assets. This model is gradually becoming popular, and professional institutions such as Vield in Australia and Coinbase in the United States have launched related services.
With this kind of loan, users can use Bitcoin as collateral while retaining their potential appreciation opportunities. With the popularity of digital assets, Bitcoin mortgage loans are becoming a powerful supplement to traditional financing.
However, this loan model is also accompanied by high risks. Unlike traditional collateral such as real estate, Bitcoin prices fluctuate dramatically, which may lead to forced liquidation of loans and cause losses to borrowers.
In addition, the regulatory environment for cryptocurrency lending is not yet clear. Governments and financial institutions are still exploring how to incorporate such services into the existing financial system. Therefore, both lenders and borrowers need to move forward cautiously in this market full of opportunities and challenges.
This report will explore its potential in the Asian market by analyzing classic cases of Bitcoin mortgage loans and assessing related risks and regulatory issues.
2. Case Study from the West: Coinbase and Vield’s Crypto-Borrowing Model
2.1 Vield: Integrating Bitcoin lending into traditional finance

Vield CEO Johnny Phan dominated the $35 million cryptocurrency mortgage business last year. Source: afr.com.
The Australian-based lending company is working to build itself into a "crypto-native bank". Vield offers Bitcoin mortgages and a hybrid loan product combining digital assets and real estate mortgages, aiming to establish Bitcoin as a legal asset class in the financial system, similar to traditional mortgage securities. Unlike traditional banks that rely mainly on real estate as collateral, Vield innovatively secured Bitcoin and Ethereum as loans, creating a completely new asset class.
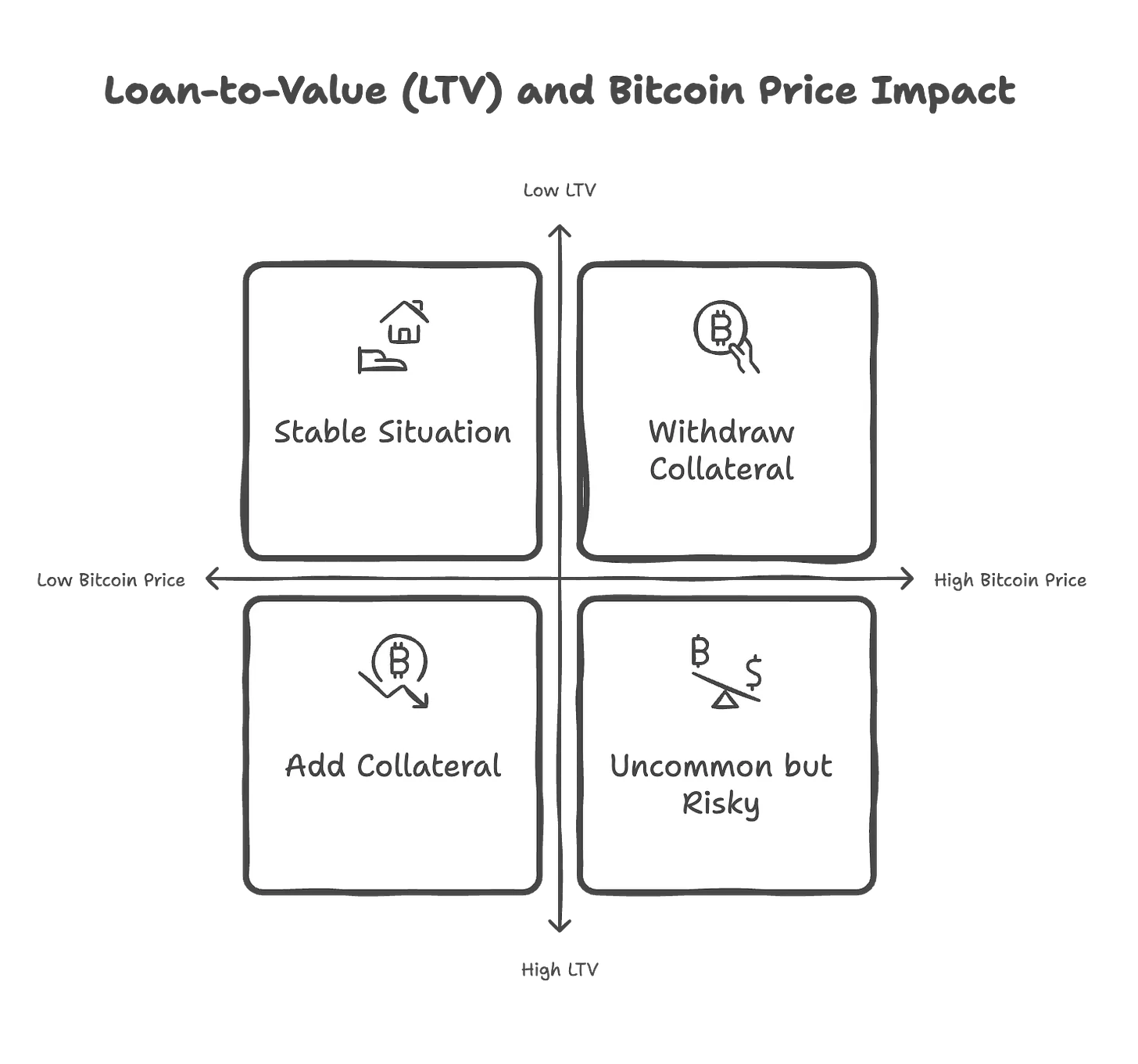
Vield offers loans ranging from $2,000 to $2 million, with a term of 12 months, an annual interest rate of 13%, and a 2% handling fee, according to Tiger Research. Taking a loan of $120,000 as an example, the borrower needs to deposit 1.5 bitcoins (approximately $240,000) as collateral. If the price of Bitcoin falls, resulting in a loan-to-value ratio (LTV) reaching 75%, borrowers must add collateral to maintain the 65% LTV requirement. If the price of Bitcoin rises, the borrower can apply to withdraw some of the collateral.
To ensure the security of the funds, Vield stores borrowers’ collateral in a separate secure digital wallet and does not mix or use these assets for other purposes. All collateral transactions can be traced through blockchain, further improving the transparency of loans. Currently, Vield manages about $35 million in loans and has not seen any defaults. This shows that Bitcoin mortgages show real potential in the financial services sector, although the market itself is volatile.

However, traditional financial institutions still have doubts about this model. Many institutions refuse to accept cryptocurrencies as collateral, mainly because of their excessive price volatility and lack of intrinsic value. Economist Saul Eslake warned that Bitcoin mortgages could exacerbate financial instability under market pressure, forcing borrowers to conduct costly asset liquidations.
This phenomenon reflects the complexity of cryptocurrencies integrating into the mainstream financial system. Some institutions are beginning to accept digital assets, while others are cautious about them.
2.2 Coinbase: DeFi-powered Bitcoin lending
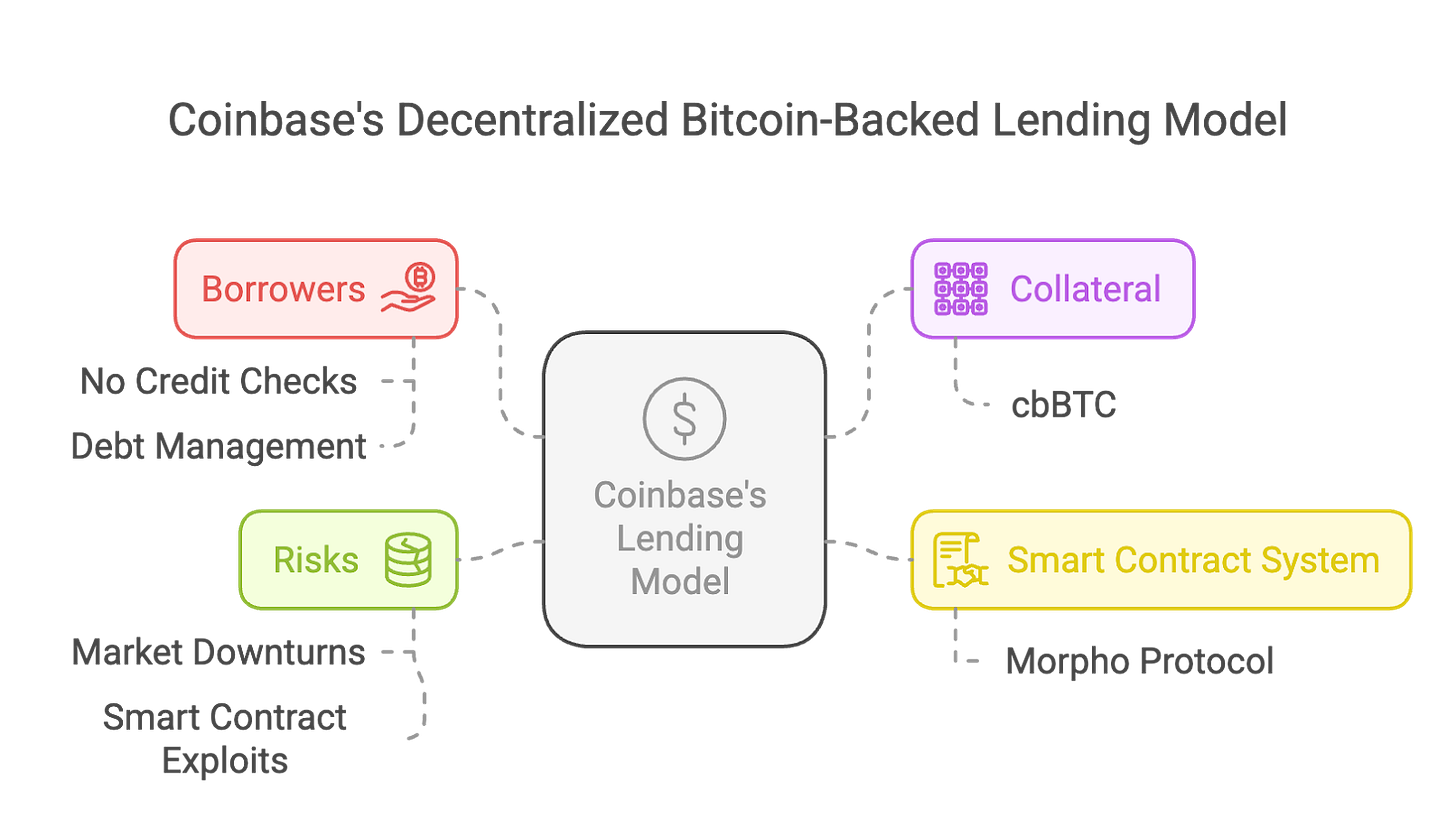
Source: Tiger Research.
Coinbase has launched a decentralized Bitcoin mortgage loan service through integration with the Morpho protocol on the Base blockchain. Users can use Bitcoin as collateral to borrow up to $100,000 USD stablecoins. This model does not require a credit check or a fixed repayment plan, but instead determines the amount of borrowing through a mandatory loan-to-value ratio (LTV ratio), ensuring that the collateral can always cover outstanding debts.
Coinbase uses Coinbase Wrapped Bitcoin (cbBTC) to implement this model. cbBTC is a tokenized Bitcoin form hosted in Morpho smart contracts. While this design enhances liquidity and decentralization, it also introduces smart contract vulnerabilities and potential risks of being attacked.
For borrowers, the biggest risk is the automatic liquidation of assets. If the price of Bitcoin falls, the LTV ratio exceeds 86%, the system will automatically liquidate the collateral and charge additional fines. Although this mechanism protects the interests of lenders, it also puts borrowers at risk of passive liquidation in market fluctuations. Unlike traditional loans, Coinbase’s automated liquidation model requires borrowers to always pay attention to their collateral value to avoid loss of assets.
From a regulatory perspective, Coinbase's decentralized lending model has both pros and cons. On the one hand, the use of the Morpho protocol improves transaction transparency and reduces counterparty risks; on the other hand, the legal and tax status of cbBTC has not yet been clarified, which may cause tax compliance issues. Although this model avoids the risk of failure of centralized platforms such as BlockFi and Genesis, it still faces challenges in regulation, security and market stability.
At the same time, concerns about financial stability remain. Economists point out that large-scale adoption of Bitcoin mortgages can pose systemic risks. If the price of Bitcoin suddenly plummets, it may trigger large-scale liquidation, which in turn triggers market selling. For lenders that rely on private funds, high volatility in Bitcoin could lead to liquidity crisis. In addition, regulatory pressures may further intensify as policy makers demand for investor protection and risk disclosure.
Nevertheless, if Bitcoin mortgages continue to evolve, it could have a profound impact on the traditional lending structure. However, its long-term sustainability will depend on the ability to properly manage risks and achieve compliance within the regulatory framework.
3. Asian market case study: Fintertech
Fintertech is a subsidiary of Daiwa Securities, Japan, focusing on cryptocurrency mortgage services. This is an important case in the cryptocurrency loan field in Asia. Fintertech allows users to obtain loans from yen or USD with Bitcoin or Ethereum as collateral, with an annual interest rate of 4.0% to 8.0%. Borrowers can get up to 500 million yen (about 3.3 million US dollars) in loans within 4 business days as soon as possible, providing cryptocurrency holders with a fast and flexible financing option.
In Japan, Bitcoin mortgages are popular for their tax advantages. According to the Japanese tax law, the tax rate for cryptocurrency investment income is as high as 55%. With Bitcoin mortgage loans, users can obtain liquidity without selling cryptocurrencies, effectively reducing tax burdens. Whether it is a business or an individual, this method can be used to meet a variety of financial needs. This shows that in markets with higher tax rates, Bitcoin mortgages are an efficient financing tool.
Despite this, compared with traditional financial products, Fintertech's model faces certain challenges. Cryptocurrency prices fluctuate greatly, posing risks to lenders. To ensure the sustainability of the model, institutions need to establish a complete risk management framework and optimize the valuation system of collateral. If other Asian financial institutions can introduce similar models, Bitcoin mortgages have the potential to become an innovative financial product and build a bridge between traditional finance and digital finance.
4. Advantages of Bitcoin Loan Service in Asia
With the popularity of cryptocurrencies in Asia, Bitcoin mortgages are becoming an emerging source of income for financial institutions (FIs). According to forecasts, the global cryptocurrency loan market will reach US$45 billion by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.4%. More and more investors and businesses want to obtain liquidity in this way without selling their Bitcoins.
Financial institutions in Singapore and Hong Kong have advantages in this area. This is due to their advanced regulatory frameworks, such as Singapore’s Payment Services Act and Hong Kong’s Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASP) licensing regime. As of the beginning of 2024, cryptocurrency lending platform Ledn has achieved a loan business of US$1.16 billion. This suggests that similar services are expected to achieve significant results in the Asian market.
In addition, traditional banks can attract more customers familiar with cryptocurrency by working with cryptocurrency exchanges and fintech companies. This kind of cooperation can not only expand the user base, but also increase income by charging loan interest, handling fees and fiat currency exchange fees.
5. Key risks and regulatory challenges
The following table summarizes the main risks of Bitcoin mortgage loans and helps to understand these risks more intuitively with regulatory challenges through actual cases or hypothetical examples.
5.1. Risk Factors: Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory environment for Bitcoin mortgages varies significantly across the globe. Different countries have different attitudes towards cryptocurrency loans. For example, Japan has incorporated cryptocurrency loans into existing financial regulatory frameworks, while China has banned such activities altogether. To prevent illegal activities, businesses must comply with the relevant regulations of Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Know Your Customer (KYC), and Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASP). Example: South Korea has introduced stricter anti-money laundering policies due to concerns about the potential risks of cryptocurrency loans. This requires lenders to submit detailed compliance documents and conduct rigorous due diligence. Some companies have to terminate their cryptocurrency loan business because they are unable to meet these requirements. This suggests that changes in regulatory policies may directly affect the sustainable operations of businesses.
5.2. Risk factors: price fluctuations and liquidation risks
Bitcoin prices fluctuate dramatically, which poses significant challenges for both lenders and borrowers. When the price of Bitcoin suddenly falls, margin notifications or forced liquidation may be triggered, bringing financial pressure to borrowers. To reduce risks, lenders often require borrowers to provide over-collateral and protect investments by monitoring the value of collateral in real time. Example: A Singapore borrower secured a $100,000 loan with Bitcoin as collateral. However, after the sudden drop of Bitcoin price by 30%, lenders quickly liquidated their Bitcoin collateral to make up for the losses, resulting in borrowers not only losing collateral, but also facing a huge financial gap. This situation highlights the potential impact of price fluctuations on borrowers.
5.3. Risk factors: Asset custody and security
Ensuring the security of Bitcoin collateral is an important challenge for lenders. Because cryptocurrencies are vulnerable to hacking or fraud, institutions need to adopt professional custodial solutions and work with trusted custodial service providers to ensure assets are properly protected. Example: A decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platform was hacked due to a smart contract vulnerability, resulting in the stolen $50 million in Bitcoin collateral. This incident shows that technical security is a key issue that cannot be ignored in the cryptocurrency loan model.
5.4. Risk factors: Market liquidity
Large-scale Bitcoin lending business relies on high liquidity in the market. However, when markets fluctuate, lenders may be forced to liquidate large amounts of collateral assets. If the market liquidity is insufficient, asset prices will fall rapidly, which will trigger chain liquidation and even have a serious impact on the entire market. Example: After the FTX crash, Genesis and BlockFi declared bankruptcy because they were unable to cope with the plunge in collateral value and large-scale withdrawal requests. Their failure to sell crypto assets at reasonable prices has caused problems to spread throughout the industry, causing widespread market chaos. This event shows that insufficient market liquidity is a major risk that cannot be ignored in the Bitcoin loan model.
6. Conclusion and future prospects
Bitcoin mortgage is a potential financial innovation that provides cryptocurrency holders with solutions to obtain liquidity without selling digital assets. However, this model still faces challenges such as price volatility, regulatory uncertainty and security, which limit the sustainable development of the industry.
In the future, the growth of Bitcoin mortgage loans may be concentrated in regulated environmentally friendly areas such as Singapore and Hong Kong. These regions have a sound regulatory framework and high cryptocurrency penetration, providing ideal conditions for innovation and revenue growth for financial institutions. Through Bitcoin mortgage loans, financial institutions can not only expand their market influence, but also diversify their business and open up new growth channels.
For businesses and financial institutions, the key to success lies in implementing effective risk management strategies. For example, adopt a conservative loan-to-value ratio (LTV), requiring borrowers to provide over-collateral, and choosing reliable custody solutions to ensure assets are secure. In addition, cooperation between traditional financial institutions, cryptocurrency platforms and regulators will also play an important role. This collaboration can build industry trust and lay the foundation for the long-term development of Bitcoin mortgages.

