Should traditional businesses buy Bitcoin?

Reprinted from panewslab
01/04/2025·5MAuthor: Chi Anh, Ryan Yoon and Yoon Lee, Tiger Research
Compiled by: Luffy, Foresight News
summary
Bitcoin’s decentralized and anti-inflation properties make it a versatile tool for institutions to hedge against economic uncertainty and preserve long-term value.
Institutional buying of Bitcoin often signals confidence and innovation, while selling is for profit taking or cash flow management.
Asia is increasingly adopting Bitcoin as an investment asset, and at the same time, governments such as El Salvador and the United States have introduced relevant measures to recognize Bitcoin as a strategic asset. These highlight Bitcoin’s growing influence in shaping global economic strategy.
1. Introduction
As an investment asset, Bitcoin has attracted much attention due to its different characteristics from traditional assets such as gold. Bitcoin’s decentralized and anti-inflation properties bring new possibilities to institutional asset management strategies.
MicroStrategy is a notable example of an institution strategically leveraging the benefits of Bitcoin. The company effectively uses Bitcoin to combat inflation risks and strengthen its financial position. This success story has prompted many companies and financial institutions around the world to re-examine their investment strategies.
However, investing in Bitcoin may not be suitable for all institutions. While Bitcoin purchases often attract public attention, many companies have cautiously sold their Bitcoin holdings. This report aims to analyze the reasons behind institutional investment in Bitcoin, explore the key factors affecting the buying and selling decisions of different institutions, and study institutional strategies under similar market conditions. As Bitcoin continues to rise as a corporate investment asset, this report will also analyze Asian market perspectives and corresponding strategies.
2. Bitcoin as an investment asset
Institutions have traditionally favored investment assets such as bonds, gold and foreign currencies for their ability to hedge risks and sometimes preserve value during times of economic uncertainty. Bitcoin has emerged as a strategic investment asset, providing institutions with an efficient, inflation-resistant and profitable alternative to traditional assets such as bonds and gold. The total number of Bitcoins is fixed at 21 million, which ensures scarcity and makes it an attractive long-term value store option.
2.1. Bitcoin’s role as an inflation hedge
Rodriguez and Colombo conducted a 2024 study "Is Bitcoin an Inflation Hedge?" ”, they analyzed Bitcoin’s response to inflationary pressures using key economic indicators such as U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) data over the past decade. The results show that Bitcoin returns are significantly higher following a positive inflationary shock. However, this effect is sensitive to price indices (mainly applicable to CPI shocks) and is more pronounced in the early stages before Bitcoin is widely adopted by institutions. This suggests that Bitcoin’s ability to hedge against inflation is context-specific and may diminish as its adoption expands.
2.2. Bitcoin’s profitability as an investment asset
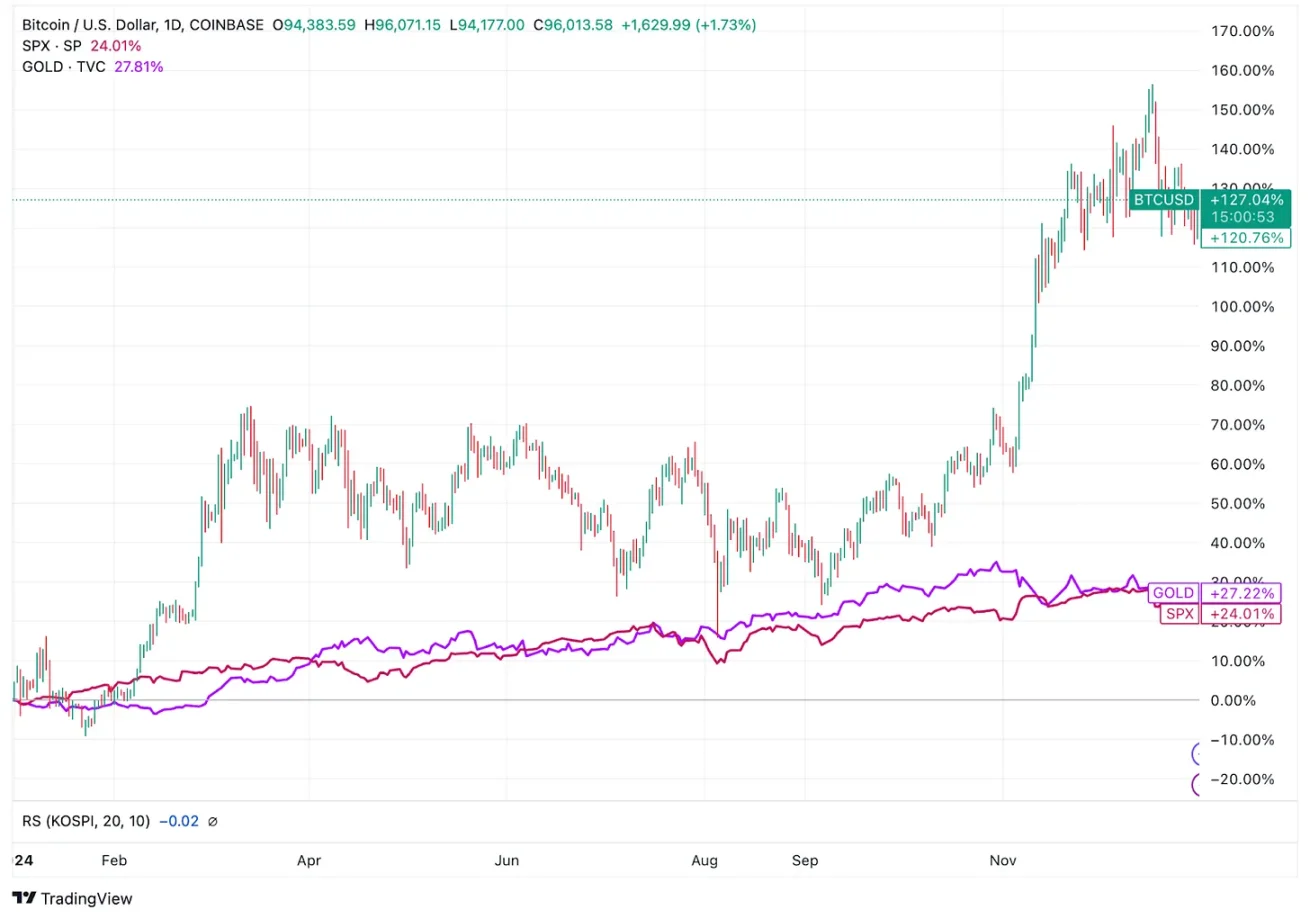
Source: TradingView
In 2024, Bitcoin will return about 127%, significantly outperforming gold, which is up 27%, and the S&P 500, which is up about 24%, during the same period.
However, the value of Bitcoin as an institutional investment asset lies not only in its investment returns. Traditional investment assets have limited trading time and complex transaction processes, making it difficult to respond quickly to interest rate changes or market shocks.
In contrast, Bitcoin has global liquidity, is not restricted by borders or time zones, and can achieve 7*24 real-time transactions. High liquidity The ability to quickly exchange Bitcoin for cash in any country sets it apart from traditional financial assets. These characteristics enable institutions to effectively manage assets and respond to market conditions.
With high profitability and utility, Bitcoin is expected to become an increasingly important investment asset in institutional portfolios.
2.3. The role of Bitcoin as a lever for the attention economy
The number of listed companies on NASDAQ exceeds 3,300, and the number of listed companies worldwide has grown to a very large scale. As a result, it's becoming increasingly difficult to attract investors' attention based on strong fundamentals alone. To increase market visibility, companies are now investing more in marketing.
In such a market environment, Bitcoin creates additional publicity effects. Since only a handful of public companies hold Bitcoin, simply announcing a Bitcoin purchase as part of a portfolio diversification strategy can generate huge media exposure.
Such media coverage has produced many positive results for the company, boosting brand value, attracting interest from retail investors, and enhancing its image as an innovative and forward-thinking company. In addition to increasing the value of assets, Bitcoin also plays a role in increasing the value of businesses.
3. Institutional buying and selling behavior
As Bitcoin becomes an integral part of institutional portfolios, a unique trading model has emerged. Institutions often publicly announce their Bitcoin purchases, sending a strong signal to the market. This strategy helps highlight the company's innovative stance and enhance market confidence. In contrast, Bitcoin sales are done discreetly, often occurring when profits are realized and funds are reinvested to strengthen core business operations.
3.1. Institutional buying behavior: MicroStrategy
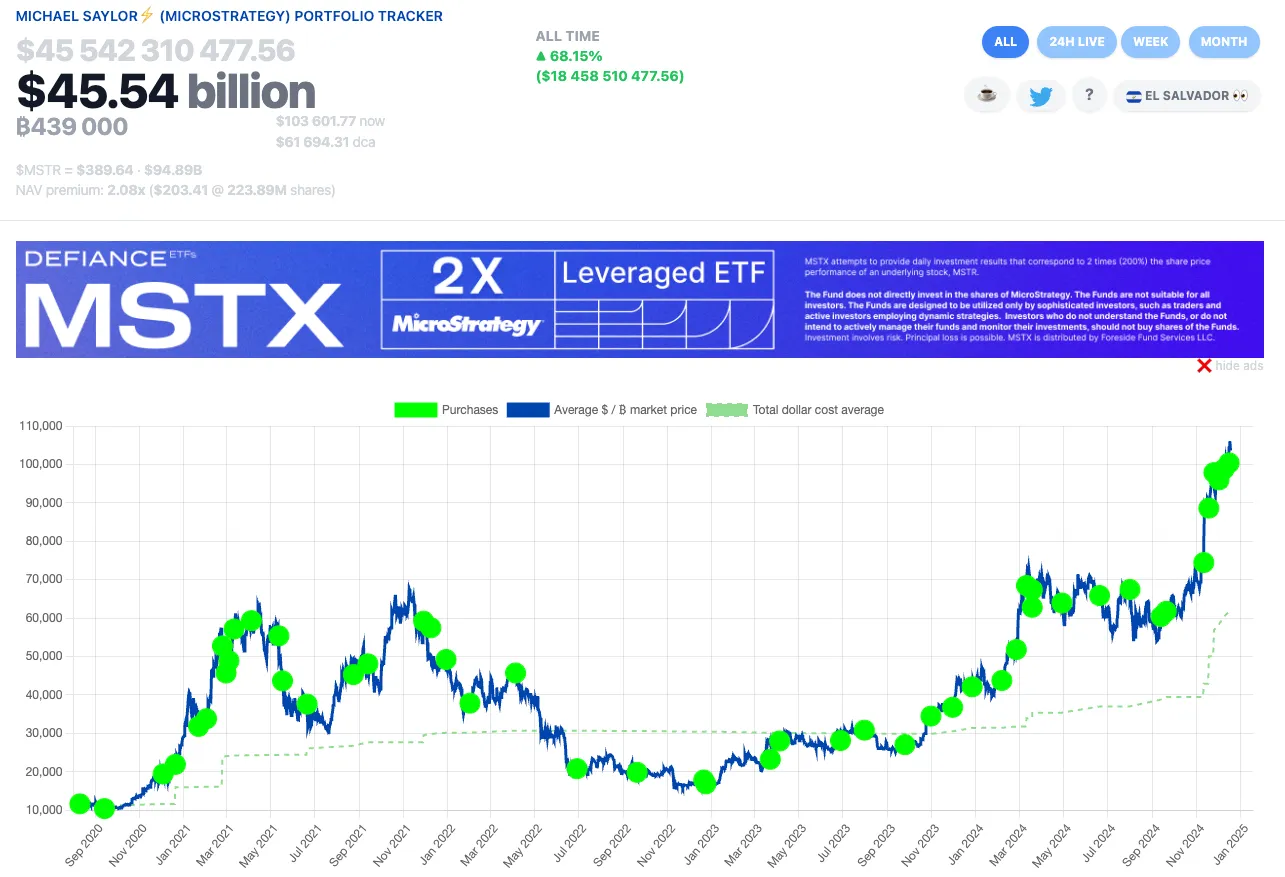
MicroStrategy’s Bitcoin purchase history, source: saylortracker.com
MicroStrategy is a leading example of leveraging Bitcoin as an investment asset. With over 446,400 BTC allocated, the company has gained widespread attention from the market. This strategy is designed to achieve two key goals: protect against inflation and enhance financial stability.

Source: Michael Saylor\'s X account
CEO Michael Saylor has captured the market’s attention by revolutionizing the perception of Bitcoin. A former skeptic turned passionate advocate, he emphasized that "cash, low-yield bonds and overvalued technology stocks are vulnerable to inflation and should be avoided." In the current market environment, Saylor It is proposed that stock buybacks and Bitcoin are the best uses of corporate surplus funds, and Bitcoin is chosen as a long-term means of hedging unlimited quantitative easing.
Contrary to early fears, MicroStrategy’s Bitcoin investment strategy has broad support from a number of firms. In addition to being an inflation hedge, Bitcoin is now viewed as “digital gold,” reshaping the way companies manage their assets. In addition to traditional assets, this innovative move to use Bitcoin to disperse reserves points to a new direction for global corporate financial strategies.

Boyaa Interactive Announcement
MicroStrategy's success story is also impacting the Asian market. Boyaa Interactive has converted its Ethereum holdings into Bitcoin, and MetaPlanet is actively buying Bitcoin in 2024. The moves reflect growing recognition in Asia of Bitcoin’s utility in managing volatility and preserving long-term value.
3.2. Institutional selling behavior: Tesla
Tesla, one of the most high-profile corporate adopters of Bitcoin, provides a very different case than companies like MicroStrategy. The company sold 75% of its Bitcoin holdings in 2022 and attributed the decision to liquidity needs amid uncertain economic conditions. Most recently, in October 2024, Tesla moved $760 million worth of Bitcoin to an unknown wallet, sparking speculation about further sales.
Tesla’s Bitcoin investments have been used strategically to support its operations and expansion needs, including building new factories in Austin, Texas, and Berlin. Tesla Chief Financial Officer Zachary Kirkhorn said an investment in Bitcoin provides the company with liquidity and a level of return, demonstrating its flexibility as a financial instrument for capital-intensive businesses.
Likewise, when Bitcoin hit $100,000, Meitu made a substantial profit from its sales. Compared with Tesla's strategic profit-taking, Meitu's decision seems to be a deliberate move to sell off at market highs. Unlike Tesla, which keeps a low profile, Meitu publicly explained the sale as a step to shore up its financial position amid challenges to its core business. This contrasts with Tesla's secretive sale and suggests that public disclosure can help reduce market uncertainty caused by institutional sales.
The strategic reasons why institutions buy and sell Bitcoin are directly related to their financial goals and operational needs. Companies often sell Bitcoin to profit during market peaks, such as Tesla did in 2022, or to convert cryptocurrency holdings into working capital to reinvest in core operations. The main reasons behind sales generally fall into the following categories: 1) profiting from favorable market conditions to expand and improve business operations; or 2) needing capital to address cash flow challenges. This raises questions about whether any future sales will be driven by strategic financial planning or as a stop-gap solution to cash flow issues. Furthermore, if the motive for the sale is to make a profit, it raises questions about how those profits will be used. Are they being reinvested to enhance the business or primarily benefit stakeholders? Regardless, such action could result in missed opportunities for further appreciation and diminish the long-term advantages of holding Bitcoin as an investment asset.
4. Bitcoin buying and selling behavior of Asian institutions
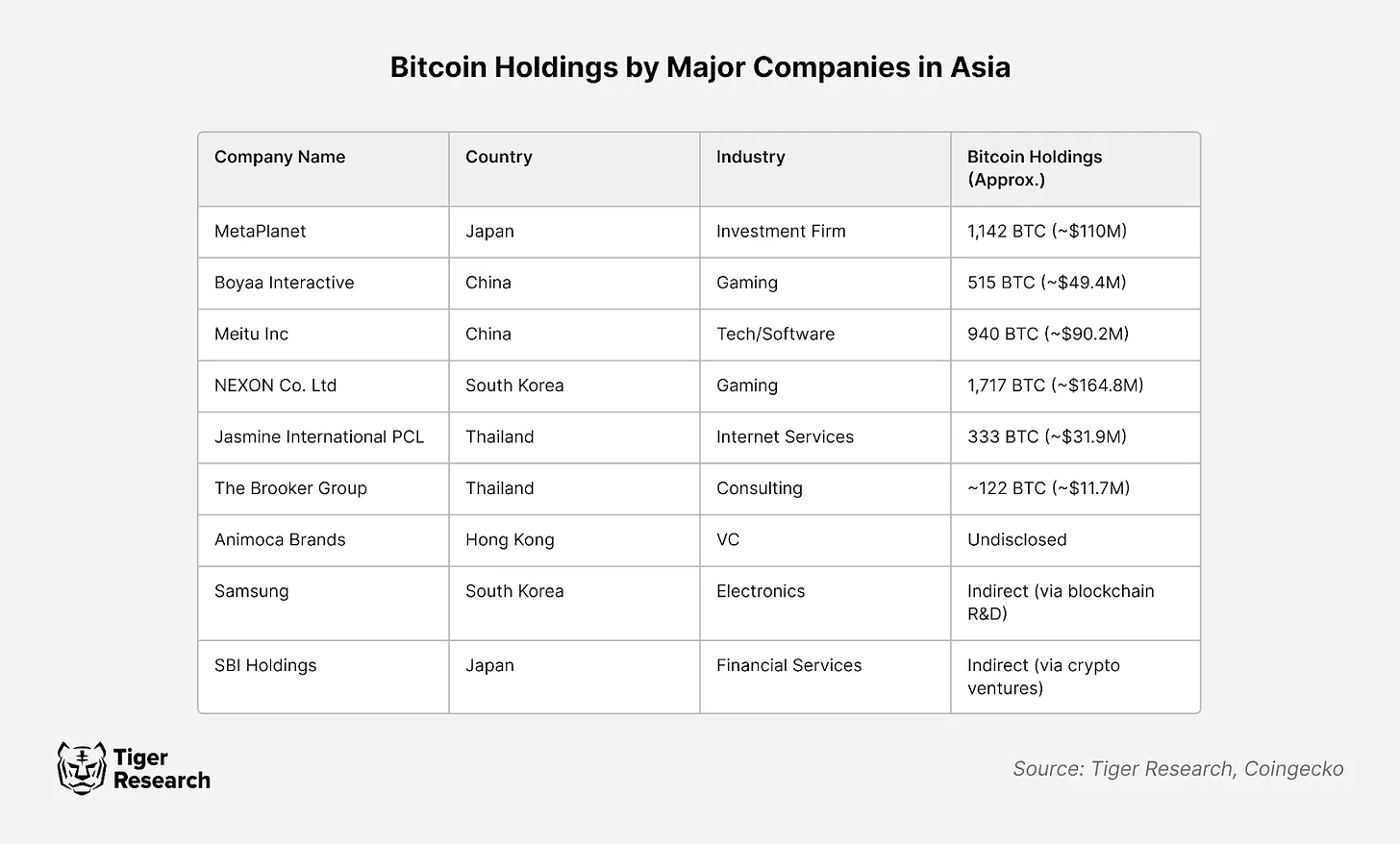
MetaPlanet is an example of Asia’s aggressive adoption of Bitcoin. True to its nickname "Asia MicroStrategy," the firm purchased 1,018 Bitcoins in 2024 alone, demonstrating its strong commitment to long-term Bitcoin investing.
The case of MetaPlanet highlights the successful transformation of "zombie companies". Zombie companies generate just enough profits to cover operating costs and repay debt, but lack the capital to fuel growth. Despite its large cash hoard, MetaPlanet has failed to capture the attention of the stock market. By benchmarking MicroStrategy's strategy, the company successfully turned a profit.
In addition to Bitcoin investments, MetaPlanet also announced plans to expand into new business areas. The company's strategy includes using a variety of financial instruments such as loans, stocks and convertible bonds to buy Bitcoin, while also generating profits through put options. This practice is considered an active profit model that goes beyond a simple asset holding model.
However, this strategy is not applicable to all zombie companies. Success depends on whether companies that have already established a foothold in their respective stock markets can implement differentiated strategies. Blind imitation by latecomers may aggravate risks, and they need to be treated with caution, taking into account factors such as corporate cash reserves, market conditions, and risk management capabilities.
5. Conclusion
All in all, Bitcoin’s evolution as an investment asset marks a major shift in the world of institutional finance. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, anti-inflation properties, and unparalleled liquidity make it an attractive option for asset diversification and long-term preservation of value.
Some governments are also exploring Bitcoin’s potential. El Salvador’s adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender is one example, underscoring the asset’s role in the national strategy for economic growth and financial inclusion. Recently, Trump announced that the United States will treat Bitcoin as an investment asset, or as he put it, "a permanent national asset that benefits all Americans." These government moves illustrate Bitcoin’s growing importance not only for businesses but also for policymakers aiming to modernize the financial system.
Buying and selling Bitcoin has proven to be good for companies, especially during rising markets. In an uptrend, buying signals confidence in Bitcoin’s growth potential, while selling allows companies to realize profits and reinvest in core operations. However, in a downward market trend, these operations may have negative consequences. Buying could raise concerns about whether corporate funds are being used for speculative investments, while selling could raise questions about whether the company is cutting losses or liquidating assets to cover operating expenses.
For policymakers, the implications are clear: Bitcoin has great potential as an investment asset, but it needs to be carefully integrated into corporate strategy. Businesses must weigh the financial benefits of holding Bitcoin, such as liquidity and protection against inflation, against the operational risks and associated market volatility. Whether for long-term reserves or short-term liquidity needs, effectively leveraging Bitcoin requires careful alignment with corporate goals and market conditions.

