Interpretation of the new track decentralized space intelligent network: core concepts, major projects and future development

Reprinted from panewslab
03/24/2025·2MAuthor: cookies
Compiled by: Deep Tide TechFlow
With the continuous development of Web3 technology, Decentralized Spatial Intelligence Network (DeSPIN) is becoming a highly concerned field. By analyzing and leveraging visual data in the real world, DeSPIN not only provides innovative solutions for map construction, urban planning and robotics, but also opens up a new "Contribute-to-Earn" economic model. This article will explain in detail the core concepts, main protocols and their future development directions of DeSPIN.

What is DeSPIN?
Spatial Intelligence is a technology that extracts insights through the analysis of visual data in the real world. Its core lies in combining geographic information with environmental contexts to support human decision-making. Decentralized Space Intelligent Network (DeSPIN) combines this technology with the decentralized concepts of blockchain and Web3 to form an open and shared ecosystem. Imagine that you can earn money by sharing photos of roads taken in daily life, or environmental data recorded in shopping malls or streets. This model not only lowers the threshold for data collection, but also encourages ordinary users to contribute to the development of spatial intelligence.
Before understanding the specific application of DeSPIN, we need to master the basic framework of spatial intelligence. Space intelligence consists of four core parts:
- Data collection: Use sensor networks (such as cameras, GPS) and IoT devices (such as mobile phones, notebooks).
- Data processing and analysis: Use machine learning technology to process geographic metadata, identify patterns in the data, and build a spatial query database.
- Knowledge representation: associate data with the environment context through semantic mapping to provide users with visual geographic information.
- Decision support system: build a spatial prediction model to provide users with application services, such as route optimization, obstacle avoidance, etc.
Major protocols in the DeSPIN field
At present, multiple innovative protocols have emerged in the DeSPIN field, focusing on different application scenarios. Here are eight projects worth paying attention to:
1.Hivemapper
Hivemapper is a decentralized map building protocol that adopts the "Drive-2-Earn" model. Users report road problems in real time through mobile applications, while drivers collect data through dash recorders installed on vehicles. These data are processed by AI algorithms to generate maps and verify their accuracy through human feedback reinforcement learning (RLHF). Hivemapper provides an overlay map where users can view which areas have been mapped and access data through the API. Data contributors receive a $HONEY token reward, which can be used to purchase map data or other services.
2.NATIX Network
NATIX Network is a decentralized map economic protocol that focuses on collecting road data through mobile devices and dash recorders, and adopts the "driving earn" model. Its core technology VX360 supports 360-degree panoramic data acquisition, and the collected data can be used to develop driving assistance functions, such as autonomous driving optimization. At present, NATIX Network has covered 171 countries, with more than 223,000 registered drivers and a cumulative mapping mileage of 131 million kilometers. Data contributors and network nodes can receive $NATIX token rewards, further inspiring ecological development.
Both Hivemapper and NATIX are committed to building better maps with crowdsourcing road data. The potential application scenarios of these data are very wide, mainly including the following aspects:
- Optimize urban traffic: By analyzing real-time road data collected, traffic flow management can be improved, congestion can be reduced, and travel efficiency can be improved.
- Monitor road conditions: Timely detect and report road damage, obstacles or other potential problems, which help maintain the safety and reliability of infrastructure.
- Detecting Crime and Violence: Using map data combined with AI algorithms can help identify and locate abnormal behaviors and provide support for public safety.
These applications not only enhance the functionality of the map, but also bring practical value to urban management and social security.
3.FrodoBots
FrodoBots is a protocol for gamified data acquisition through robots. Users can remotely control ground robots to collect geographic data, supporting multiple operating methods (such as controllers, keyboards or gaming steering wheels). In addition, researchers can deploy AI navigation models on the platform for testing. Users earn FrodoBot Points (FBPs) by completing driving tasks. Points are related to the task distance and difficulty. The longer the distance and higher the difficulty, the more points they earn. FrodoBots has been tested in multiple cities and has held a navigational capability competition between AI and humans. In addition, FrodoBots has also established a system like "guilds", Earth Rovers School, which allows new users to participate in data collection by renting Earth Rovers.
4.JoJoWorld
JoJoWorld is a protocol focused on 3D spatial data acquisition, and users help train three-dimensional models by contributing data. The platform provides high-quality 3D data for creating various digital scenarios, suitable for virtual reality, urban planning and other fields. Users can also purchase this 3D data directly for personalized digital model development.
The next four protocols also focus on collecting real-world spatial data, but their application areas are more segmented, covering specific scenarios such as robot model training. These protocols inject more possibilities into the ecosystem of Decentralized Space Intelligent Networks (DeSPIN) by focusing on long-tail data and specific needs.
5.PrismaXAI
PrismaXAI is a protocol that collects specific scene data from a first-person perspective, suitable for complex scenarios such as hand-object interaction, dynamic movement and social gatherings. Its core technology, Proof-of-View, ensures the authenticity of data, and improves the accuracy of data annotation through a decentralized verification mechanism. This protocol has great potential in acquiring long-tail data, providing unique advantages for model training.
6.OpenMind AGI
OpenMind AGI focuses on real-world understanding through visual-language-action models (VLAMs). Its core system, OM1, is a multi-platform operating system that can interact with a dynamic real environment and is particularly suitable for customized development of robotics technology. The platform collects data through mobile phones and robots and shares this data with robot developers for improving and innovating robot application scenarios.
7.MeckaAI
MeckaAI is a decentralized robot AI model training protocol. Users help train robot behavior models by uploading video data. The platform provides mobile applications, and users can earn OG Mecka Points by completing tasks, further incentivizing data contributions. MeckaAI is committed to promoting the development of robotics through crowdsourcing models and lowering the barriers to obtaining training data.
8.Xmaquina DAO
Xmaquina DAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that supports open source robot projects. Unlike other protocols that directly participate in model training, Xmaquina DAO’s core goal is to support research and innovation in the field of robotics through resource allocation. Its internal innovation center, Deus Lab, focuses on the research and development of robotics, while MachineDAO decides on which projects resources are allocated to the $DEUS vote. This model provides financial support for the open source development of robotics technology, while ensuring transparency and fairness in resource allocation.
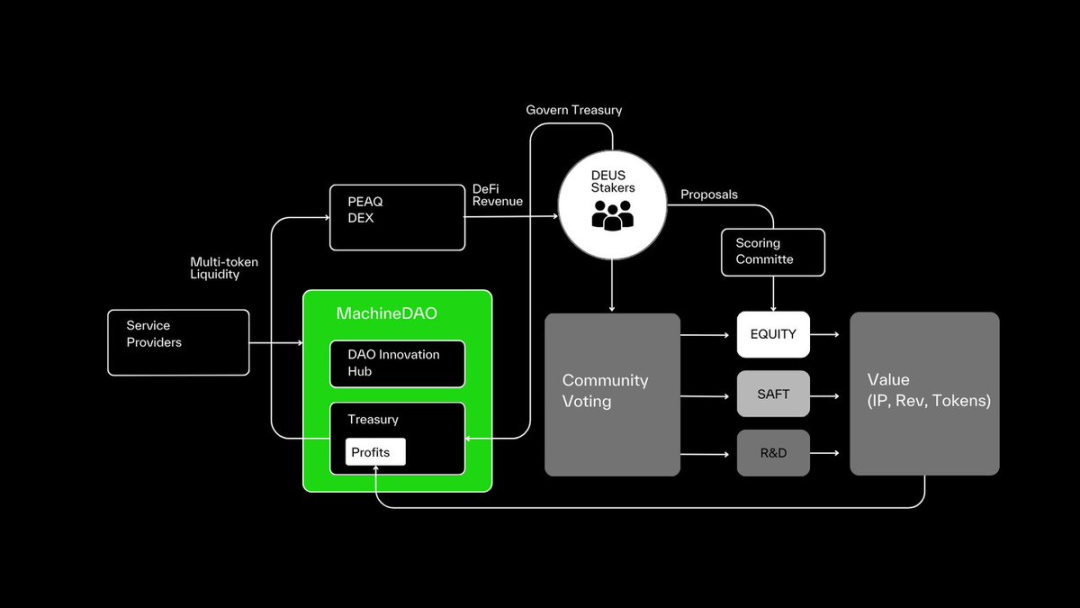
MachineDAO\'s Organizational Structure
Due to space, some application protocols in similar fields have not been expanded in detail here, such as Alaya_AI, Gata_xyz, KrangHQ, etc., which are also worth paying attention to.
The Future of DeSPIN: From Contribution to Value
Although DeSPIN is still in its infancy, its potential cannot be ignored. With the development of physical AI and Embodied AI, and the rise of new concepts such as Human Data Fleet, DeSPIN is expected to lead a new technological revolution.
A possible trend is the popularization of the "Train-to-Earn" (T2E) model, where users contribute value through the spatial data obtained in their daily lives and receive rewards based on data quality. For example, the emergence of decentralized glasses equipment can greatly improve the accuracy and diversity of data acquisition. The data captured by smart glasses can not only reflect the way humans perceive the world most realistically, but also collect many long-tail data such as environmental noise and facial features, bringing wider possibilities to the field of spatial intelligence.
However, DeSPIN development also faces some challenges, such as:
- Data Verification: How to ensure the authenticity and accuracy of crowdsourcing data?
- Ethical questions: How to regulate the use of data and avoid privacy leakage and abuse?
- Demand-side acceptance: Are traditional institutions willing to adopt decentralized data sets?
The solution to these problems will determine the future direction of DeSPIN and need further research and resolution in the future.


 chaincatcher
chaincatcher

