Ethereum Governance Observation: EIP-2537 Preassembly History

Reprinted from panewslab
03/27/2025·1MAuthor: shew
Overview
EIP-2537 is the EVM pre-assembled instruction that was determined to be added in the latest Pectra fork upgrade. This instruction adds multiple calculation functions of the BLS12-381 curve to EVM, such as pairing calculations on the curve domain.
EIP-2573 was initially proposed in 2020 and was not confirmed to join the Ethereum upgrade until 2025. This article mainly introduces the governance history of EIP-2537 and explores why this proposal was included in the upgrade after 5 years.
Proposal background
In January 2017, Vitalik Buterin first introduced the pairing algorithm and
the alt_bn128 curve at Exploring Elliptic Curve
Pairings .
Then in February 2017, Vitalik Buterin and Christian Reitwiessner proposed
EIP-196 and
EIP-197 proposals, which were to add
alt_bn128 curve calculation support to EVM.
In the October 2017 Byzantium
upgrade, the alt_bn128 curve was officially included. Simply put,
alt_bn128 implements the curve domain pairing calculation inside the EVM for
the first time, which allows the ZK-Snarks proof verification to be done
within the EVM.
But with the development of cryptography, in November 2017, the zcash
development team gave the BLS12-381 curve for the first time at BLS12-381:
New zk-SNARK Elliptic Curve Construction . Compared with alt_bn128 , BLS12-381 has higher security
and better performance. A considerable number of blockchain protocols have
since used the BLS12-381 curve and abandoned alt_bn128 curve.
In May 2018, Justin Drake released an article on Pragmatic signature
aggregation with BLS in ethresear , pointing out that in Ethereum's future PoS and
sharding upgrades can use the BLS multi-signal algorithm based on BLS12-381
curve. At that time, Ethereum researchers wanted to use
EIP-1011 to solve the consensus
layer problem, but the EIP-1011 solution can accommodate up to 900 validators,
so a huge staking scale of 1,500 ETH was set for each validator. With the
introduction of the BLS multi-signature plan, EIP-1011 has withdrawn from the
stage of history. As it turns out, the subsequent ETH2 upgrade also ended up
using the BLS12-381 curve.
With ETH2 development, the introduction of BLS12-381 used by ETH2 into the
ETH execution layer has begun to be called upon. In February 2020, some
researchers proposed EIP-2537 and
hoped that the proposal could be tested together on the ETH2 test network.
EIP-2537 Author Alex Stokes calls for the inclusion of EIP-2537 in the Berlin
hard fork in the article What eth2 needs from eth1 over the next six
months .
Interestingly, the author of EIP-2537 is also the co-founder of Matter Labs, and the most famous product of Matter Labs is ZKSync
Berlin Turbulence
Before we introduce the follow-up content, we need to first introduce EIP-1962 . EIP-1962 is the first proposal by Matter Labs for pre-assembly of elliptic curve domain pairing proposed in April 2019. This proposal supports three curves, namely:
- BLS12
- BN
- MNT4/6 (Ate pairing)
This EIP is prepared to add 10 pre-assembled instructions at once to handle different curves. However, after the proposal was born, quite a lot of developers questioned that the proposal was too complicated and it was difficult for developers to implement it. At the same time, because EIP1962 is highly generalized, calling is also very troublesome for smart contract engineers. Of course, as the proposer of EIP-1962, Matter Labs has essentially completed the development of the elliptic curve algorithm and provided a Rust/Go/C++ reference implementation.
In order to solve the problem of EIP-1962, Matter Labs proposed in February 2020 to split EIP-1962, all of which inherit the EIP-1962 interface. These EIPs include:
- EIP-2537 provides support for BLS12-381
- EIP-2539 provides support for BLS12-377
- PR#2541 provides BLS12-377 (Zexe curve) support, but note that the proposal did not obtain the EIP number in the end and cannot be found on the official website of the EIP document.
The most important thing inside these EIPs is EIP-2537, because the consensus layer also uses the BLS12-381 curve. The core purpose of including EIP-1962 and EIP-2537 is to implement the verification of consensus layer BLS signatures within the main network. At that time, ETH2 was developing a consensus layer deposit contract design. When the deposit contract was initially designed, since the execution layer did not contain the BLS verification algorithm, the deposit contract would not verify the signature. The specific BLS signature will be verified by the consensus layer after the user deposits. If it is found that it is incorrect (for a new verifier), the deposit will fail and the ETH deposited by the user will be lost.
Against this background, core developers hope to introduce BLS12-381 pre-assembly to achieve signature verification within the deposit contract to avoid possible losses from users depositing ETH2 funds. This was also the reason why a large number of developers paid attention to EIP-1962 and EIP-2537 at that time.
When EIP-2537 was just proposed, Vitalik immediately discovered a series of problems with EIP :
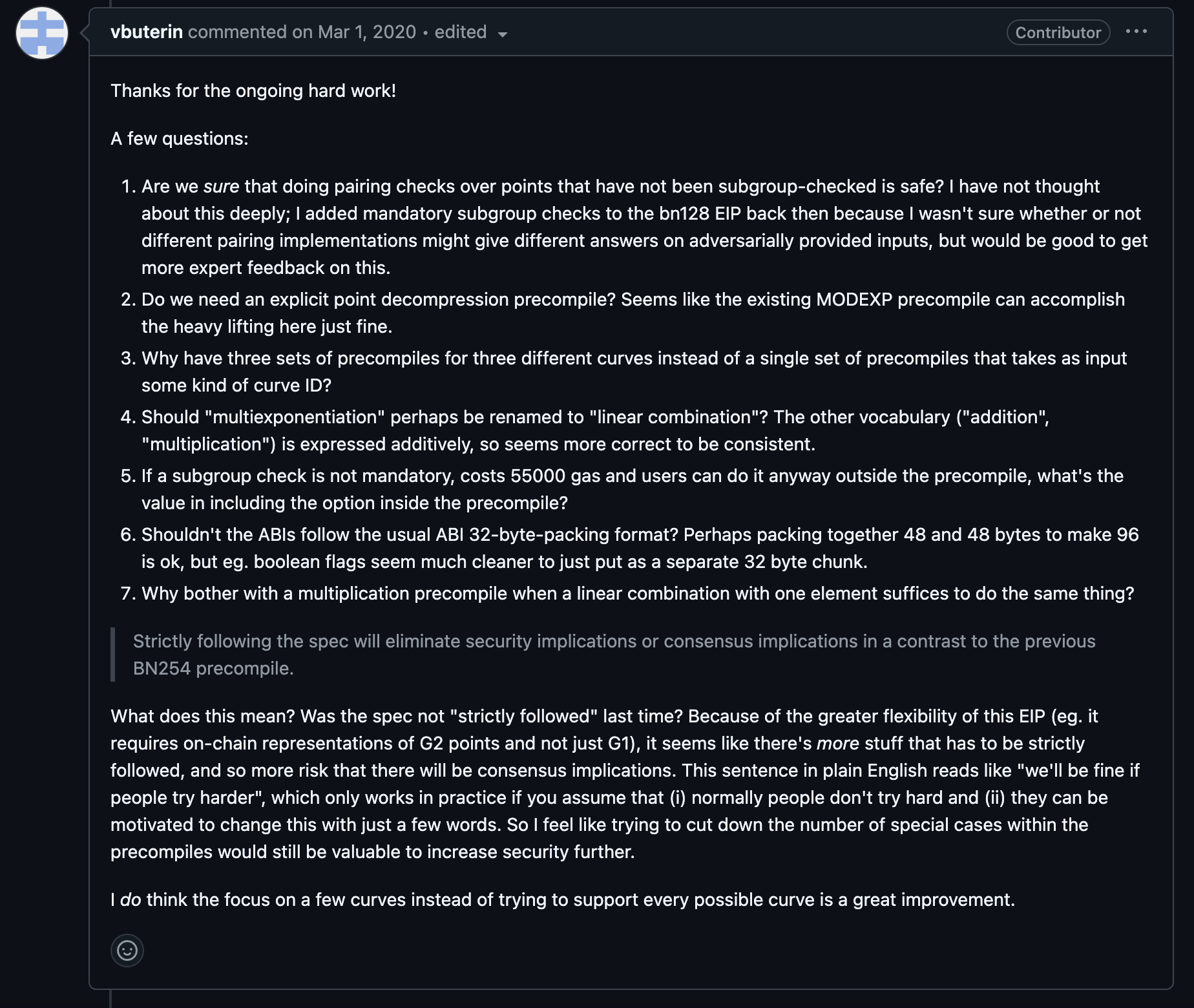
These questions were only focused on the content of the EIP document, and the EIP authors then responded and discussed it. Then, on March 6, 2020, Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #82 , Ethereum core developers discussed EIP-2537. In this meeting, Vitalik believed that EIP-2537, such as EIP, proved very effective for recursive SNARK, and would not damage Ethereum in the long run. At the same time, the meeting also confirmed the priority of EIP-2537, and all clients agreed to implement EIP-2537 as soon as possible and planned to complete all developments before the Berlin upgrade.
Then, EIP-2537 became a higher priority task. On March 20, 2020, EIP-2537 is still the first proposal to be discussed in Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #83 . The meeting confirmed the proposal to replace EIP-2537 as the core BLS and to become the pre-selected EIP list for Berlin upgrades (ie Eligibility for Inclusion (EFI)).
During the Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #84 meeting in April 2020 , the meeting formally included EIP-2537 in the Berlin hard fork upgrade and determined the Berlin upgrade timeline to be implemented in April and tested in May-June. It is worth noting that in this discussion, EIP-2537 was listed as the highest priority.
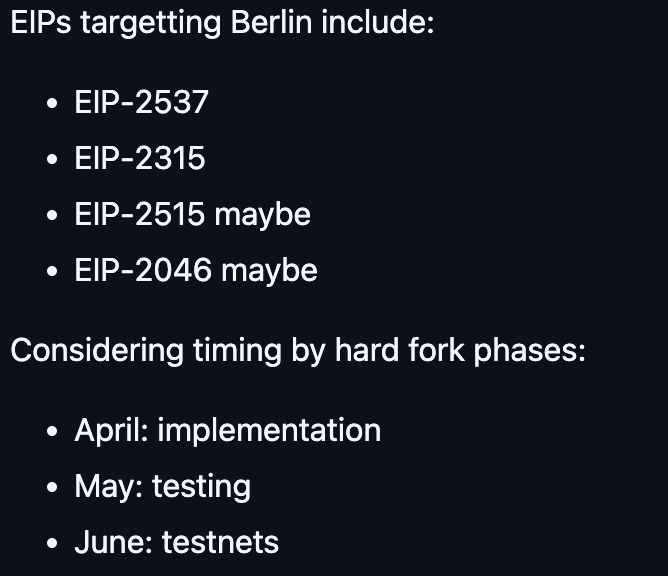
Subsequently, EIP-2537 entered a large number of development and testing stages. In the next nearly 20 core developer meetings, each meeting basically involved discussions on EIP-2537. Next, we can see what questions are discussed about EIP-2537 in each meeting.
Within Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #85 , Danno and Axic discussed the ABI coding issue of EIP-2537. Subsequently, the core developers synchronized the current implementation situation. Since Matter Labs, the proposer of EIP-2537, had basically completed the implementation of the Rust version, the Besu client declared that it had basically implemented the functions of EIP-2537, but Geth said that no one is currently working on the implementation of EIP-2537.
Within Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #86 , different Ethereum node implementations synchronize the implementation of EIP-2537 again, where Geth indicates that some of the work has been completed, but there is still a lot of work waiting to be completed.
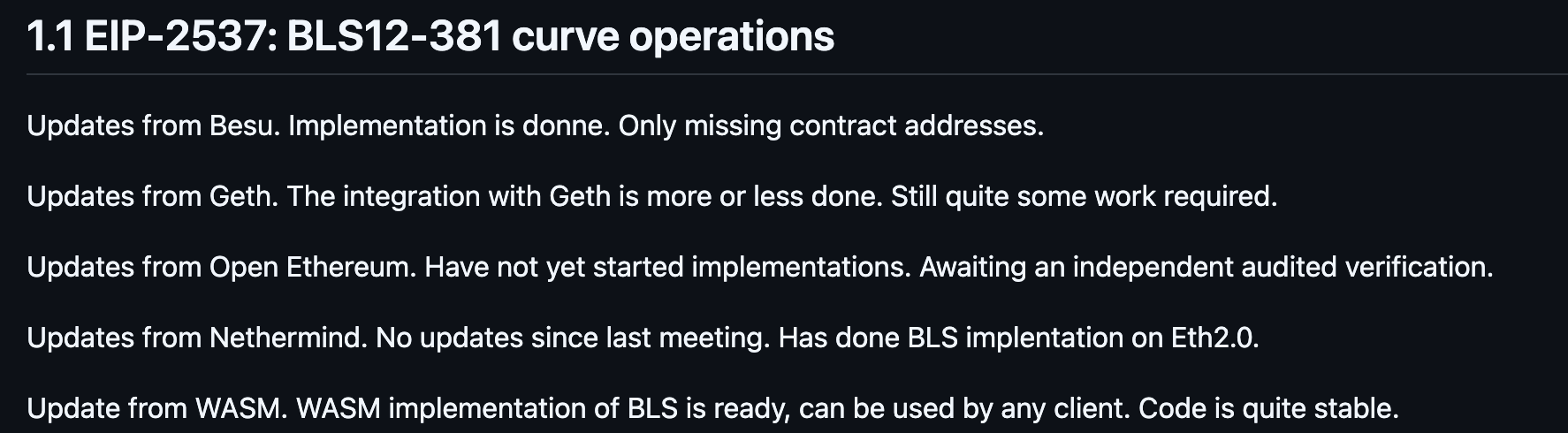
In Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #87 , the core content of this developer meeting is the implementation of EIP-2537. Geth developers said that there is currently a 16,000-line PR implementation EIP-2537, but Geth developers cannot determine whether PR implements EIP-2537 safely and effectively, so developers can only judge the code through the simplest and most crude fuzzy test.
Geth developer said: "So my gut reaction is that there is no chance that Geth will be ready with the BLS curve operations for mainnet launch in July." That is, Geth is likely to be unable to complete the related development of EIP-2537 before Berlin's scheduled time.
Hudson Jameson proposed finding cryptography engineers for Geth to assist with PR reviews and proposed using a testnet to test EIP-2537 for security. Because the ETH2 development team is also implementing BLS signature verification at this time, the ETH2 team can participate in the test.
Here, we need to add a background knowledge, that is, Geth's EIP-2537 implementation PR is used in order to ensure efficiency, and this part of the assembly code is very difficult to read and understand. Therefore, Alex Vlasov recommends removing complex assembly optimizations inside PR to reduce the difficulty of review.
We have already introduced that one of the core goals of EIP-2537 is to assist ETH2 deposit contracts, but at this meeting, the deposit contract developers said that the deposit contract that does not use EIP-2537 has been audited, so some developers suggested that it is best not to launch a deposit contract that uses EIP-2537.
In the end, the meeting decided to add the YOLO test network, which is the core of the test network to test EIP-2537. In fact, in this meeting, we can see that the importance of EIP-2537 has dropped significantly with the completion of the deposit contract, and at the same time, Geth developers have already believed that the EIP is most likely not to be implemented before the Berlin upgrade. It seems that EIP-2537 is not accepted by Berlin's upgrade.
Within Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #88 , Geth developers found a series of problems in implementing PR in EIP-2537, and the developers said that further testing and fixing are needed. At this time, there are two implementations of EIP-2537 in the Geth system, one of which contains assembly optimization, while the other is completely written in the go language. Some developers propose to use the go language to write the version directly to reduce the difficulty of code review.
In Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #89 , more serious problems occurred. Some problems occurred in YOLO testing. The developers suspected that it was caused by the BLS signature, but the EIP2537 developers refuted this, believing that the test network problem was not caused by the BLS signature. The good news for EIP-2537 is that the deposit contract based on EIP-2537 is basically developed, and the contract is awaiting the contract audit.
Within Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #90 , the meeting locked in the DDL that will be launched in July for Berlin upgrades. Of course, another interesting argument in this conference is the issue of client diversity. In this conference, developers mainly discussed the situation where Geth is dominant, and some developers proposed to freeze the current EIP implementation to reduce the development costs of other clients. Even more interestingly, in the #91 conference, some developers proposed to use modular solutions to reduce development costs to increase client diversity. If readers are interested in the diversity of Ethereum clients, they can read the minutes of these two meetings.
Within Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #92 , 2537 is still recognized as the EIP required for Berlin upgrades.
In Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #96 , EIP-2537 and EIP-2539 have been included in its network hard fork upgrades, so Matter Labs hopes to put the EIP-2539 proposed at the same time as EIP-2537 on the YOLO v2 test network and enter the Berlin upgrade. However, Geth developers objected, believing that the current EIP-2537 has not been fully tested within Geth. The final meeting decided not to add 2696 to the Berlin upgrade, and it will be left to future discussions.
In Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #99 , the meeting decided to move EIP-2537 out of the YOLO v3 test network and Berlin to upgrade. The most important reason is that EIP-2537 wasted too much time by core developers, resulting in the hinderment of other EIP development within the Berlin upgrade. The secondary factor is that the Ethereum Foundation proposed EVM384 as an alternative to EIP-2537, and EVM 384 provides a more general elliptic curve calculation solution. But the core developers expressed concerns about security issues during the conference discussion.
The above content is the early history of EIP-2537. We can see that EIP-2537 was one of the most important EIPs in Berlin upgrade in the early days, but it was eventually abandoned due to implementation problems. Finally, in April 2021, Ethereum completed the Berlin upgrade. The actual implementation of EIP-2565 and other core included in the upgrade are not complicated. The Berlin upgrade seems to be a little thin, because the most complex EIP-2537 was kicked out of the Berlin upgrade.
Follow-up development
As we all know, Ethereum will have a core proposal every time it upgrades. For example, the London upgrade after Berlin introduced the most important handling fee proposal in Ethereum's history, EIP-1559. For EIP-2537, which was once the core proposal, it is difficult to include this proposal in subsequent upgrades.
In the London upgrade after Berlin, developers considered adding EIP-2537 to the London upgrade in issues#369 . In Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #109 , the developer synchronized the current development of EIP-2537. At this time, because other libraries are used to implement EIP-2537, a discussion on the use of gas for EIP-2537 was introduced. At the same time, some developers proposed to use EVM384 to replace EIP-2537. But within Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #111 in April 2021 , EIP-2537 was removed from the London upgrade due to complexity. The core complexity is that the EIP-2537 standard implementation replaces the dependency library, which leads to possible changes in gas pricing, and different client implementations take considerable time to reevaluate gas consumption.
In June 2021, issues#343 officially proposed to include EIP-2537 in Shanghai upgrade. However, it should be noted that after London is upgraded, Pairs upgrade, or known as The Merge, actually takes up a lot of time for developers, and the execution layer developers need to write a lot of code to implement PoS upgrades. In September 2022, the Pairs upgrade was completed, and the executive layer developers finally had the opportunity to continue discussing some goals of Shanghai upgrade.
In November 2022, Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #150 briefly discussed whether EIP-2537 is included in Shanghai upgrade, but developers believe that EIP-2537 needs to be postponed, and the core of Shanghai upgrade is to support PoS withdrawals. Ultimately, EIP-2537 was not included in the Shanghai upgrade, which focuses on implementing withdrawal functions.
What's even more miserable is that the Cancun upgrade has not discussed EIP-2537, because the core of the Cancun upgrade is that the execution layer node supports EIP-4844. EIP-4844 provides blobs for Ethereum layer 2 to facilitate the use of Ethereum as the data availability layer.
Finally, in Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #181 in February 2024 , the developers discussed incorporating EIP-2537 into the Pectra upgrade, and at this time, the developers believed that the implementation of EIP-2537 is no longer a problem, only some of the problems are in the pricing of Gas consumption.
In Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #202 on December 19, 2024 , the Netherlands developers finally identified the pricing model for EIP-2537. Yes, Matter Labs, the original sponsor of EIP-2537, is almost out of discussion at this time. In the subsequent January 2025 Ethereum Core Devs Meeting #203 , developer discussions included repricing BLS precompilation, and Geth developer Jared Wasinger suggested increasing gas costs by 20%, and supported by Besu team benchmarks.
Summarize
| date | event |
|---|---|
| February 2020 | Split EIP-1962 and formally propose EIP-2537 |
| April 2020 - October 2020 | The developer meeting discussed the implementation |
| of EIP-2537 many times, and was eventually abandoned by Berlin because it | |
| could not be implemented. | |
| March 2021 - April 2021 | Developers' meeting discusses the cost of EIP-2537 |
| gas, and is eventually abandoned by London upgrade due to complexity | |
| November 2022 | Developer meeting discusses whether to include Shanghai |
| upgrade, but it is fruitless | |
| February 2024 | The developer believes that EIP-2537 has no implementation |
| problems and still has some gas cost problems. He believes that it can be | |
| included in the Pectra upgrade. | |
| December 2024 - January 2025 | The developer meeting discusses the specific |
| cost calculation model and formally solves the cost problem of EIP-2537 |
It can be seen that whether EIP is included in the Ethereum upgrade "of course, it depends on one's own struggle, but it also takes into account the historical itinerary." Every Ethereum upgrade will have its own theme, just as EIP-2537 once became the most important EIP for Berlin upgrade, but it was abandoned due to its implementation difficulty and complexity. Ethereum subsequently entered the historical process of PoS. Complex pure execution layer EIPs were not valued, while a large number of PoS-related execution EIPs were regarded as core upgrade targets, which led to the unacceptable EIP-2537 for a long time.

