EigenLayer’s new competitors – Symbiotic and Karak

Reprinted from jinse
01/02/2025·4MSource: unchainedcrypto Translation: Shan Oppa, Golden Finance
The EigenLayer protocol is popular for being the first to re-stake Ethereum tokens. However, the protocol’s recent decision to ban US and Canadian users from participating in the upcoming EIGEN token airdrop has put other staking protocols like Karak and Symbiotic in the spotlight.
But how do Symbiotic and Karak differ from EigenLayer?
In this guide, we’ll look at the emerging proof-of-stake protocols Symbiotic and Karak, how they differ from the EigenLayer protocol, and how they differ from each other.
What is re-pledge?
Re-hypothecation refers to further staking of pledged assets or liquid pledged assets to protect other networks or applications.
The concept aims to repurpose idle assets to cover the startup costs of a new protocol and incentivize restakers with restaking rewards in the process.
What is EigenLayer? What role does it play in the Ethereum restaking
ecosystem?
EigenLayer facilitates the re-staking of staked ETH and allows stakers to receive additional re-staking rewards for their contributions.
The protocol leverages restaking to export Ethereum’s trust infrastructure to new protocols that lack sufficient resources to incentivize new validators.
That being said, EigenLayer is currently focused on re-staking ETH assets and Lido’s Liquid Staked Tokens (LST), with plans to expand the network’s coverage in the future.
This initial scope creates opportunities for its two emerging competitors, Symbiotic and Karak.
What is Symbiotic?
Symbiotic is a new competitor in the re-staking space, a permissionless protocol where validators can re-stake their assets to achieve shared security.
Symbiotic uses a modular design to support re-staking of various ERC-20 tokens (including stETH) and gives developers full control over the entire re-staking process. The protocol's minimal coordination layer can be plugged into existing or new protocols. Additionally, its flexible re-staking logic allows developers to choose their preferred staking assets, validator nodes, rewards and slashing systems.
Key features of Symbiotic
The following are the main components of the Symbiotic protocol:
-
Multi-asset staking : Symbiotic supports re-staking from a variety of networks, including ERC-20 compatible assets, LP tokens, and other digital assets.
-
Vaults : These are custom contracts used to handle the delegation of collateral to operators across the network.
-
Operators : These are entities that represent the network management infrastructure.
-
Resolver : A multifunctional contract responsible for approving or denying curtailment penalties incurred by an operator on the network it provides services.
-
Network : These protocols require a set of validating nodes to provide trusted minimal services.
Pros and cons of symbiosis
Here are the pros and cons of Symbiotic:
advantage :
-
Provide flexibility to developers, allowing them to tailor the restaking protocol to their needs: the network is responsible for the implementation of restaking, and restakers can opt in or out of the shared security contract.
-
Providing security at an affordable cost: Providing high-quality security by leveraging collateralization of multiple assets not only makes it affordable to share the security costs of new blockchain networks, but also eliminates the need to build security protocols from scratch complexity.
-
Increased Capital Efficiency: Symbiotic’s permissionless network provides cryptocurrency re-holders with a scalable way to fund the startup costs of new projects.
shortcoming:
- Collateral size limit: The number of collateral assets is limited during the launch phase, and only collateral assets from major protocols are supported.
What is Karak?
Karak is another new entrant into the restaking space, differentiating itself from EigenLayer and Symbiotic by offering a more comprehensive approach to shared security.
The protocol supports a variety of assets such as EigenLayer core products such as ETH and LST, but further adds LP tokens, stablecoins, WBTC, StaFi’s Liquid Equity Token (LRT), and more.
Karak allows stakers to re-stake their staked tokens and submit their assets to the Distributed Security Service (DSS) on the Karak protocol and grant additional execution rights to their staked assets.
Key Features of Karak
The main features of the Karak protocol are as follows:
-
Re-holders : These participants secure Ethereum and other networks in exchange for rewards.
-
Distributed Security Service : DSS utilizes re-hypothecated assets to improve security while reducing operating costs.
-
Chain : A chain or aggregation of services provided using distributed security services.
-
Operator : Can be a person or entity that authenticates the distributed security service.
Pros and Cons of Karak
The pros and cons of Karak are as follows:
advantage:
-
Multi-asset re-hypothecation: This component enables re-hypothecaters to provide a basket of assets to DSS, thus preventing the failure of a single asset from endangering DDS.
-
Unlimited re-staking: This protocol allows developers to build products on L2 and sidechains instead of focusing on Ethereum L1.
-
Turnkey Development: Karak’s powerful protocols allow developers to seamlessly iterate and deploy new and unique services.
shortcoming:
- Reward staking is not feasible for ETH assets: a sustainable yield model can only be achieved by accepting assets with a lower cost of capital than ETH.
Comparing EigenLayer vs. Karak vs. Symbiotic
Here is a comparison of the three re-pledge protocols:
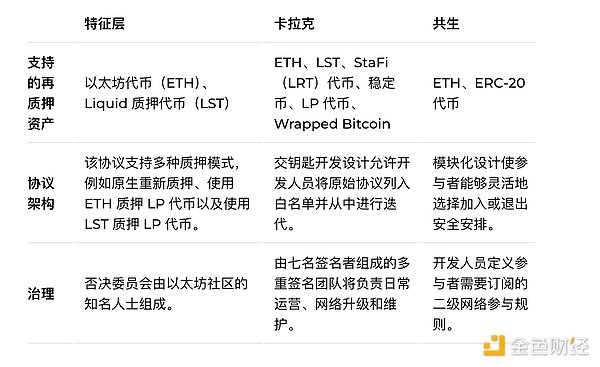
Symbiotic and Karak offer two compelling ways to change restaking as we currently know it. EigenLayer focuses on Ethereum’s core infrastructure, providing a powerful and solid foundation for building secure decentralized applications.
But this only scratches the surface of the many possibilities.
Symbiotic is becoming a leader in enabling networks to gain financial security from multiple collateral assets. Its scalable network enables other networks to customize their re-staking implementation.
Karak opens up new possibilities for interoperability and capital efficiency across multiple ecosystems through its broad set of supporting assets. The protocol may introduce a double-sided staking method in the future, encouraging users and service providers to actively participate in the network.
Summarize
As Symbiotic and Karak continue to contribute to the restaking space, network builders and users will gradually realize their respective capabilities and limitations. By increasing the utility and security of collateral assets, these protocols are expected to drive further innovation in the Ethereum ecosystem.




