Deep Analysis Bless Network: New Computing Infrastructure Drives the AI Age

Reprinted from panewslab
03/10/2025·2MTL;DR
- Bless Network provides a new distributed infrastructure solution to meet explosively growing demand for AI computing. Traditional centralized cloud infrastructure cannot solve key challenges in stability, accessibility, and cost.
- Bless powers its distributed edge computing by leveraging idle resources from everyday devices such as MacBooks and PCs. The platform ensures stability through automatic orchestration, enhances security through WASM-based isolation, and reduces costs to 10% of traditional cloud services.
- Bless provides decentralized support for blockchain, provides developers with an efficient platform, and improves computing accessibility for retail users. The platform will become the core infrastructure for industries that require real-time computing, from autonomous driving to smart cities.
1. AI: From the era of productivity to the era of production
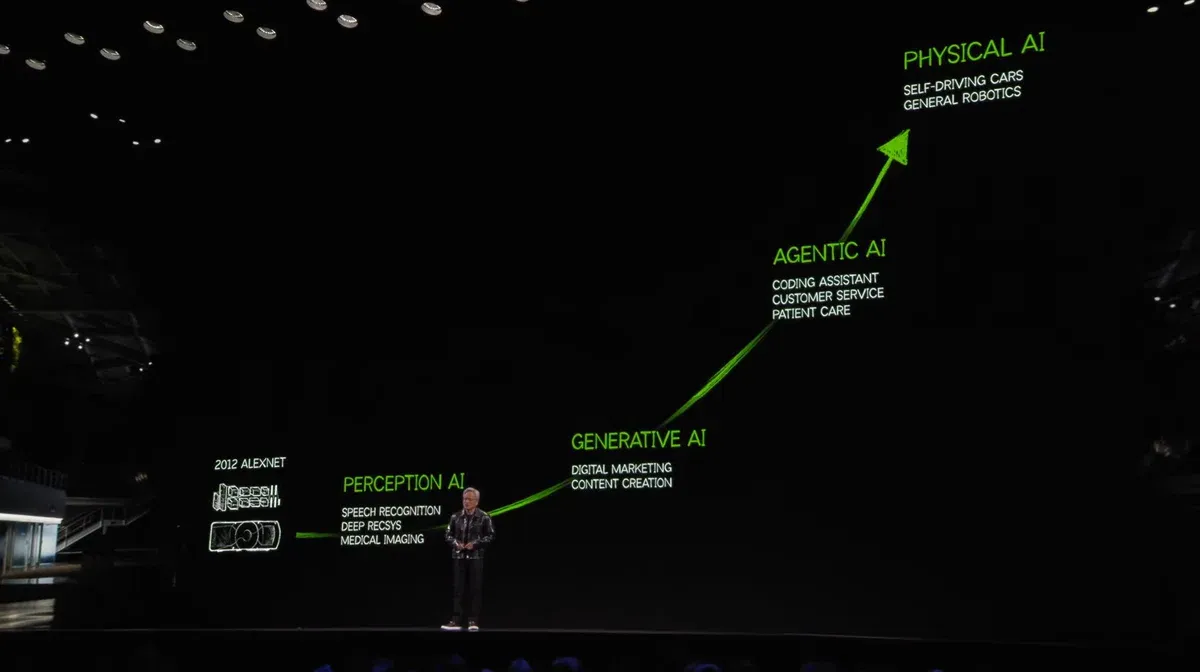
AI technology has reached a turning point. It is no longer just a tool to enhance human productivity. Today, AI can do meaningful work with minimal human guidance and generate independent value. Today’s AI agents can analyze complex scenarios, make decisions independently and perform advanced tasks. Agents can generate in-depth reports and program at the level of a senior developer.
**Source: CES 2025**
Once considered a distant future, now this is just the beginning of subversion. At the 2025 CES, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang said: "AI technology is redefining the fundamental way every industry works." Huang believes that AI will change the way business operates, reshape value creation, and affect every aspect of daily life.
2. AI Challenges: Stability, Accessibility, and Cost
With the leap of technology, AI adoption has surged. Just two months after OpenAI’s ChatGPT launched, it reached 100 million monthly active users (MAU). This achievement marks its growth rate faster than other applications. This growth trend is not limited to initial user interest. The ongoing momentum shows a fundamental shift in how we use technology.
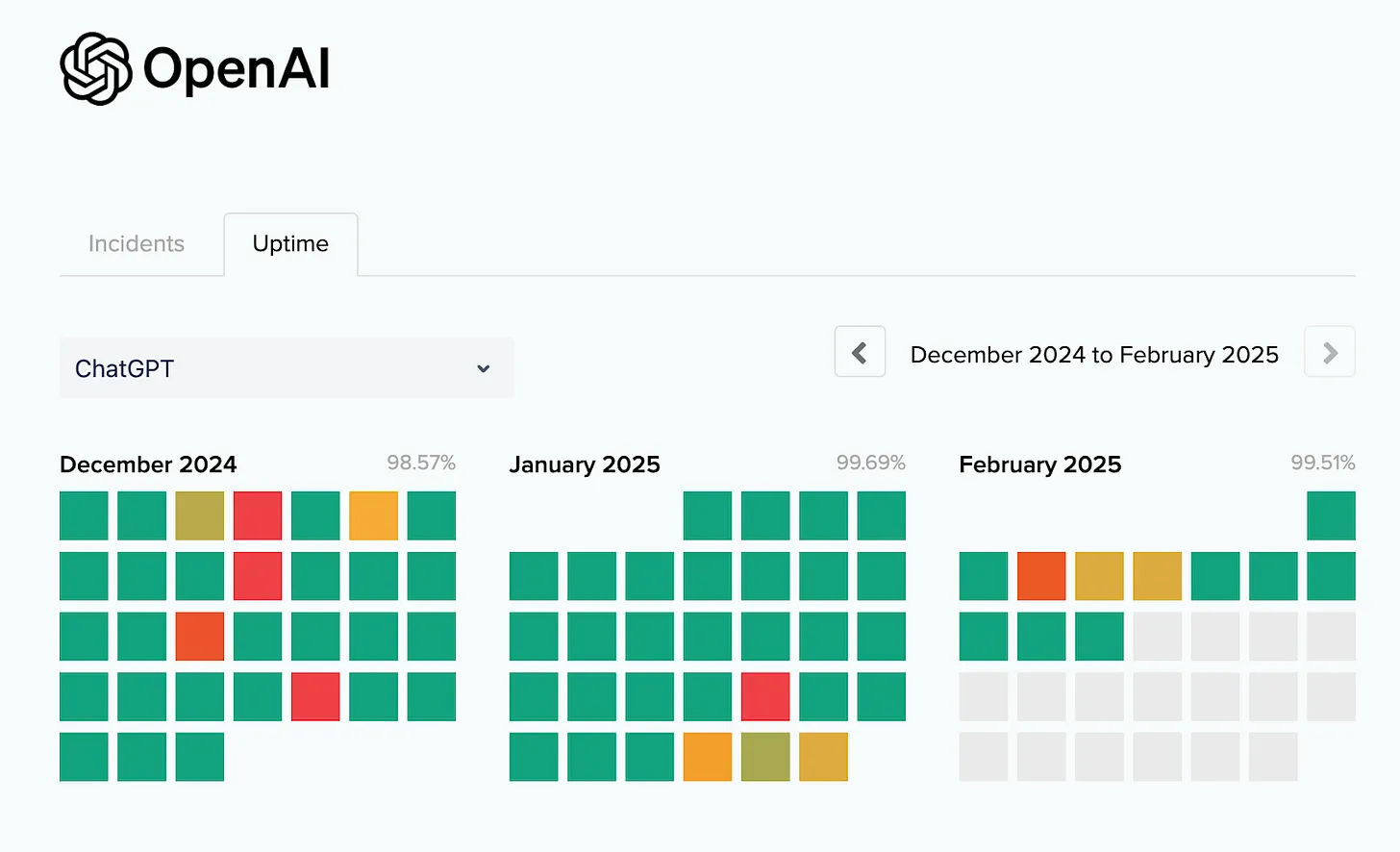
**OpenAI \'s service availability heat map, source: OpenAI**
However, the widespread use of AI tools among consumers puts huge pressure on existing power infrastructure. Large-scale language models (LLMs) require a large amount of computing resources, and high user traffic often leads to service outages. OpenAI's service availability heat map for the past three months shows frequent congestion.
To meet the growth in AI usage demand, enterprises and governments are expanding their data center infrastructure. The Stargate project in the United States is an example of this trend. However, centralized systems alone cannot maintain the operation of AI. As usage increases, the pressure on existing servers is also increasing. Additionally, users away from the data center will experience slower response times, which will degrade performance.
Cost is another major challenge. Training and running AI models requires a lot of investment, which makes it difficult to establish a sustainable business model. For example, Deepseek initially gained market attention at a low price, but recently increased its API fees by five times. Similarly, OpenAI is still in a loss-making state and relies on external funds to maintain operations.
Centralized infrastructure cannot solve these core challenges. The industry needs a more distributed solution. Bless provides a decentralized solution that solves key issues in today's AI field. By leveraging distributed edge computing, Bless creates a scalable and efficient infrastructure that meets the growing demands of AI services. This decentralized model improves accessibility, reduces costs, and provides more reliable AI solutions for the expanding market.
3. Bless Network: New computing paradigm in the AI era

**Source: Bless Network**
Founded by Binance Labs and Akash Network alumni, Bless has raised $8 million in seed funding. The project is developing a distributed edge computing network to meet the growing demands of the AI era. Currently, Bless runs a test network on Solana and has attracted more than 2.7 million users.
Bless takes advantage of idle computing power for everyday devices such as MacBooks and PCs. The network utilizes community computing resources instead of relying on centralized data centers. It handles diverse tasks including AI inference, data processing, and web hosting. The system allocates workloads according to the capabilities of the equipment. High-performance devices run AI model training, while other devices handle simpler tasks. Developers can access a transparent, stable, and cost-effective computing environment. This decentralized approach provides scalable and flexible computing infrastructure for anyone who needs computing resources.
**4. Clear incentive mechanism for distributed computing
infrastructure**
Bless provides clear incentives through its token economic model. Node operators obtain Bless tokens by providing idle computing resources. Service users use these tokens to purchase computing resources based on their needs.
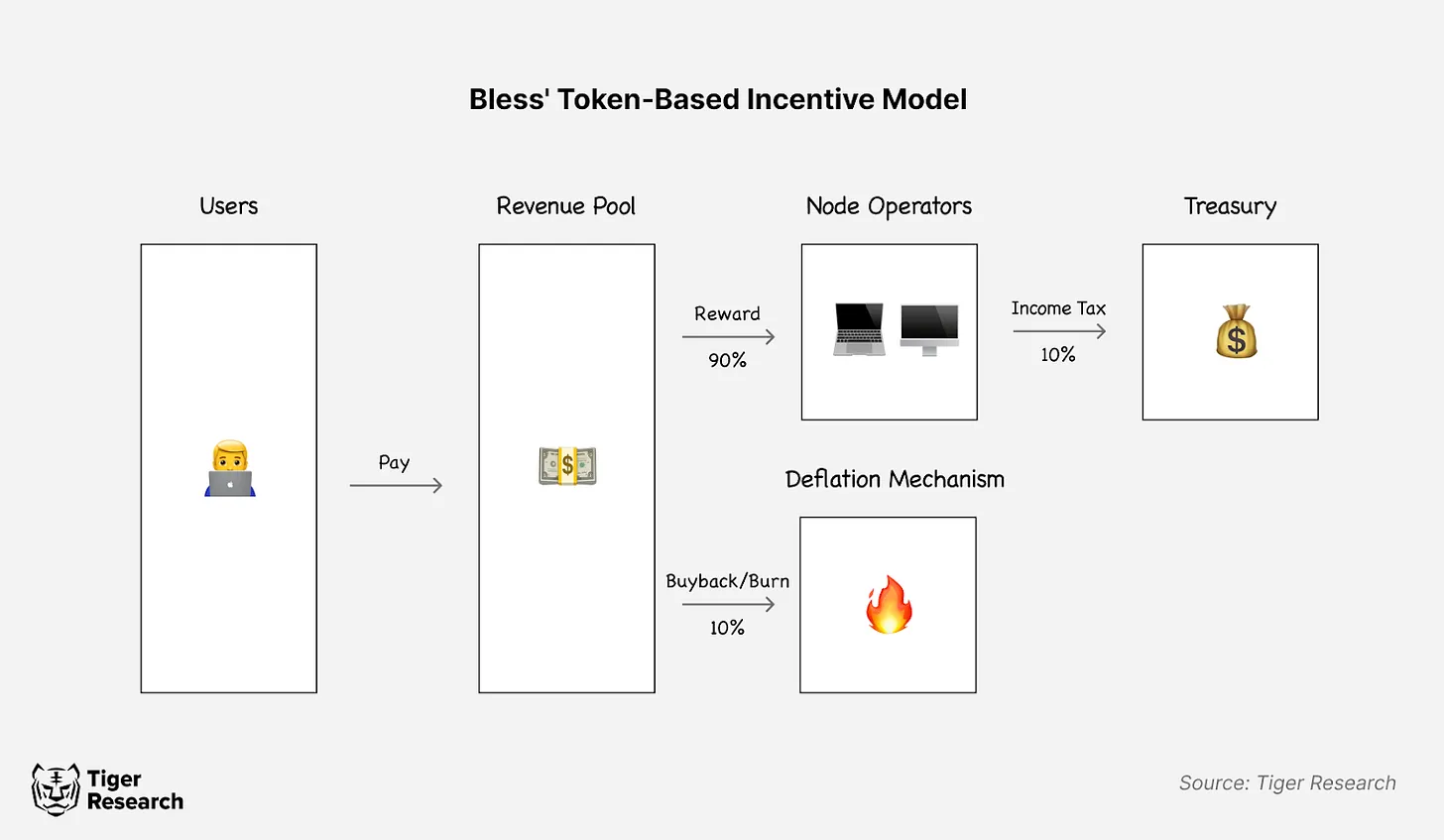
The platform allocates 90% of the tokens paid by users to node operators. From this income, 10% of the income entered the treasury. Another 10% is used to support network value stability through repurchase and token destruction. This transparent economic structure creates clear incentives for participants, facilitating sustainable growth and expansion of the network.
Web3-based token economics provides an ideal framework for building distributed computing infrastructure. Unlike traditional centralized cloud systems that are restricted by enterprises and regulation, Bless builds an open, token-based network that welcomes global participation. This decentralized approach operates independently of national regulations and allows users to access computing resources without being restricted by centralized payment systems.
Bless allows anyone to participate without professional equipment or technical knowledge. As personal device performance continues to improve, it becomes easier to contribute to the network. This design attracts more participants as it enables users to earn a stable income through rewards. Over time, this structure has the potential to evolve into a universal basic income (UBI) model.
5. Bless 's three major advantages: cost, stability and security
**5.1. Stability: Dynamic management is achieved through automatic
orchestration**
Bless ensures the stability of the infrastructure through automatic orchestration. The system analyzes the network status in real time and assigns tasks to the most appropriate nodes. This approach is similar to Uber's carpooling model. Traditional taxis have limited responsiveness due to fixed locations and vehicle restrictions, while Uber optimizes driver allocation based on real-time demand and traffic conditions. Similarly, Bless provides reliable services by leveraging globally distributed user equipment rather than relying on centralized infrastructure.
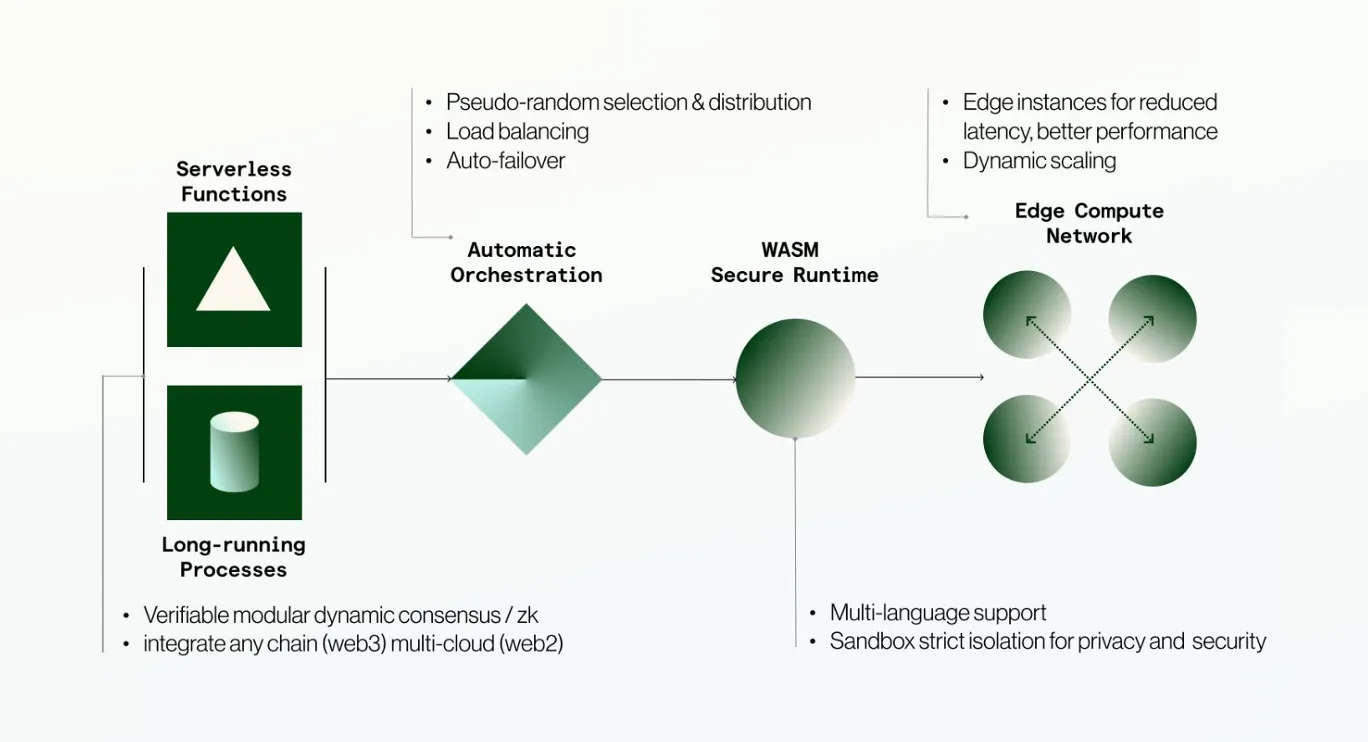
**Source: Bless Network**
Bless optimizes task allocation by evaluating factors such as workload type, node performance, historical reliability, current status, and geographical proximity. It assigns long-running processes to highly stable nodes and places serverless capabilities on nearby nodes to ensure faster execution speeds and reduce latency.
Bless improves network efficiency and security through advanced technologies. It uses simulated annealing, an optimization technique, to evaluate node response time and hardware performance. In addition, it adopts a mathematical method called the Greek-Latin square distribution, randomly allocating workloads to multiple nodes, preventing manipulation and enhancing network security.
Automatic orchestration also supports fast failover. Geolocation-aware gateways and continuous health check systems monitor node performance in real time. When a node fails, the system immediately redistributes the workload to the nearest qualified node, minimizing downtime. Bless ensures sub-second failover, reassigns tasks within 800 milliseconds, ensuring uninterrupted service.
5.2. Cost reduction: economic benefits of idle resource utilization
Bless provides a cost-effective alternative by leveraging distributed edge computing, replacing traditional cloud services. Traditional cloud services require a lot of investment in data centers. Companies must build physical infrastructure, manage facilities, and ensure a continuous supply of electricity. These fixed costs increase service costs for end users.
However, Bless reduces end-user costs by leveraging the idle computing power of personal devices and achieves sustainable delivery through automatic orchestration (as described in the previous section). This model eliminates the need for data center construction and reduces operating costs to about 10% of traditional cloud services.
Hosted cloud services simplify IT operations, but the growing demand for AI computing power has brought new challenges. Global public cloud spending is expected to reach $805 billion in 2024 and double in 2028, according to IDC (International Data Corporation). To remain competitive, companies must adopt cost-effective solutions.
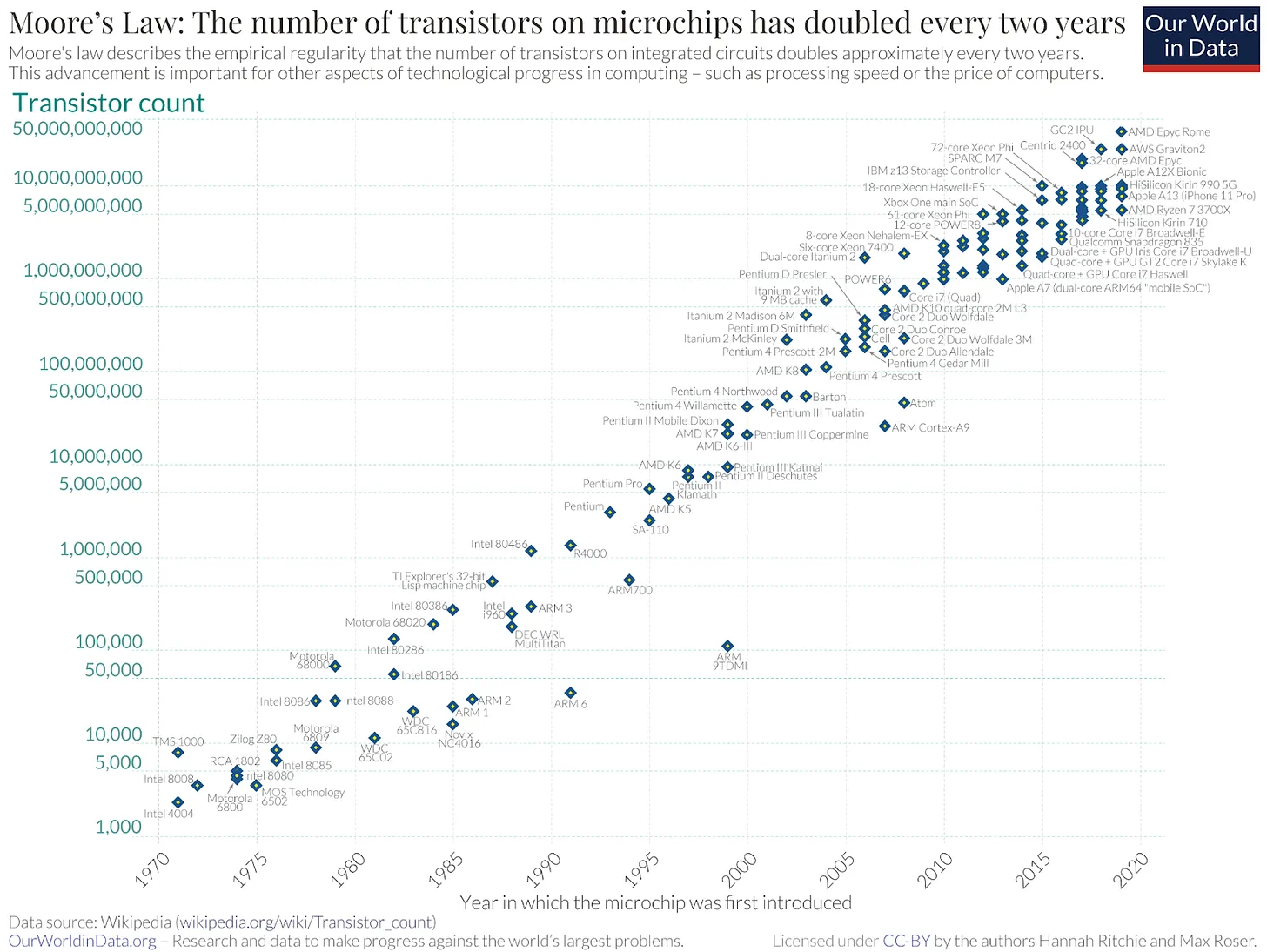
**Source: Our World in Data**
Bless provides a scalable and affordable alternative. The improvement of personal equipment technology capabilities has led to an increase in the potential supply of idle computing resources, thereby strengthening the decentralized and sustainable infrastructure that supports the AI era.
5.3. Security: Isolated environment based on WASM
Security is crucial to distributed computing. The system must block malicious code and protect the developer code and data. Bless solves these risks through a secure runtime environment based on WebAssembly (WASM).
Bless's WASM security framework is like a bank vault. The developer (client) stores the code and data in the WASM environment (vault). Node operators (bank employees) perform tasks but cannot access these storages, ensuring strict security.
In addition, WASM optimizes performance and protects business logic through early compilation (AOT) and bytecode obfuscation. It protects runtime data through memory encryption. WASM provides TEE-like security through software-based isolation. This approach eliminates dependence on hardware-based isolation systems such as Intel SGX or AMD SEV.
This secure environment ensures transparent operation of AI agents. Because the code runs in an isolated environment, the system can verify that the AI agent runs autonomously without human intervention. With the advancement of Zero Knowledge Proof-of-the-Signature (ZKP) technology, this security framework will become even stronger.
6. Explore new possibilities for distributed edge computing
**6.1. Solve the problem of centralization of blockchain
infrastructure**
At present, the blockchain ecosystem relies heavily on centralized cloud infrastructure. Most blockchain validators run on AWS, Google Cloud Platform, or Microsoft Azure. Decentralized applications (dApps) also run on the same centralized platform. These services provide stability but conflict with the core decentralization principles of blockchain.
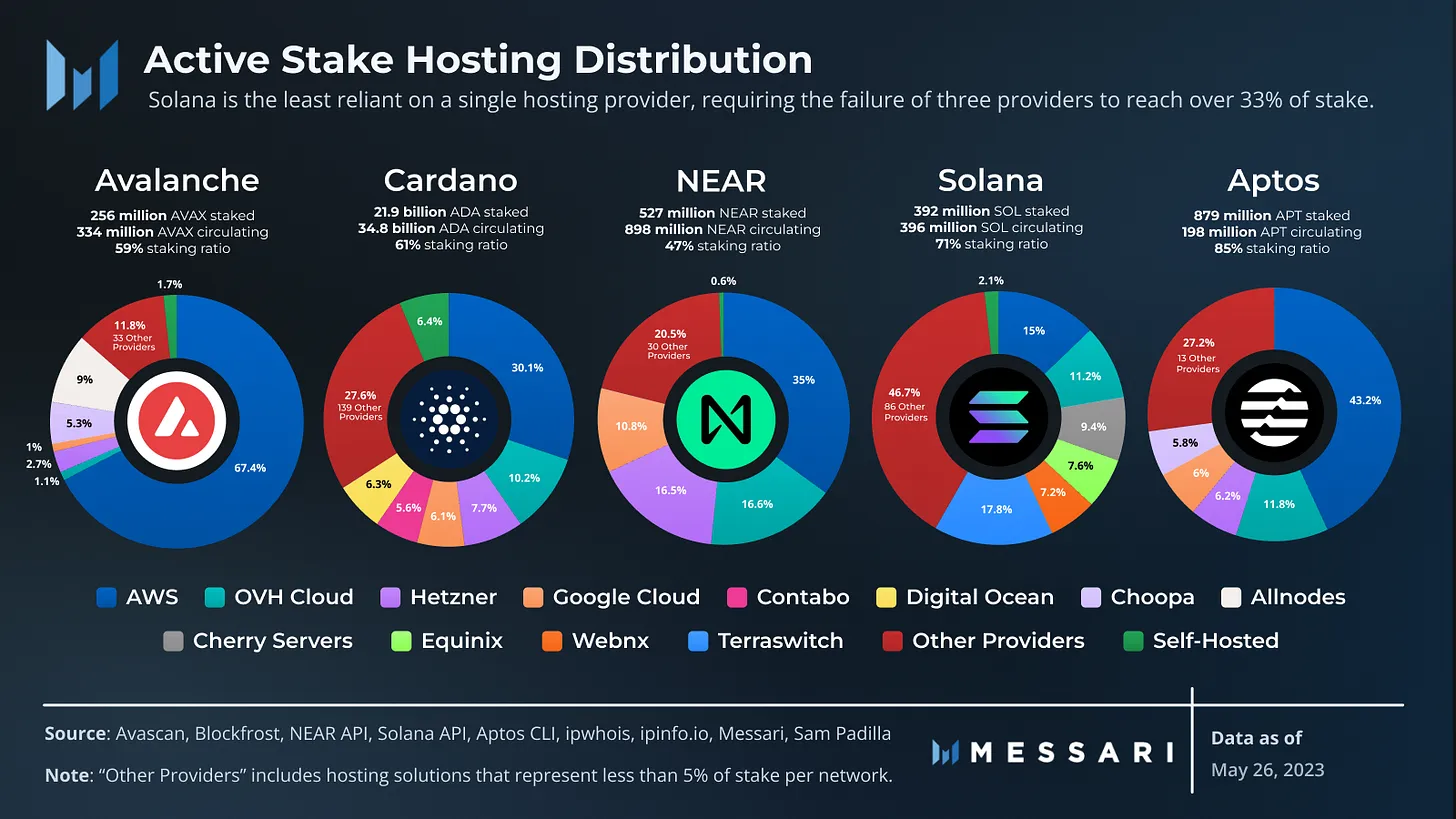
Bless provides solutions through a geo-distributed network of nodes, enhancing security and stability, and providing additional failure protection. More participants increased the level of decentralization and increased the resilience of the network. This model supports blockchain validators and dApp developers, providing a more independent and scalable infrastructure.
6.2. Provide developers with an efficient development platform
Bless provides developers with an efficient development environment through distributed edge computing, using a local priority method to run tasks on nearby nodes. This approach reduces latency and improves service stability. Netflix's CDN (Content Distribution Network) adopts a similar model to ensure a smooth streaming experience for users around the world.
The Bless CLI provides everything you need from project management to deployment processing. Developers can deploy websites or front-end applications to Bless's infrastructure through a command. The platform provides testing and monitoring functions. The WASM runtime environment supports programming languages such as Python, JavaScript, Go, and Rust. Developers are free to encode in their favorite language.
Bless provides serverless computing environment functions similar to AWS Lambda. Triggers automatically perform tasks based on network and on-chain events. These features provide a flexible and efficient development environment.
6.3. Provide new possibilities for retail users
Demand for high-performance computing is growing rapidly. In many cases, advanced AI models like Deepseek's 70B+ model require more computing power than a personal computer's processing power. Bless's distributed infrastructure enables users to quickly and easily access these LLMs.
Bless also has strong potential in the gaming industry. As game graphics advance, players need high-performance hardware. Bless uses distributed computing to deliver high-quality rendering at a lower cost. It provides a viable alternative.
Additionally, users can share their computing power and earn income. This creates new economic opportunities for the digital age.
7. Bless: Scaling to global computing grids
Bless supports not only AI. The network can also support industries such as autonomous driving, smart cities and medical diagnosis that require real-time processing. These industries require low latency computing, making edge computing more efficient than a single data center. Bless meets this need with a flexible distributed architecture, aiming to be a critical infrastructure for the industry.
Bless is expanding to meet growing demand. Through the Chrome extension, the network now supports 800,000 daily active users (DAUs) and has registered over 2.7 million nodes.
The Bless plan introduces three new node types:
-
Desktop Node : A standalone application for long-term workloads.
-
CLI Node : Docker-based solution for institutions and professional operators.
-
Nested node : The node that opts out, automatically contributes computing power when the user opens a supported application.
Nested nodes enable easy network scaling. Users don't need to install anything, and computing power automatically expands as more users access supported applications. This pattern follows the Bless network neutral application (nnAPP) paradigm.
The system connects MacBook, PC, server and other devices in real time to distributed nodes to achieve instant access to global computing resources. This eliminates geographical restrictions and lays the foundation for global computing grids. Bless aims to create a general infrastructure that can support computing needs in a variety of high-tech fields.
8. Conclusion
The AI era needs infrastructure that can handle surges in workloads. Data centers alone cannot meet this need, especially as cost and latency issues persist. Bless addresses these challenges through a decentralized model that utilizes idle resources.
This approach is more than just a technical solution. It prioritizes fair distribution of accessibility and computing power to reduce global computing gaps. Just as the Internet expands access to information, Bless aims to expand access to AI worldwide. This vision opens up new possibilities for a more inclusive AI-driven future.

