Comparison of the four major Crypto X AI frameworks: ELIZA, GAME, ARC and ZEREPY

Reprinted from jinse
12/31/2024·4MAuthor: Deep Value Memetics, Translation: Golden Finance xiaozou
In this article we will explore the prospects of the Crypto X AI framework. We will look at the four main current frameworks (ELIZA, GAME, ARC, ZEREPY) and their technical differences.
1. Preface
We have researched and tested the four major Crypto X AI frameworks ELIZA, GAME, ARC, and ZEREPY in the past week, and we have drawn the following conclusions.
We believe AI16Z will continue to dominate. The value of Eliza (market share is about 60%, market value exceeds 1 billion US dollars) lies in its first- mover advantage (Lindy effect) and its use by more and more developers, 193 contributors, 1800 forks This is proven by data such as more than 6,000 stars, making it one of the most popular code bases on Github.
So far, GAME (with a market share of about 20% and a market value of about $300 million) has been developing very smoothly and is gaining rapid adoption. As VIRTUAL just announced, the platform has more than 200 projects and 150,000 daily requests. and a weekly growth rate of 200%. GAME will continue to benefit from the rise of VIRTUAL and will become one of the biggest winners in its ecosystem.
Rig (ARC, ~15% market share, ~$160 million market cap) is compelling because its modular design is very easy to operate and can dominate the Solana ecosystem (RUST) as a "pure-play" .
Zerepy (~5% market share, ~$300 million market capitalization) is a relatively niche application catering specifically to the avid ZEREBRO community, and its recent partnership with the ai16z community may create synergies.
We note that our market share calculations cover market capitalization, development record, and underlying operating system end markets.
We believe that the framework segment will be the fastest growing area during this market cycle, with a total market cap of $1.7 billion that could easily grow to $20 billion, which is still relatively conservative compared to the peak valuation of L1 in 2021 , at that time the valuation of many L1s reached more than 20 billion US dollars. While these frameworks all serve different end markets (chains/ecosystems), a market cap-weighted approach is probably the most prudent approach given that we believe the space is on an upward trend.
2. Four major frameworks
In the table below, we list the key technologies, components and advantages of each major framework.
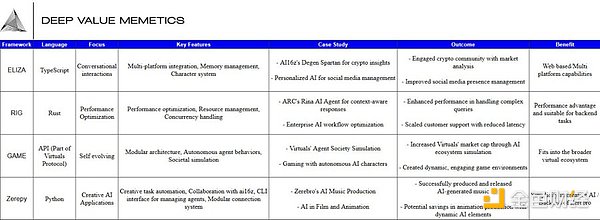
(1) Framework overview
At the intersection of AI X Crypto, there are several frameworks that promote the development of AI. They are AI16Z's ELIZA, ARC's RIG, ZEREPY's ZEREBRO, and GAME's VIRTUAL. Each framework addresses different needs and philosophies in the development of AI agents, from open source community projects to performance-focused enterprise solutions.
This article first introduces frameworks, telling you what they are, what programming languages, technical architectures, algorithms they use, what unique functions they have, and what potential use cases the frameworks can use. We then compare each framework in terms of usability, scalability, adaptability, and performance, exploring their respective strengths and limitations.
ELIZA (developed by ai16z)
Eliza is a multi-agent simulation open source framework designed to create, deploy and manage autonomous AI agents. Developed in the TypeScript programming language, it provides a flexible and extensible platform for building intelligent agents that are capable of interacting with humans across multiple platforms and maintaining consistent personality and knowledge.
Core features of the framework include a multi-agent architecture that supports simultaneous deployment and management of multiple unique AI personalities, as well as a character system that uses the character file framework to create different agents, and provides long-term memory and context through an advanced Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) system Aware memory management capabilities. Additionally, the Eliza framework provides smooth platform integration for reliable connections with Discord, X, and other social media platforms.
Eliza is an excellent choice in terms of communication and media capabilities of the AI agent. On the communication side, the framework supports integration with Discord’s voice channel feature, X features, Telegram, and direct API access for custom use cases. On the other hand, the framework's media processing capabilities can be extended to PDF document reading and analysis, link content extraction and summarization, audio transcription, video content processing, image analysis and dialogue summarization, and can effectively handle various media input and output.
The Eliza framework provides flexible AI model support through local inference of open source models, cloud inference of OpenAI, and default configurations such as Nous Hermes Llama 3.1B, and integrates support for Claude to handle complex tasks. Eliza uses a modular architecture with broad operating systems, custom client support, and comprehensive APIs to ensure scalability and adaptability between applications.
Eliza's use cases span multiple areas, such as: AI assistants for customer support, community moderation, and personal tasks, as well as social media roles such as automated content creators, interactive bots, and brand representatives. It can also act as a knowledge worker, performing roles such as research assistant, content analyst, and document processor, and support interactive roles in the form of role-playing bots, educational tutors, and entertainment agents.
Eliza's architecture is built around an agent runtime that is seamlessly integrated with its role system (supported by the model provider), memory manager (connected to the database), and operating system (linked to the platform client). The unique features of the framework include a plug-in system that supports modular function expansion, supports multi-modal interactions such as voice, text, and media, and is compatible with leading AI models (such as Llama, GPT-4, and Claude). With its versatile and powerful design, Eliza stands out as a powerful tool for developing AI applications across domains.
GAME (developed by Virtuals Protocol)
The Generative Autonomous Multimodal Entity Framework (GAME) is designed to provide developers with API and SDK access for experimenting with AI agents. This framework provides a structured approach to managing the behavior, decision-making and learning process of AI agents.
Its core components are as follows: First, the Agent Prompting Interface is the entry point for developers to integrate GAME into the agent to access agent behavior. The Perception Subsystem starts a session by specifying parameters such as session ID, agent ID, user and other relevant details.
It synthesizes incoming information into a format suitable for the Strategic Planning Engine and serves as a sensory input mechanism for AI agents, whether in the form of conversations or reactions. At its core is a dialogue processing module that processes messages and responses from agents and collaborates with the perception subsystem to efficiently interpret and respond to input.
The strategic planning engine works with the conversation processing module and on-chain wallet operators to generate responses and plans. The engine functions at two levels: as a high-level planner that creates broad strategies based on context or goals; and as a low-level strategy that converts these strategies into actionable strategies, which are further divided into action planners and user action planners for specified tasks. Plan executor for executing tasks.
Another independent but important component is the World Context, which references the environment, global information, and game state to provide the necessary context for the agent's decision-making. In addition, the Agent Repository is used to store long-term attributes such as goals, reflections, experiences, and personality, which together shape the agent's behavior and decision-making process.
The framework uses short-term working memory and long-term memory processors. Short-term memory retains information about previous actions, results, and current plans. In contrast, long-term memory processors extract key information based on criteria such as importance, recency, and relevance. Long-term memory stores knowledge such as the agent's experience, reflections, dynamic personality, world context, and working memory to enhance decision- making and provide a basis for learning.
The learning module uses data from the perception subsystem to generate general knowledge, which is fed back into the system to improve future interactions. Developers can input feedback about actions, game states, and sensory data through the interface to enhance the AI agent's learning capabilities and improve its planning and decision-making capabilities.
The workflow begins with the developer interacting through the agent prompt interface. Input is processed by the perception subsystem and forwarded to the dialogue processing module, which is responsible for managing the interaction logic. The strategic planning engine then develops and executes plans based on this information, leveraging high-level strategies and detailed action plans.
Data from the world context and agent repositories inform these processes, while working memory keeps track of immediate tasks. Meanwhile, long-term memory processors store and retrieve long-term knowledge. The learning module analyzes the results and integrates new knowledge into the system so that the agent's behavior and interactions can be continuously improved.
RIG (developed by ARC)
Rig is an open source Rust framework designed to simplify the development of large language model applications. It provides a unified interface for interacting with multiple LLM providers such as OpenAI and Anthropic, and supports a variety of vector stores, including MongoDB and Neo4j. The framework’s modular architecture is unique in its core components such as Provider Abstraction Layer, vector storage integration, and proxy system to facilitate seamless interaction with LLM.
Rig's primary audience includes developers building AI/ML applications using Rust, followed by organizations looking to integrate multiple LLM providers and vector stores into their own Rust applications. The repository uses a workspace architecture with multiple crates to support scalability and efficient project management. Its key functionality is the provider abstraction layer, which provides standardization for completing and embedding APIs across different LLM providers, with consistent error handling. The Vector Store Integration component provides an abstract interface to multiple backends and supports vector similarity searches. The agent system simplifies LLM interaction and supports retrieval augmentation generation (RAG) and tool integration. In addition, the embedding framework also provides batch processing capabilities and type-safe embedding operations.
Rig utilizes several technical advantages to ensure reliability and performance. Asynchronous operations leverage Rust’s asynchronous runtime to efficiently handle large numbers of concurrent requests. The framework’s inherent error handling improves resilience to failures in AI provider or database operations. Type safety can prevent errors during compilation, thereby enhancing the maintainability of the code. Efficient serialization and deserialization processes support data processing in formats such as JSON, which is critical for AI service communication and storage. Detailed logging and instrumentation further aid in debugging and monitoring applications.
Rig's workflow begins when a client initiates a request, which interacts with the appropriate LLM model through the provider abstraction layer. The data is then processed by the core layer, where agents can use tools or access the context’s vector store. Responses are generated and refined through complex workflows (such as RAG) involving document retrieval and context understanding before being returned to the client. The system integrates multiple LLM providers and vector stores, making it adaptable to model availability or performance updates.
Use cases for Rig are diverse and include question-and-answer systems that retrieve relevant documents to provide accurate responses, document search and retrieval systems for efficient content discovery, and chatbots or virtual assistants that provide context-aware interactions for customer service or education. It also supports content generation, enabling the creation of text and other materials based on learning models, making it a universal tool for developers and organizations.
Zerepy (developed by ZEREPY and blorm)
ZerePy is an open source framework written in Python language and designed to deploy agents on X utilizing OpenAI or Anthropic LLM. Derived from a modular version of the Zerebro backend, ZerePy allows developers to launch agents with similar Zerebro core functionality. While the framework provides a foundation for agent deployment, fine-tuning the model is essential to generate creative output. ZerePy simplifies the development and deployment of personalized AI agents, especially for content creation on social platforms, cultivating an AI-driven creative ecosystem for art and decentralized applications.
Developed in Python, the framework emphasizes agent autonomy and focuses on creative output generation, consistent with ELIZA’s architecture and partnership with ELIZA. Its modular design enables in-memory system integration and enables the deployment of agents on social platforms. Key features include a command line interface for agent management, integration with Twitter, support for OpenAI and Anthropic LLM, and a modular connectivity system for enhanced functionality.
ZerePy's use cases span social media automation, where users can deploy artificial intelligence agents to post, reply, like, and retweet to increase platform engagement. In addition, it also caters to content creation in areas such as music, memes, and NFTs, making it an important tool for digital art and blockchain-based content platforms.
(2) Comparison of four major frameworks
In our opinion, each framework provides a unique approach to AI development that matches specific needs and circumstances, and we shift the focus from the competing relationships of these frameworks to the uniqueness of each framework.
ELIZA stands out with its user-friendly interface, especially for developers familiar with JavaScript and Node.js environments. Its comprehensive documentation helps set up artificial intelligence agents on a variety of platforms, although its extensive feature set may come with a bit of a learning curve. Developed in TypeScript, Eliza is ideal for building agents embedded in the web, as most front-ends of web infrastructure are developed in TypeScript. The framework is known for its multi-agent architecture, which enables the deployment of different AI personalities on platforms such as Discord, X, and Telegram. Its advanced memory management RAG system makes it particularly effective for artificial intelligence assistants in customer support or social media applications. While it offers flexibility, strong community support, and consistent cross-platform performance, it's still in its early stages and may pose a learning curve for developers.
GAME is specifically designed for game developers, providing a low-code or no- code interface through APIs, making it accessible to users with less technical skills in the gaming field. However, its focus on game development and blockchain integration may pose a steep learning curve for those without relevant experience. It excels in procedural content generation and NPC behavior, but is limited by the complexity added by its segmentation and blockchain integration.
Because it uses the Rust language, Rig may not be user-friendly given the complexity of the language, which poses a significant learning challenge, but it has intuitive interactions for those versed in systems programming. The programming language itself is known for its performance and memory safety compared to typescript. It features strict compile-time checks and zero-cost abstractions, which are required to run complex AI algorithms. The language is very efficient and its low level of control makes it ideal for resource- intensive AI applications. The framework provides high-performance solutions with a modular and extensible design, making it ideal for enterprise applications. However, for developers who are not familiar with Rust, there is a steep learning curve when using Rust.
ZerePy leverages Python, offering high usability for creative AI tasks, a low learning curve for Python developers, especially those with an AI/ML background, and benefits from strong community support thanks to Zerebro's crypto community. ZerePy specializes in creative artificial intelligence applications such as NFTs, positioning itself as a powerful tool for digital media and art. While it thrives on creativity, the scope is relatively narrow compared to other frameworks.
In terms of scalability, ELIZA has made great strides in its V2 update, which introduced a unified message line and an extensible core framework to support effective management across multiple platforms. However, the management of this multi-platform interaction can pose scalability challenges if not optimized.
GAME excels at the real-time processing required for games, and scalability is managed through efficient algorithms and an underlying blockchain distributed system, although it may be limited by the specific game engine or blockchain network.
The Rig framework leverages Rust's scalability performance and is designed for high-throughput applications, which is particularly effective for enterprise- level deployments, although this may mean complex setup is required to achieve true scalability.
Zerepy's scalability is geared toward creative output and is supported by community contributions, but its focus may limit its application in broader AI contexts, and scalability may be limited by the diversity of creative tasks rather than the number of users. test.
In terms of adaptability, ELIZA leads the way with its plug-in system and cross-platform compatibility, and its GAME in the game environment and Rig that handles complex AI tasks are also excellent. ZerePy shows high adaptability in creative fields, but is less suitable for wider artificial intelligence applications.
In terms of performance, ELIZA is optimized for fast social media interactions, where fast response times are key, but its performance may vary when dealing with more complex computing tasks.
GAME developed by Virtual Protocol focuses on high-performance real-time interaction in game scenarios, utilizing efficient decision-making processes and underlying blockchain for decentralized artificial intelligence operations.
The Rig framework is based on the Rust language and provides excellent performance for high-performance computing tasks and is suitable for enterprise applications where computing efficiency is critical.
Zerepy's performance is tailored for the creation of creative content, and its metrics are centered around the efficiency and quality of content generation, which may be less generalizable outside of the creative field.
The advantage of ELIZA is that it provides flexibility and scalability, making it highly adaptable through its plug-in system and role configuration, which is conducive to cross-platform social AI interaction.
GAME provides unique real-time interaction capabilities in games, with novel AI engagement enhanced through blockchain integration.
Rig's strength lies in its performance and scalability for enterprise AI tasks, with a focus on clean, modular code for long-term project health.
Zerepy specializes in nurturing creativity and is a leader in the application of artificial intelligence in digital art, supported by a vibrant community- driven development model.
Each framework has its own limitations. ELIZA is still in its early stages, with potential stability issues and a learning curve for new developers. Niche games may limit wider applications, and blockchain also adds complexity. Rig's steep learning curve due to Rust's composition may scare off some developers, while Zerepy's narrow focus on creative output may limit its use in other AI fields.
(3) Summary of framework comparison
Rig (ARC):
Language: Rust, focus on safety and performance.
Use Case: Ideal for enterprise-level AI applications as it focuses on efficiency and scalability.
Community: Less community driven and more focused on technical developers.
Eliza (AI16Z):
Language: TypeScript, emphasizing web3 flexibility and community participation.
Use cases: Designed for social interaction, DAOs and transactions, with special emphasis on multi-agent systems.
Community: Highly community driven, with extensive GitHub participation.
ZerePy (ZEREBRO):
Language: Python, making it available to a wider base of AI developers.
Use cases: Suitable for social media automation and simpler AI agent tasks.
Community: Relatively new, but expected to grow due to Python's popularity and support from AI16Z contributors.
GAME (VIRTUAL):
Focus: Autonomous, adaptive artificial intelligence agents that evolve based on interactions in virtual environments.
Use case: Best suited for AI agents to learn and adapt to scenarios such as games or virtual worlds.
Community: A community that is innovating but still determining its position among the competition.
3. Star data trends on Github
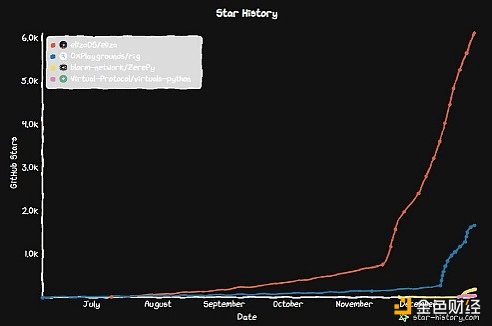
The picture above is the GitHub star following data since the release of these frameworks. It is worth noting that GitHub star is an indicator of community interest, project popularity, and project perceived value.
ELIZA (red line):
The rise from a low base in July to a significant increase in the number of stars in late November (to 61,000 stars) shows that interest is rapidly increasing and attracting the attention of developers. This exponential growth shows that ELIZA has gained significant traction due to its features, updates and community involvement. Its popularity far exceeds that of its competitors, suggesting that it has strong community support and broader applicability or interest in the AI community.
RIG (blue line):
Rig is the oldest of the four major frameworks. Its number of stars is modest but continues to grow, and it is likely to increase significantly in the next month. It has reached 1700 stars and is still rising. Continuous development, updates and a growing number of users are the reasons for the continued accumulation of user interest. This may reflect that the framework has a niche user base or is still building a reputation.
ZEREPY (yellow line):
ZerePy was launched just a few days ago and has already accumulated 181 stars. It's worth emphasizing that ZerePy needs more development to increase its visibility and adoption. Collaboration with AI16Z may attract more code contributors.
GAME (green line):
This project has a minimal number of stars, and notably, the framework can be applied directly to agents in the virtual ecosystem via API, eliminating the need for Github visibility. However, the framework became publicly available to builders just over a month ago, and more than 200 projects are being built using GAME.
4. Reasons for the bullish framework
The V2 version of Eliza will integrate the Coinbase proxy suite. All projects using Eliza will support native TEEs in the future, allowing agents to run in a secure environment. An upcoming feature of Eliza is the Plugin Registry, which will allow developers to seamlessly register and integrate plugins.
Additionally, Eliza V2 will support automated anonymous cross-platform messaging. The Token Economics white paper is scheduled to be released on January 1, 2025, and is expected to have a positive impact on the Eliza Framework’s underlying AI16Z token. AI16Z plans to continue to enhance the utility of the framework and continue to attract high-quality talent, and the efforts of its major contributors have already demonstrated its ability to do so.
The GAME framework provides code-less integration for agents, allowing both GAME and ELIZA to be used in a single project, each serving a specific purpose. This approach is expected to appeal to builders who focus on business logic rather than technical complexity. Although the framework has only been publicly available for 30 days, it has made substantial progress, supported by the team's efforts to attract more contributors. All projects launched on VIRTUAL are expected to use GAME.
Rig, represented by the ARC token, has huge potential, although its framework is still in its early stages of growth and plans to drive adoption of the project have only been live for a few days. But high-quality projects using ARC are expected to appear soon, similar to Virtual Flywheel, but focusing on Solana. The team is optimistic about working with Solana, comparing ARC's relationship with Solana to Virtual's relationship with Base. Notably, the team not only encourages new projects to be launched using Rig, but also encourages developers to enhance the Rig framework itself.
Zerepy is a newly launched framework that is gaining more and more traction thanks to its partnership with Eliza. The framework attracts Eliza contributors who are actively improving it. Driven by ZEREBRO fans, it has a cult following and provides new opportunities for Python developers who were previously underrepresented in the competition for artificial intelligence infrastructure. This framework will play an important role in AI creativity.



 chaincatcher
chaincatcher

 panewslab
panewslab