Bankless: Ethereum's expansion endgame—Native Rollups

Reprinted from jinse
03/18/2025·3MAuthor: David C Source: bankless Translation: Shan Oppa, Golden Finance
Is the end-of-schedule solution for Ethereum expansion finally here?
Despite fierce debates surrounding the expansion roadmap, Ethereum's expansion still relies on Rollups. Rollups undoubtedly drive the success of Ethereum expansion, but the problem of them being out of sync with the main chain remains.
Rollups need to maintain a dedicated proof mechanism, adding a lot of complexity and operational costs to each Rollup team. Furthermore, they rely heavily on security committees or governance votes to follow up on Ethereum’s upgrades, which leads to lag and disconnect. The security assumptions and centralization levels adopted by different Rollups vary, resulting in ecological fragmentation and reducing interoperability. At the same time, every time Ethereum is hard forked, the Rollup team needs to update manually to maintain compatibility, increasing the governance burden and introducing new risks.
Against the backdrop of the debate over Ethereum expansion route, many people are beginning to think about whether there is a simpler solution— a L2 solution that does not require heavy maintenance and is always synchronized with Ethereum.
This is the philosophy of Native Rollups – a new Rollup design framework that fundamentally aligns with Ethereum, taking full advantage of the security of the main chain without relying on external supervision or custom logic. Let us gain insight into this concept and its related principles.
Parsing native Rollups
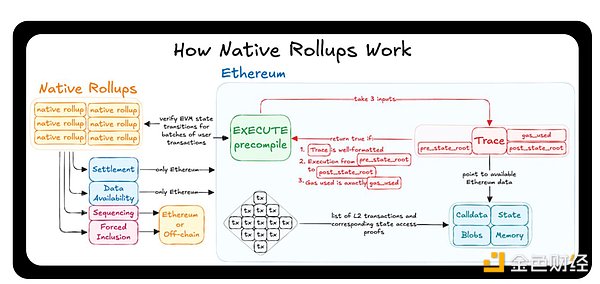
Native Rollups were proposed by members of the Ethereum community such as Justin Drake and Dan Robinson, which are directly integrated into Ethereum's core trading rules, allowing Ethereum itself to verify transactions rather than relying on external proof systems.
Currently, most L2 solutions execute transactions off-chain and use complex proof mechanisms to verify withdrawals and state changes. Native Rollups adopts a different approach, using EXECUTE precompilation - a built-in function in Ethereum, allowing Rollups to directly use Ethereum's verification rules to process transactions without the need for an independent proof system.
Under this architecture, native Rollups directly publishes transaction data to the Ethereum main chain, and Ethereum itself enforces its correctness. This allows them to automatically adapt to Ethereum’s network upgrades without governance votes or security committee intervention, eliminating many of the complexities and interoperability issues that are currently present.
By eliminating the need to repetitively build Ethereum logic, native Rollups reduces maintenance costs, simplifies security mechanisms, and makes L2 easier to adapt to Ethereum 's continuous evolution while maximizing the security of the main chain .
Comparison of native Rollups with other Rollups
To better understand the importance of native Rollups , we can compare them with other Rollup solutions currently being explored.
▪️ Based Rollups
Based Rollups was first proposed by Vitalik Buterin in 2021 and formally defined by Justin Drake in 2023. This type of Rollups relies entirely on Ethereum L1 validators to sort transactions , thereby improving the decentralization of transactions.
Although there are no fully online Based Rollups yet, teams such as Taiko and Spire Labs are actively promoting their deployment. While Ethereum’s participation enhances decentralization, Based Rollups still needs to manage its own proof system . Due to the long block time of Ethereum L1, the user experience may be affected, but improvements in the pre- confirmation mechanism are alleviating this problem.
▪️ Booster Rollups
Booster Rollups enhances scalability by replicating the execution and stored procedures of Ethereum L1 as much as possible in Layer 2, allowing applications to scale without major refactoring.
This approach, while making existing applications easier to scale, is more complex than traditional Rollups because it requires more complex engineering and unique proof mechanisms . Although Booster Rollups aims to enable stronger composability and easier application deployment, it still faces challenges in economic incentives and user experience .
▪️ Native Rollups
As mentioned earlier, unlike the two solutions mentioned above, native Rollups does not require a separate proof framework or external validator , as all verifications are done by Ethereum itself. This greatly reduces the complexity of L2 and simplifies its interaction with L1.
Key benefits of native Rollups:
Greatly improve security : Users can hold assets on native Rollup and trust it as much as Ethereum L1. The risk of multi-signal or security committees that traditional Rollups rely on will be significantly reduced.
Simpler development : no longer requires custom fraud proofs or zero- knowledge proofs, reducing the complexity of deployment and maintenance.
Align Ethereum more closely : Native Rollups automatically inherit the upgrade of Ethereum , ensuring consistency and improving interoperability. At the same time, they will also benefit from Ethereum's future quantum security mechanism.
More efficient ZK proof : Native Rollups can efficiently bundle multiple zero-knowledge proofs , reducing the verification cost of ZK Rollups.
Suitable for new application chains : For decentralized applications that want to obtain the highest level of security , they can choose to be "native" to avoid redeveloping EVMs, but simply add their own special features.
If a Rollup is both native and based - that is, Ethereum manages transaction sorting and transaction verification at the same time, then it becomes a "ultrasonic Rollup". This Rollup makes full use of Ethereum 's security and is fully in line with Ethereum's long-term expansion roadmap, and is the most ideal Rollup form.

Issue that native Rollups cannot be solved
Although native Rollups solve governance and security challenges, they do not completely eliminate Ethereum's expansion restrictions and even impose additional constraints on ecological diversity in some ways.
The L1 Gas limit remains : the Gas cap on the Ethereum mainnet is still valid, and if each transaction has to be re-execute on L1, it may result in inefficiency. Therefore, additional combinations of zero-knowledge or Optimistic solutions are required to scale more efficiently.
Lack of support for diverse virtual machines : Native Rollups must strictly adhere to the EVM model , which means they cannot support other emerging virtual machine architectures such as SVM or MoveVM , which are gradually attracting market attention.
Increased data availability cost : Native Rollups-dependent EXECUTE precompilation significantly increases data availability costs , which can result in a 5–10-fold increase in L2 overhead, affecting its economic viability.
In addition, many Rollups are currently only compatible with EVM , but are not exactly equivalent to EVM. Converting to native Rollup requires large-scale architectural adjustments and is difficult. Native Rollups may not support certain custom transaction formats or Gas calculations , such as the mode where users' Gas fees are subsidized by applications or wallets. This brings some trade-offs in user experience (UX).
Take an important step
Although native Rollups is a major advancement on the Ethereum expansion roadmap, not all Rollups will adopt this model . On the contrary, industry insiders (such as Cyber Fund's Dogan) believe that the Rollup ecosystem may form three main types in the future:
-
Enterprise-level Rollups: customized and controlled by the enterprise to meet their specific needs, such as transaction sorting, privacy protection , etc.
-
Performance-optimized Rollups: Increase transaction speed and reduce costs through alternative data availability solutions (such as EigenDA) .
-
Native Rollups: Fully integrated into Ethereum, inherit L1 security, and automatically upgrade without external governance or independent proof mechanisms.
This classification method not only encourages the coexistence of multiple scaling solutions , but also allows different Rollups to innovate technologically while retaining Ethereum’s trust and security. Justin Drake expects the first batch of native Rollups to go live next year . However, to achieve full technological maturity (such as native support for ZK proofs and improving L1 Gas restrictions ), broader community coordination and verification are still needed, and full implementation may be further delayed to the further future.
While native Rollups may not be the only solution for Ethereum expansion , they offer a simpler, safer, and deeper integration with Ethereum. Ultimately, native Rollups provides a clear direction for L2s to always keep pace with the Ethereum main chain , thus bringing a smoother and safer experience to users, developers and the entire ecosystem.


 panewslab
panewslab