Analyze Lumoz: Decentralized computing infrastructure for the AI, ZK and RaaS era

Reprinted from panewslab
01/24/2025·5MMain points
- Advantages and Challenges of ZKP : ZKP is a powerful blockchain technology that solves privacy and scalability issues. However, it requires a large amount of computing resources, resulting in high computational costs and risks of centralization.
- The power of decentralized modular computing layer : In order to solve the problems of ZKP, Lumoz uses modular infrastructure to aggregate network computing capabilities and accelerate ZK technology through ZK-RaaS.
- AI and TEE are reshaping future innovation : Lumoz enables technology applications beyond ZK. By providing high-performance AI computing and using TEE and DROT to protect the AI process, it enhances data security and result verification, and promotes the integration of Web3 and AI.
1. Introduction
Vitalik Buterin's defensive accelerationism (d/acc) philosophy emphasizes two key principles. First, resist the concentration of power by accelerating technological progress, and second, advocate the development of decentralization. Blockchain technology is the embodiment of this concept. It can decentralize power and prevent centralization.
However, blockchain technology also has some drawbacks. As the network scales, decentralized systems can slow down, limiting their performance. At the same time, the amount of data storage increases exponentially, resulting in insufficient scalability. Although on-chain transparency provides traceability, it also reduces user privacy protection.
Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP), an emerging solution to blockchain privacy challenges, allows users to prove the authenticity of a fact without sharing actual information. For example, users can prove they are of voting age without revealing their date of birth, a method that both verifies facts and protects sensitive information.
When zero-knowledge proofs are applied to a blockchain, the network is able to verify the validity of a transaction without disclosing private information such as the amount transferred or the person transferring it. This enables users to protect their personal information while ensuring the trustworthiness of the system.
ZKP technology solves two main challenges in blockchain. The first is the issue of privacy. ZKP can verify the validity of transactions without revealing detailed information such as the amount or the identity of the trader. The second is scalability. The blockchain can perform calculations externally and use ZKP to verify the results, thereby reducing the computational burden of the network and improving efficiency.
ZKP excels in Layer 2 scaling solutions. Layer2 processes transactions off-chain and submits the results and proof of their correct execution to the Ethereum mainnet, which greatly improves processing speed and scalability while maintaining the integrity of the system. As an important tool to promote decentralized technology, ZKP effectively solves the issues of privacy and scalability.
2. Challenges of ZK implementation: high cost, centralization risk
The complex cryptographic operations required to generate zero-knowledge proofs require significant computing power, similar to the computational requirements of Bitcoin mining or training large artificial intelligence models.
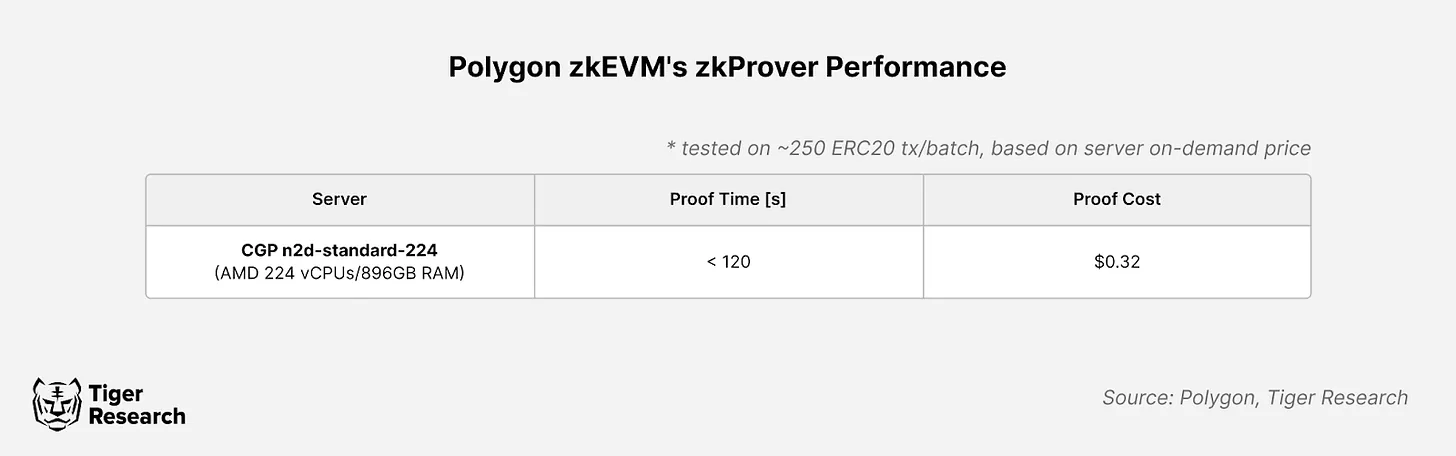
These high-performance computing requirements are particularly prominent in Layer 2 expansion solutions such as ZK-Rollups. For example, using a server with an AMD 224 vCPU and 896 GB RAM, generating ZKP for a batch of 250 ERC-20 transactions on Polygon zkEVM takes approximately 2 minutes and costs approximately $0.32 to operate, or $6,909 on a monthly basis. In comparison, a typical web server requires only 4 vCPUs and 8 GB RAM.
These high hardware requirements pose two main challenges to ZKP technology. First, only a small number of high-performance machines can generate these proofs, which defeats the goal of spreading control to more users. This dependency makes achieving true decentralization difficult. Secondly, limitations in computing resources also affect the size of the proof batch that can be processed, thereby reducing the efficiency and scalability of ZKP technology.
To overcome these challenges, ZKP infrastructure needs to become more efficient and accessible. Reducing technical complexity and lowering barriers to entry are keys to expanding the ZKP ecosystem. Lumoz addresses these issues through its modular computing infrastructure and decentralized prover network, aiming to solve the blockchain trilemma between decentralization, scalability, and security.
3. Lumoz: Lighting the road to zk/acc
Lumoz is a modular computing layer for ZK, AI and RaaS, providing powerful computing power and verification services for cross-chain ZK and AI applications. Network participants share computing power thereby reducing reliance on centralization and achieving true decentralization. In addition, Lumoz's ZK-RaaS platform lowers the threshold for ZK-Rollups and accelerates the development of ZK technology through zk/acc.
Source: Lumoz
Lumoz's technology is recognized by the market. More than 20 Layer2 including Carv, Merlin Chain, ZKFair, Ultiverse, Matr1x and Uxlink all use Lumoz infrastructure. In early 2024, Lumoz received $14 million in financing from well-known investors such as OKX Ventures, Hashkey Capital, Kucoin Ventures, and Polygon.
3.1. Lumoz Chain, ZK modular computing layer
Source: Lumoz
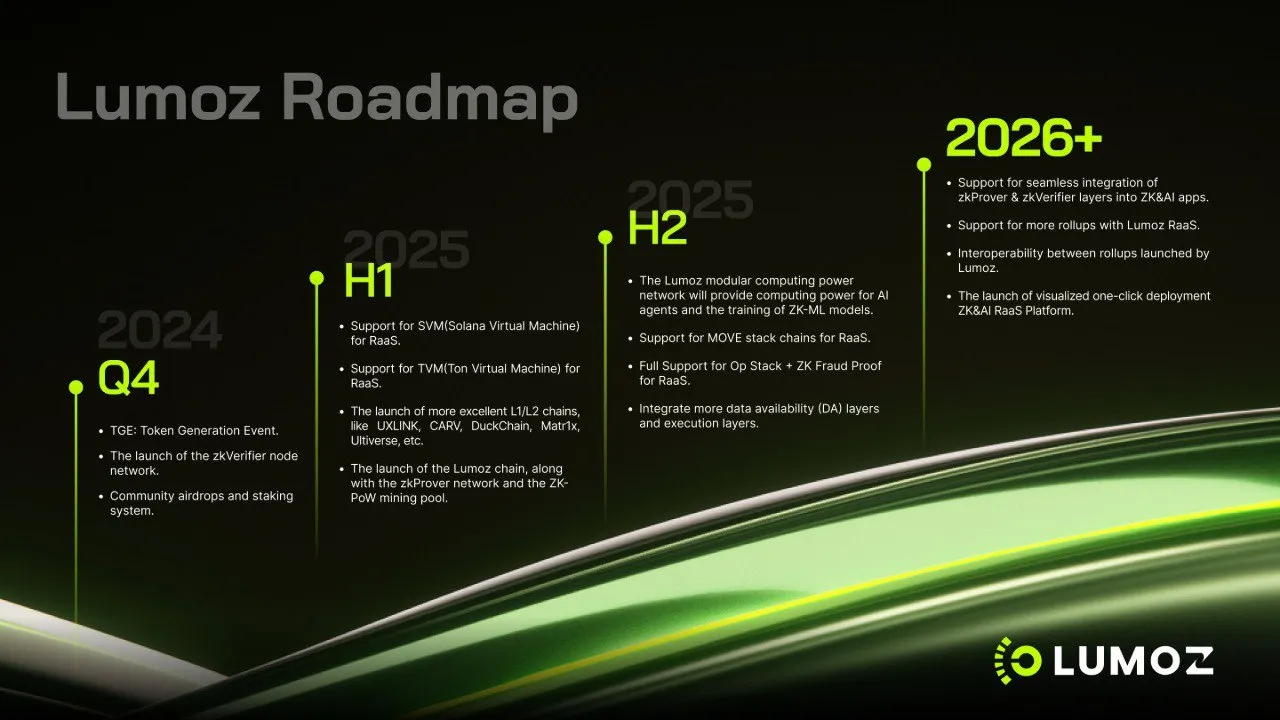
Lumoz Chain will launch the mainnet in the first quarter of 2025. It aims to create a decentralized physical infrastructure network (DePIN) for high-performance computing tasks, including ZKP technology. Lumoz offers 1) modular architecture, 2) hybrid consensus model, and 3) optimized performance for intensive computing. This will make zero-knowledge proofs more affordable and accessible while helping blockchain networks handle more users without relying on central control.
3.1.1. Modular architecture
Lumoz features a modular design that allows for customization for each project. Just like building with blocks - projects can select and arrange the required parts. Projects can configure their infrastructure according to specific needs. Each module operates independently, ensuring efficient system configuration. This approach reduces integration complexity and improves overall system efficiency.
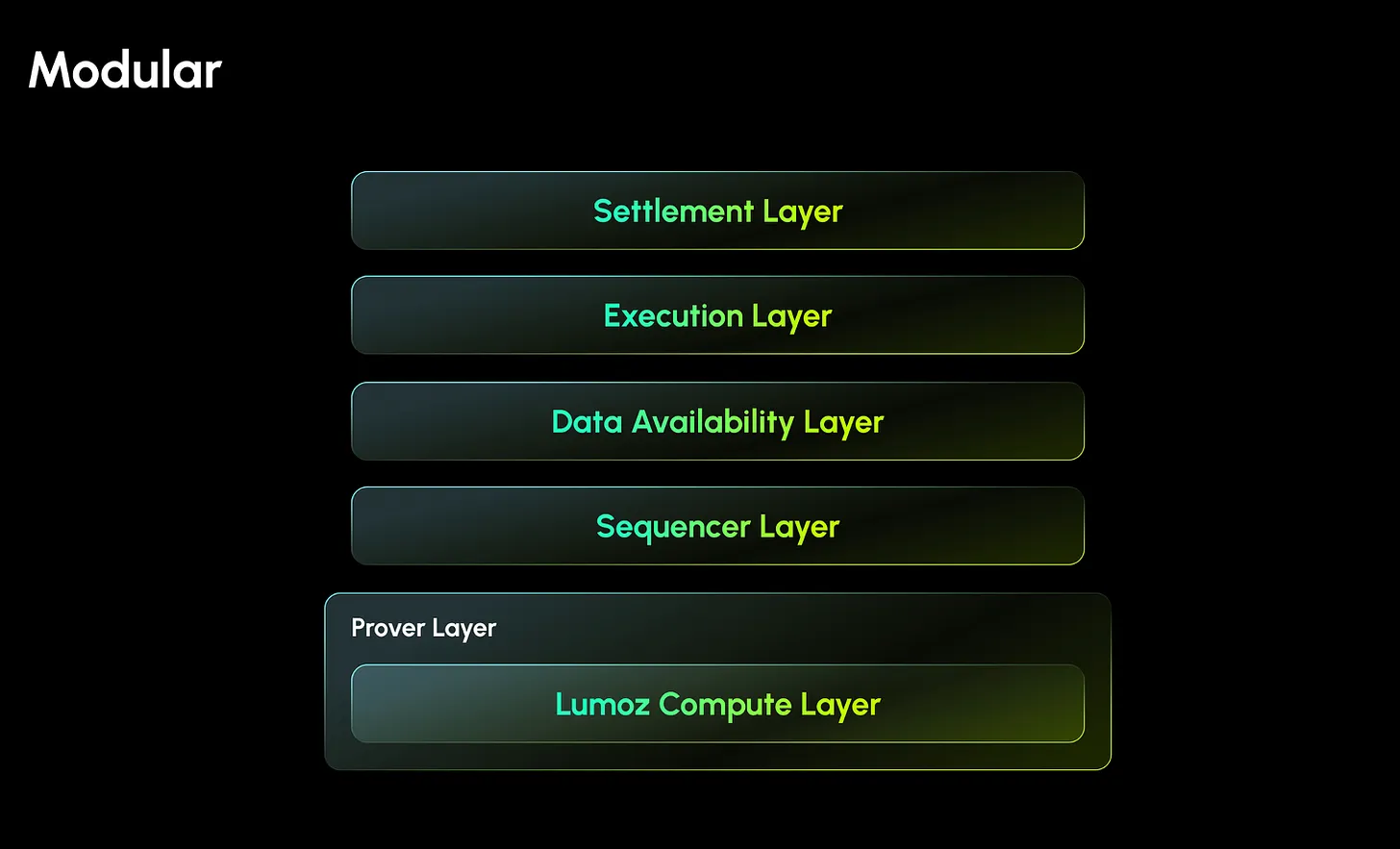
Source: Lumoz
Lumoz's modular construction offers unlimited applications. For example, it can be used as a proof layer to generate proofs for key ZK-Rollups such as polygon zkEVM, zkSync, and Scroll. It can also serve as a computing layer to handle AI model training and inference. This design ensures flexibility and supports the integration of new technologies and services.
3.1.2. Hybrid consensus mechanism
Lumoz uses a hybrid architecture to manage the generation and verification of ZKP. Its core is two components: zkProver to generate ZKP and zkVerifier to verify ZKP.
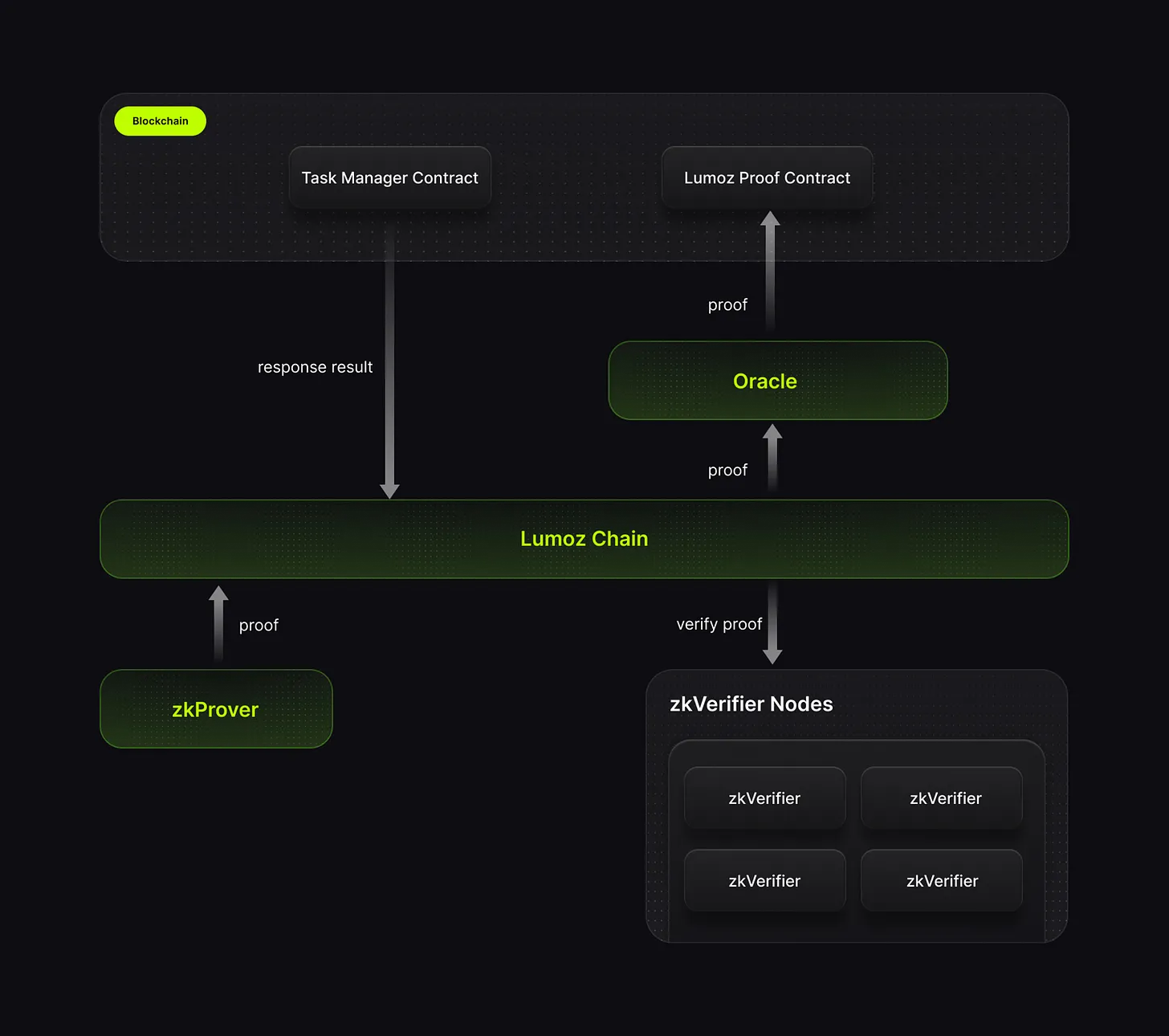
Source: Lumoz
zkProver adopts a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus structure. ZKP generation requires high-performance computing. Any individual or organization with GPU/CPU resources can join and use their own computing power to generate ZKP and perform other tasks.
zkVerifier is a verification network based on Proof of Stake (PoS). It consists of 100,000 zkVerifier nodes issued through the sale of node licenses. License holders can run these nodes as dedicated clients or delegate them to others. zkVerifier ensures the trustworthiness of the network by verifying the proofs generated by zkProver.
This hybrid structure uses a consensus mechanism appropriate to the role of each component. PoW handles high-performance computing generated by ZKP. PoS manages verification tasks. This approach reduces reliance on centralized high-performance equipment and instead ensures efficient verification through a distributed network of provers. Therefore, the core elements of ZKP, proof generation and verification, are efficiently processed in a decentralized manner.
3.1.3. Optimizing performance
Lumoz continues to improve performance through ongoing research and various technological advancements. Notably, it optimizes the process of proof generation and verification.
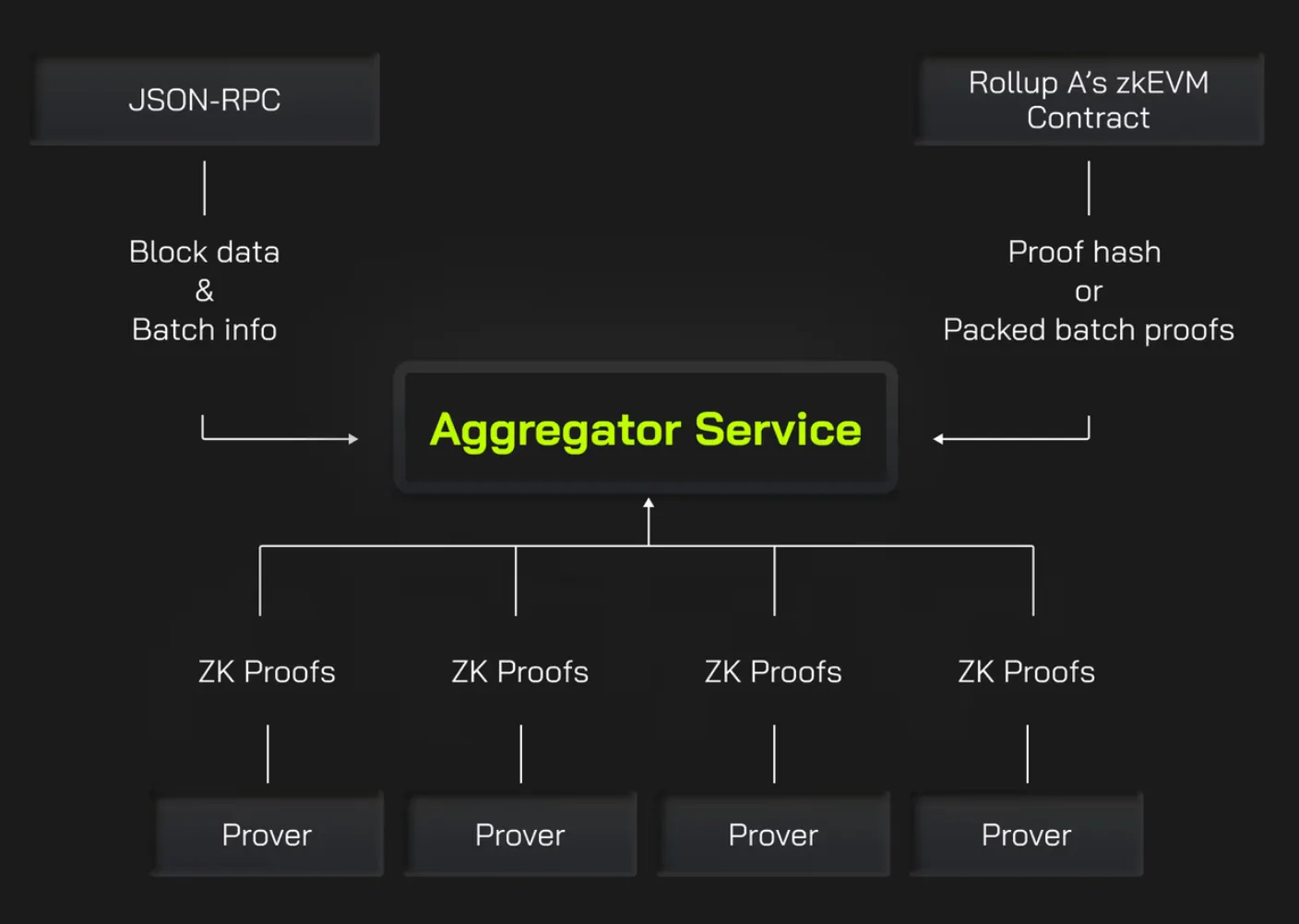
Source: Lumoz
Lumoz improves the efficiency of ZKP generation and verification through aggregator services. The service is able to process multiple proofs in parallel and merge them into a single proof. The traditional method is to process each proof independently, resulting in inefficiency due to repeated calculations. Lumoz eliminates this bottleneck and significantly increases processing speed.
Additionally, Lumoz has optimized the verification process. Historically, proofs required two separate steps: the prover submitted a proof hash containing their identity and work information in the first step, and submitted their ZKP in the second step. Lumoz simplifies this process by combining identity, work information, and ZKP into a single contract. This improvement cuts the number of on-chain transactions in half, reduces gas costs by 50-60%, and shortens verification times.
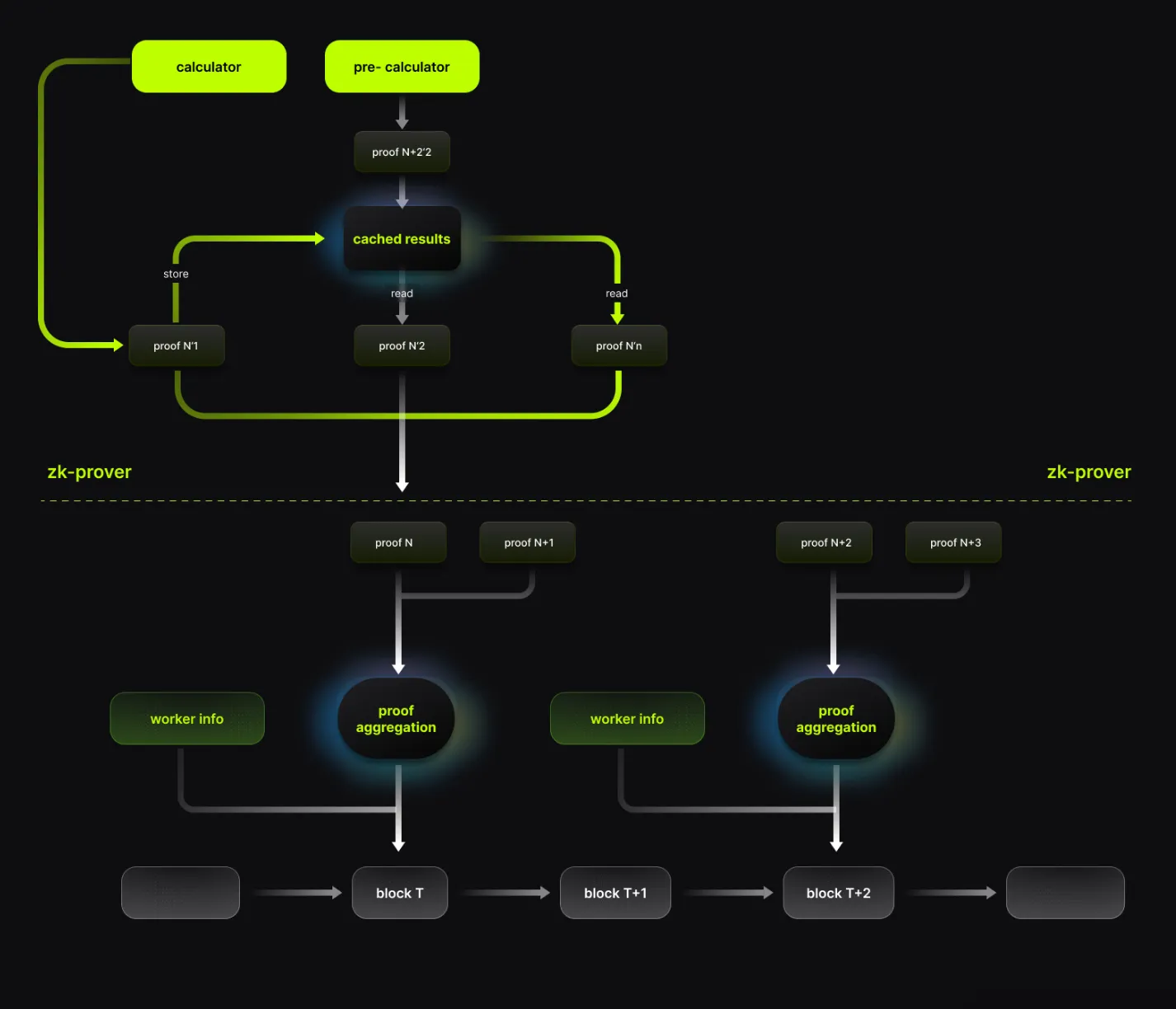
Source: Lumoz
Lumoz further optimizes the proof generation process. First, it breaks large tasks into smaller tasks that can be handled individually. Then, when parts of different calculations are the same, Lumoz saves and reuses the cached results instead of recalculating them. Additionally, when computers in the network are not busy, they prepare calculations that may be needed soon rather than waiting for new tasks to arrive. These changes increase proof generation speed by 25%. They also significantly improve cost efficiency and processing performance.
3.2. zk-RaaS platform
Lumoz provides RaaS services to help developers build ZK-Rollup-based L2 chains without complex infrastructure. The service simplifies the process just as AWS simplifies cloud computing.
RaaS provides the infrastructure needed to build and run a blockchain using Rollup technology. Its intuitive interface simplifies development and operation. This improves user convenience and efficiency.

zk Moat & Castle by Lumoz, source: Tiger Research
Lumoz's core strength comes from its proprietary network. The network includes a decentralized computing layer, zkProver and zkVerifier. It is specifically designed to handle the complex calculations required for ZK-Rollups – a way to quickly process large numbers of blockchain transactions. This feature differentiates Lumoz from other RaaS services that do not have a dedicated computing network. The decentralized computing layer is Lumoz’s unique moat, enhancing its competitive advantage in the ecosystem.
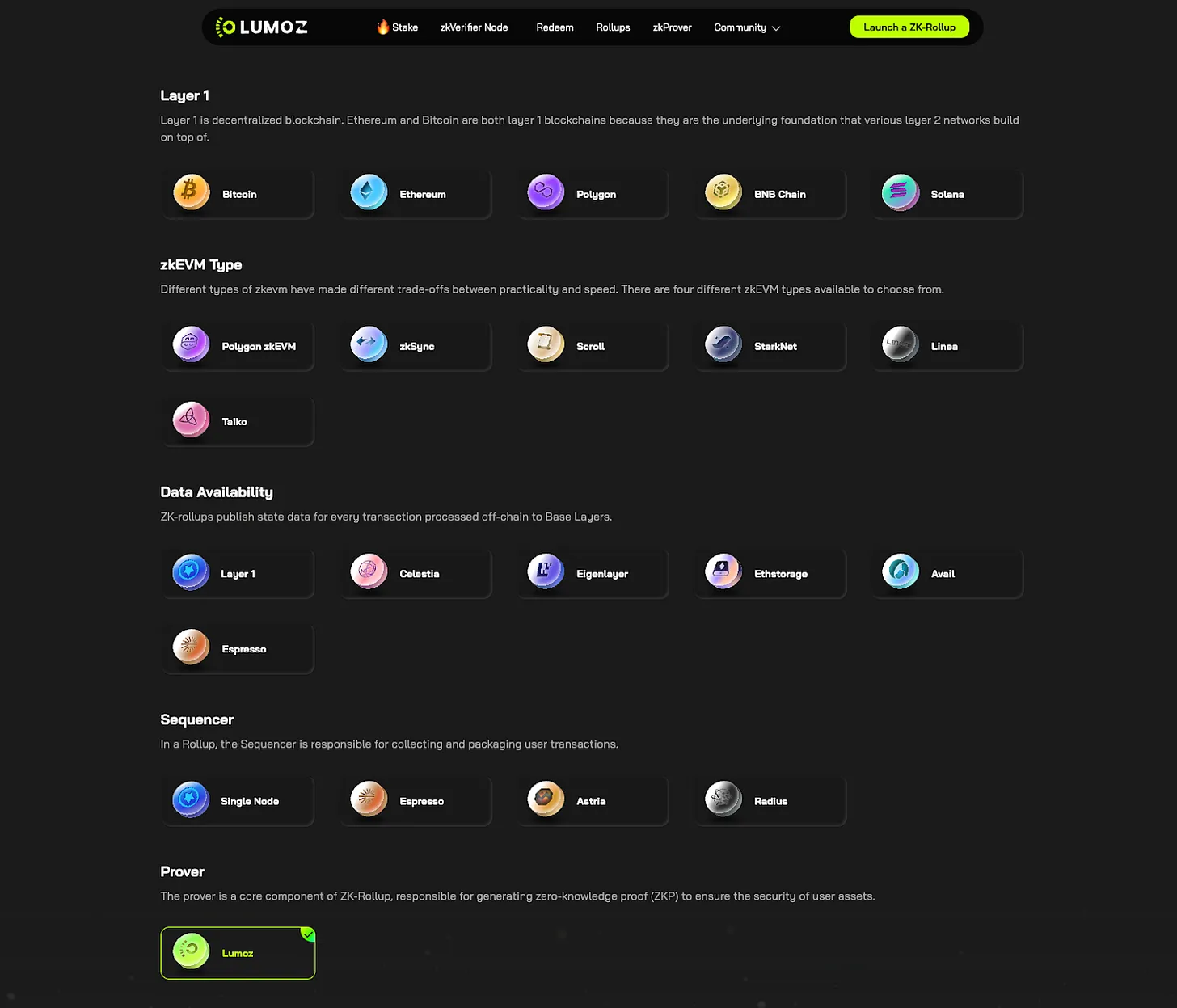
Lumoz Rollup Launchbase, Source: Lumoz
Lumoz provides an environment to connect and extend various chains and ZK-Rollups. Developers can build custom chains without having to deal with complex technical setup, making it easier to design and run the system.
Lumos' Rollup Launchbase not only supports major blockchains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon and Solana, but also supports zkEVM types such as Polygon zkEVM, zkSync and Scroll, making it easier for developers to build ZK-Rollup solutions.
Lumoz also supports Native Cross-Rollup Communication (NCRC), enabling efficient encrypted transmission and interaction across Rollups. This feature uses the Rollup System Contract (RSC) deployed on the main chain. RSC tracks information and updates between different Rollups, enabling fast and secure transfers and interactions while ensuring the security of all assets.
By the first half of 2025, Lumoz plans to support major L1 chains and will support EVM-based ZK-Rollups, including Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) and Ton Virtual Machine (TVM). This expansion meets the growing demand for ZK technology and strengthens Lumoz's position as a premier provider of ZK infrastructure.
4. Lumoz’s vision for the future
Lumoz's distributed computer network not only handles complex calculations efficiently, it can also meet growing demands while maintaining reliability. While it currently focuses on zero-knowledge proofs, this robust infrastructure can aid in the development of other advanced technologies in the future.
4.1. ETH 3.0: Make Ethereum great again
The vision of Ethereum 3.0 is to enhance the scalability, security and efficiency of the network through Snarkification and Beam Chain. Snarkification speeds up transaction processing and improves data security by introducing ZKP technology into the consensus layer and execution layer of Ethereum.
To achieve this, powerful computing resources are required. Lumoz provides this through its modular computing layer. It uses a hybrid consensus mechanism that combines PoW and PoS. PoW provides computing power for ZKP generation, while PoS handles verification tasks. This setup enables high-performance computing in a decentralized manner.
This infrastructure helps Lumoz optimize validators and speed up block generation, which is the main goal of BeamChain. The network can increase processing efficiency while remaining decentralized. By supporting these improvements, Lumoz plays an important role in helping Ethereum grow and progress.
**4.2. Building computing infrastructure in the artificial intelligence
era**
Lumoz will become the key infrastructure to promote the development of AI technology. Currently, most AI systems are controlled by large technology companies. Lumoz's distributed computer network aims to change that by making AI more accessible to everyone. This can help create an AI ecosystem:
- Give users more control
- Making AI technology easier and cheaper to acquire
- Operations are fairer and more open
This approach could lead to a new class of artificial intelligence systems that are not controlled by a handful of companies.
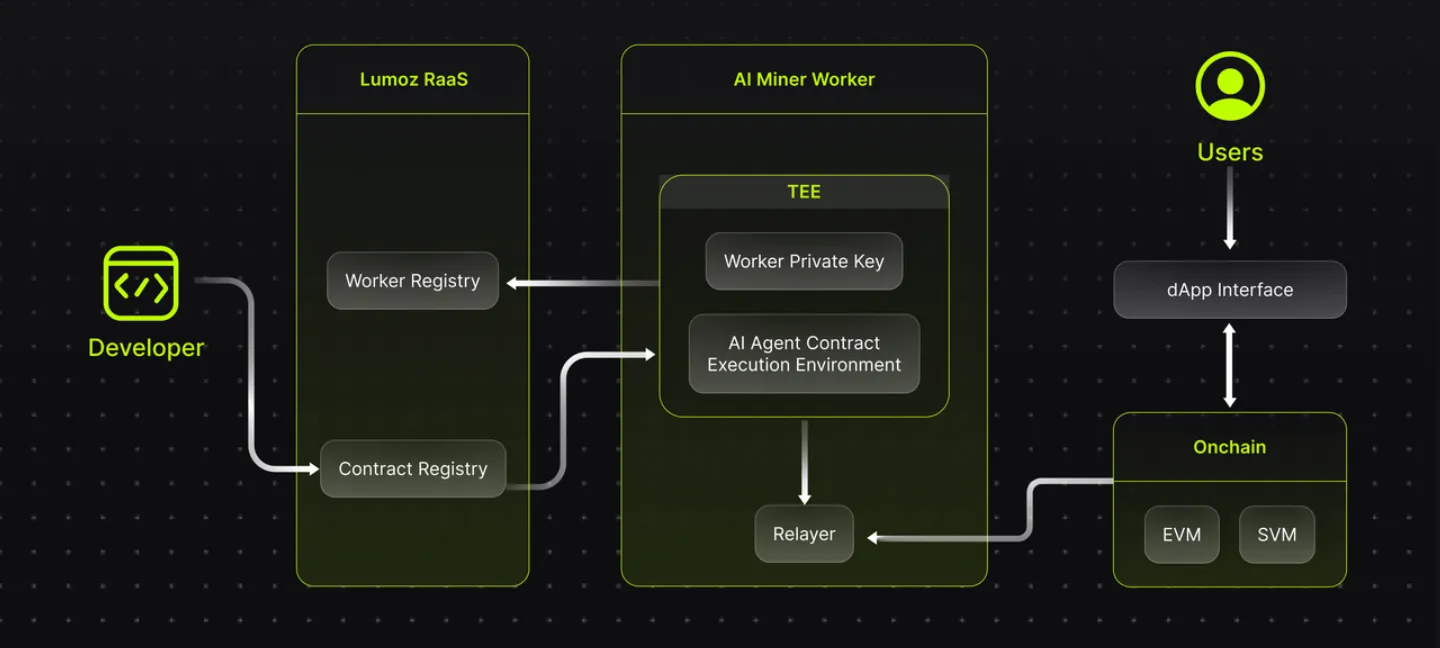
Source: Lumoz
Lumoz uses two technologies to make AI systems more secure and reliable: DROT using distributed computing and Trusted Execution Environment (TEE). AI agents can act autonomously, but currently most operate in untrusted environments, which limits their security and transparency. In these environments, protecting sensitive information and validating results is difficult, reducing the reliability of decisions.
DROT systems keep important security keys in the hardware and use a verification process called remote attestation to ensure everything is running as expected. This improves data security and execution integrity while increasing the verifiability of results. With these security measures in place, AI agents can work more safely and reliably. This brings together the best features of Web3 and AI technologies to help create next-generation AI systems that are both secure and transparent.
5. Conclusion
Lumoz has made significant progress, attracting over 3 million users on its test network and supporting over 50 major ecosystem projects. The platform provides services to more than 20 L2 chains and continues to expand its ecosystem through cooperation with UXLINK, CARV, Merlin Chain, Matr1x, Ultiverse, ZKFair, etc.
Lumoz doesn't just rest on its laurels, it also solves a core challenge in Web3. By employing zero-knowledge proof technology and distributed computing, it improves the speed and transparency of blockchain networks. The combination of this platform with artificial intelligence creates new opportunities for future growth. This approach adheres to the basic principles of Web3 distributed control while demonstrating how zero-knowledge proof technology can be combined with artificial intelligence to drive the development of the entire ecosystem.
As new technologies such as Ethereum's BeamChain increase the demand for computing power, the demand for processing power is expected to rise significantly. This increase may be similar to the increased demand for computer performance in the early days of Bitcoin and Ethereum mining. Lumoz has the potential to become an important part of blockchain and artificial intelligence development by providing the necessary infrastructure to meet these growing computing needs.
Additionally, Lumoz supports multiple technology environments, including Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) and Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE). These tools lay a stronger foundation for the future of blockchain and artificial intelligence development. Considering how Lumoz combines these capabilities with other technologies, its growth potential and impact on the industry will be of great interest.


 chaincatcher
chaincatcher