Understand ERC-7786: The Ethereum ecosystem has made great strides into the era of great unity?

転載元: jinse
06/18/2025·5DThe Ethereum ecosystem may soon enter the era of unification from the stage of the "Spring and Autumn Period and Warring States Period" melee.
The key is the ongoing ERC-7786, which is trying to set a common cross-chain communication "interface specification" for Ethereum, thereby integrating various messaging standards into a unified API, and realizing mutual communication between different blockchain network smart contracts in the Ethereum ecosystem.
As early as April 15, Ethereum Foundation member joshrudolf.eth publicly emphasized that "cross-chain messaging is one of the key elements in solving the Ethereum cross-chain user experience problem."
So what exactly is ERC-7786, what problems to solve, and why is it important? This article will take you to understand this new standard that deserves attention from all Ethereum users.
Ethereum requires unified cross-chain communication protocol
As we all know, from the initial multi-chain concept of Cosmos and Polkadot to the Rollup prosperity in the Ethereum L2 era, especially the great development of application chains such as OP Stack, Arbitrum Nova, and Starknet, liquidity has become increasingly scattered on Ethereum and L2.
According to incomplete statistics from L2BEAT, there are as many as hundreds of Ethereum L2 in a broad sense, which leads to a long-standing issue - the extreme fragmentation of liquidity.
You should know that even though they are based on the Ethereum ecosystem, different L2s do not communicate with each other. If users want to transfer assets from Arbitrum to Starknet, or to conduct contract interactions across different L2s, they can only use cross-chain bridges or cross-chain messaging protocols to achieve secure interaction between contracts, users and assets between multiple networks.
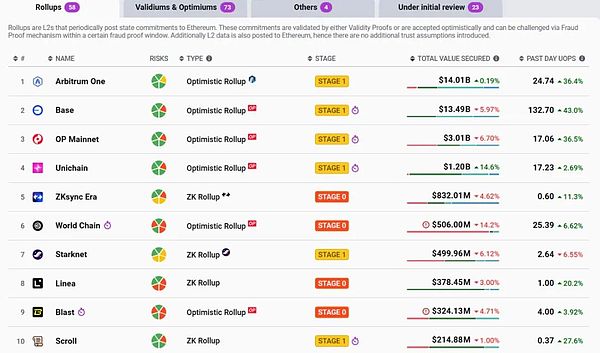
Source: L2BEAT
This not only makes users pay more friction costs due to cross-chain obstacles every year, but more importantly, the synergistic effect of the Ethereum ecosystem, especially the L2, has been severely weakened. Although many protocols have implemented inter-chain communication functions, each protocol has its own interface, calling method and security model. Developers are almost unable to reuse code or interface logic between different protocols, which directly leads to repeated "making wheels" and high operation and maintenance costs, and extremely fragmented user experience.
Therefore, the proposal of ERC-7786 is to break this fragmented fragmented ecosystem and provide a unified standard interface for all inter-chain communication protocols, so that DApps can communicate securely with any chain through the same "gateway" without binding a specific protocol:
The standard was developed by OpenZeppelin and is supported by multiple cross- chain and modular projects including the Ethereum Foundation and Axelar. As a unified cross-chain messaging interface standard for DApps, it aims to standardize the common interface for decentralized applications (DApps) for securely sending and receiving messages across multiple blockchains.

Source: erc7786.org
ERC-7786: "Unified Interface" of Cross-chain Communication
If you summarize ERC-7786 in one sentence, it is like the "ERC-20" in the field of cross-chain communications.
Just as ERC-20 provides a standard interface for tokens and ERC-721 defines a common specification for NFT, ERC-7786 also tries to establish a unified and universal "communication socket" for cross-chain messaging - you can compare it to the "USB standard" in the Web3 world. As long as you access the specification interface, any protocol can be plug-and-play.
The following figure presents the core components and processes of ERC-7786, showing how to send and receive messages between different blockchains through standardized interfaces. One of the ERC-7786 messages includes four basic elements:
-
Sender: Use CAIP-10 format identification (such as eip155:1:0xabc...)
-
Receiver: Also identify the target address for CAIP-10
-
Payload: arbitrary execution of data (bytes)
-
Attributes: Additional parameters, such as Gas limit, processing priority, etc., expressed in function signature form (such as minGasLimit(uint256))
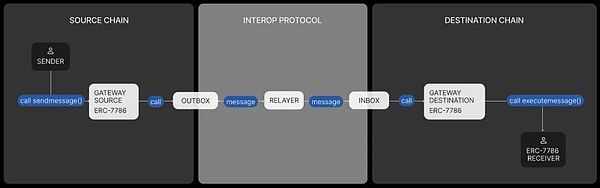
Source: erc7786.org
Among them, sendMessage() is used to initiate messages on chain A, and executeMessage() is used to receive and execute chain B. This "send-receive closed loop" forms the basic logic of cross-chain communication, and also makes DApps only need to encapsulate the standard interface at one time to be compatible with multiple cross-chain protocol modules at the same time, realizing "protocol decoupling + communication freedom" in the true sense.
At present, ERC-7786 has also announced that the interface is complete and is waiting for the final merger of the binary interoperable address specification (i.e., unified address encoding). In the future, a new "Gas Sponsorship" extension is also planned to add, so that users can prepay Gas by third parties when executing transactions on the target chain, thereby optimizing the user experience of inter-chain interaction.
More importantly, the ERC-7786 design supports modular adaptation, and developers can build Adapters for existing mainstream cross-chain protocols (such as Axelar, LayerZero, Wormhole, etc.), which can quickly be compatible with the ERC-7786 standard interface without reconstructing logic.
This means that even if users, liquidity and applications are distributed on multiple L2 or heterogeneous chains, DApps can use ERC-7786 to build native cross-chain calling capabilities without binding specific bridge protocols or relying on cumbersome UI switching, which can greatly improve the overall experience and reduce integration complexity.
It is worth mentioning that the Attributes of ERC-7786 also allows access to extended functions of different cross-chain protocols, such as verification logic, state proof, limit control, etc., without affecting the standard main process, which leaves a highly flexible interface space for the evolution of middleware and verification mechanisms.
From this perspective, the significance of ERC-7786 is no longer just "compatible with multiple cross-chain protocols", but also represents that the Web3 multi-chain architecture is moving from "cross-chain deployment" to a new era of "native interoperability".
What can ERC-7786 bring?
Because of this, ERC-7786 is widely regarded as an important infrastructure to promote Ethereum and multi-chain ecosystems toward higher interoperability. It not only breaks through long-standing protocol barriers, but also lays a unified infrastructure foundation for future cross-chain function expansion, verification mechanism upgrades, and multi-chain collaboration.
From the perspective of actual implementation, the value brought by ERC-7786 can be attributed to two core beneficiaries - developers and end users:
-
For developers, they can deploy multiple chains by just one development, without having to repeatedly adapt to different protocols, and switch to cross-chain backends at any time to improve security and maintainability, and support more customized attributes and function expansion (such as Gas, status verification, etc.);
-
For users, there is no longer a need to switch bridges and UI back and forth between Arbitrum and zkSync. Click confirm to complete the link skipping operation. From a perceptual perspective, the boundary between chains is becoming blurred, as natural as using a chain;
At present, ERC-7786 is constantly promoting the implementation of the ecosystem. According to publicly disclosed information, in the next 3 to 6 months, ERC-7786 will successively release standard adapters for mainstream protocols to promote more DApps, bridges, and verification middleware to integrate this standard, forming a truly Web3 cross-chain infrastructure.
It is worth mentioning that on June 13, Axelar developers Interop Labs and OpenZeppelin also jointly launched OpenBridge, an open source framework built on ERC-7786. This tool will allow developers to access multiple bridge protocols at one time, further improving construction efficiency and protocol redundancy, and facilitating developers to connect with multiple interoperable protocols at one time.

Source: Axelar
From a more macro perspective, ERC-7786 is more important than the specification of technical interfaces. It is more like opening up an "orderly interconnection path" for the current chaotic multi-chain ecological pattern:
This has blurred the boundaries of the "chain" in the pan-Ethereum ecosystem, laying a crucial foreshadowing for the evolution of Web3 user experience in the true sense.
Written at the end
Looking back at the development trend of Ethereum, from the composability of smart contracts to the rapid development of modular infrastructure, to the generalization of L2 and the exclusive chain trend, "cross-chain interoperability" has become a necessary condition for the next stage of explosion.
The significance of ERC-7786 is not only to make cross-chain more convenient, but also to try to establish unified norms for "multi-chain collaboration" from the root to fight "entropy increase", which can not only further promote the "unified" process of on-chain liquidity, but also promote the maturity of multi-chain ecology.
As for whether ERC-7786 can lead Ethereum to reach the critical point of transformation, it still needs to be observed.



