Discussing AI Layer1: Finding the Fertile Land of DeAI on the Chain

転載元: chaincatcher
06/11/2025·17DOriginal title: " Biteye & PANews jointly releases AI Layer 1 Research Report: Finding the Fertile Land of DeAI on the Chain "
Original author: @anci_hu49074 (Biteye), @Jesse_meta (Biteye), @lviswang (Biteye), @0xjacobzhao (Biteye), @bz1022911 (PANews)
Overview
background
In recent years, leading technology companies such as OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and Meta have continuously promoted the rapid development of the Big Language Model (LLM). LLM has shown unprecedented abilities in all walks of life, greatly expanding human imagination space, and even showing the potential to replace human labor in some scenarios. However, the core of these technologies is firmly in the hands of a few centralized technology giants. With strong capital and control over high computing resources, these companies have established insurmountable barriers, making it difficult for most developers and innovation teams to compete with.
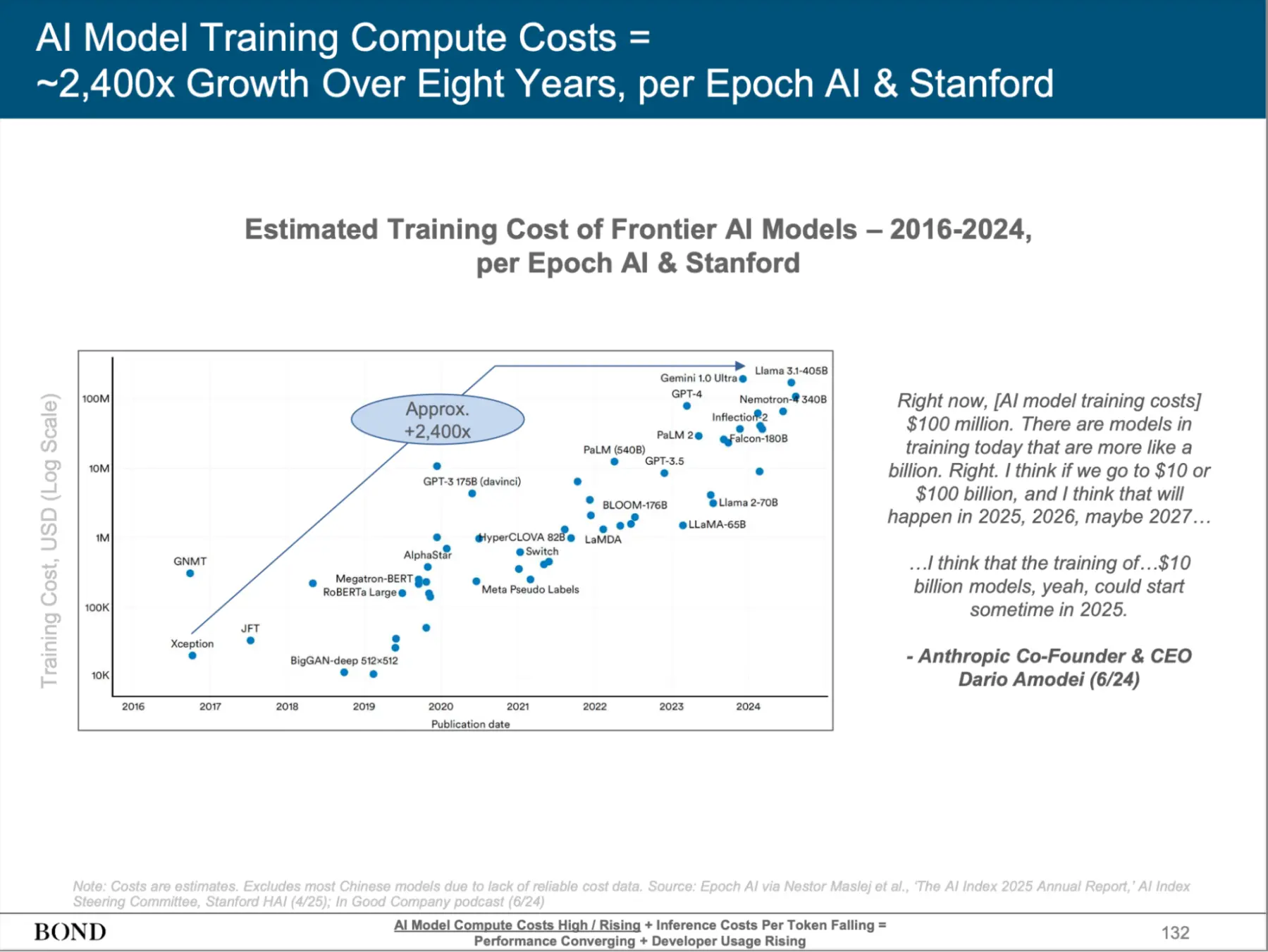 Source: BONDAI Trend Analysis Report
Source: BONDAI Trend Analysis Report
At the same time, in the early stages of rapid evolution of AI, public opinion often focused on breakthroughs and convenience brought by technology, but the focus on core issues such as privacy protection, transparency, and security is relatively insufficient. In the long run, these issues will profoundly affect the healthy development and social acceptance of the AI industry. If it cannot be properly resolved, the dispute over whether AI is "good" or "evil" will become increasingly prominent, and centralized giants, driven by profit-seeking instinct, often lack sufficient motivation to actively respond to these challenges.
With its decentralized, transparent and censor-resistant nature, blockchain technology provides new possibilities for the sustainable development of the AI industry. At present, many "Web3 AI" applications have emerged on mainstream blockchains such as Solana and Base. However, in-depth analysis shows that these projects still have many problems: on the one hand, the degree of decentralization is limited, and key links and infrastructure still rely on centralized cloud services. The meme attributes are too heavy and it is difficult to support a truly open ecosystem; on-chain AI is still limited in model capabilities, data utilization and application scenarios, and the depth and breadth of innovation need to be improved.
To truly realize the vision of decentralized AI, enable blockchains to safely, efficiently and democratically carry large-scale AI applications, and compete with centralized solutions in terms of performance, we need to design a Layer1 blockchain tailored for AI. This will provide a solid foundation for AI's open innovation, governance democracy and data security, and promote the prosperity and development of the decentralized AI ecosystem.
The core features of AI Layer 1
As a blockchain tailor-made for AI applications, its underlying architecture and performance design closely revolve around the needs of AI tasks, aiming to efficiently support the sustainable development and prosperity of the AI ecosystem on the chain. Specifically, AI Layer 1 should have the following core abilities:
Efficient incentive and decentralized consensus mechanism
The core of AI Layer 1 is to build an open shared network of computing power, storage and other resources. Unlike traditional blockchain nodes that mainly focus on account bookkeeping, AI Layer 1 nodes need to undertake more complex tasks. They not only need to provide computing power and complete the training and inference of AI models, but also need to contribute diversified resources such as storage, data, and bandwidth, thereby breaking the monopoly of centralized giants on AI infrastructure. This puts higher requirements on the underlying consensus and incentive mechanism: AI Layer 1 must be able to accurately evaluate, motivate and verify the actual contribution of nodes in AI inference, training and other tasks, so as to achieve network security and efficient allocation of resources. Only in this way can the stability and prosperity of the network be ensured and the overall computing power cost can be effectively reduced.
Excellent high performance and heterogeneous task support capabilities
AI tasks, especially LLM training and reasoning, puts forward extremely high requirements on computing performance and parallel processing capabilities. Furthermore, the on-chain AI ecosystem often needs to support diversified and heterogeneous task types, including different model structures, data processing, inference, storage and other diverse scenarios. AI Layer 1 must be deeply optimized for high throughput, low latency and elastic parallelism in the underlying architecture, and preset native support capabilities for heterogeneous computing resources to ensure that all kinds of AI tasks can run efficiently and achieve smooth expansion from "single task" to "complex and diverse ecosystem".
Verification and trustworthy output guarantee
AI Layer 1 not only prevents security risks such as model evil and data tampering, but also ensures the verifiability and alignment of AI output results from the underlying mechanism. Through the integration of cutting-edge technologies such as trusted execution environment (TEE), zero-knowledge proof (ZK), multi-party secure computing (MPC), etc., the platform can enable each model inference, training and data processing to be independently verified, ensuring the fairness and transparency of the AI system. At the same time, this verifiability can also help users clarify the logic and basis of AI output, realize "what you get is what you want", and enhance users' trust and satisfaction with AI products.
Data privacy protection
AI applications often involve user-sensitive data, and data privacy protection is particularly critical in the fields of finance, medical care, social networking, etc. While ensuring verifiability, AI Layer 1 should use encryption-based data processing technology, privacy computing protocols and data permission management to ensure the security of data in the entire process of inference, training and storage, effectively prevent data leakage and abuse, and eliminate users' worries about data security.
Strong ecological carrying and development support capabilities
As the Layer 1 infrastructure native to AI, the platform must not only have technological leadership, but also provide developers, node operators, AI service providers and other ecological participants with complete development tools, integrated SDK, operation and maintenance support and incentive mechanisms. By continuously optimizing platform availability and developer experience, we will promote the implementation of rich and diverse AI native applications and achieve the continuous prosperity of the decentralized AI ecosystem.
Based on the above background and expectations, this article will introduce in detail six AI Layer1 representative projects including Sentient, Sahara AI, Ritual, Gensyn, Bittensor and 0G. It systematically sorts out the latest progress of the track, analyzes the current development status of the project, and discusses future trends.
Sentient: Building a loyal open source decentralized AI model
Project Overview
Sentient is an open source protocol platform that is building an AI Layer1 blockchain (the initial stage is Layer 2 and will be migrated to Layer 1), and builds a decentralized artificial intelligence economy by combining AI Pipeline and blockchain technology. Its core goal is to solve the problems of model attribution, call tracking and value distribution in the centralized LLM market through the "OML" framework (open, profitable, and loyal). This enables the AI model to achieve on-chain ownership structure, call transparency and value sharing. Sentient’s vision is to enable anyone to build, collaborate, own and monetize AI products, thereby promoting a fair and open AI Agent network ecosystem.
The Sentient Foundation team brings together world-leading academic experts, blockchain entrepreneurs and engineers to build a community-driven, open source, and verifiable AGI platform. Core members include Princeton University professor Pramod Viswanath and Indian Institute of Science Himanshu Tyagi, respectively responsible for AI security and privacy protection. Polygon co-founder Sandeep Nailwal leads the blockchain strategy and ecological layout. The team members' backgrounds span well-known companies such as Meta, Coinbase, Polygon, and top universities such as Princeton University and Indian Institute of Technology, covering AI/ML, NLP, computer vision and other fields, and working together to promote the implementation of the project.
As a secondary entrepreneurial project by Sandeep Nailwal, co-founder of Polygon, Sentient has its own halo at the beginning of its establishment, with rich resources, connections and market awareness, providing a strong endorsement for project development. In mid-2024, Sentient completed a $85 million seed round led by Founders Fund, Pantera and Framework Ventures, and other investment institutions include dozens of well-known VCs including Delphi, Hashkey and Spartan.
Design architecture and application layer
1. Infrastructure layer
Core architecture
The core architecture of Sentient consists of two parts: AI Pipeline and blockchain system:
The AI pipeline is the basis for developing and training "loyalty AI" artifacts, and consists of two core processes:
· Data Curation: A community-driven data selection process for model alignment.
Loyalty Training: Ensure that the model remains consistent with the community’s intentions.
The blockchain system provides transparency and decentralized control for protocols, ensuring ownership, usage tracking, profit distribution and fair governance of AI artifacts. The specific architecture is divided into four layers:
· Storage layer: store model weights and fingerprint registration information;
· Distribution layer: Authorization contract control model call portal;
· Access layer: Verify whether the user is authorized through proof of permission;
· Incentive layer: The income routing contract allocates each call payment to the trainer, deployer and validator.

Sentient system workflow diagram
OML Model Framework
The OML framework (Open Open, Monetizable, Loyal) is the core concept proposed by Sentient, aiming to provide clear ownership protection and economic incentive mechanisms for open source AI models. By combining on-chain technology and AI native cryptography, the following features are:
· Openness: The model must be open source, with transparent code and data structures for community reproduction, auditing and improvement.
· Monetization: Each model call triggers a revenue stream, and the on-chain contract distributes the revenue to trainers, deployers, and validators.
· Loyalty: The model belongs to the contributor community, the direction of upgrades and governance are determined by the DAO, and the use and modification are controlled by the encryption mechanism.
AI-native Cryptography
AI native encryption uses the continuity of AI models, low-dimensional manifold structure and model differentiability characteristics to develop a "verifiable but not removable" lightweight security mechanism. Its core technology is:
· Fingerprint embedding: Insert a set of hidden query-response key-value pairs during training to form a model unique signature;
· Ownership verification protocol: Verify whether fingerprints are retained through a third-party detector (Prover) in the form of a query question;
· License calling mechanism: Before calling, you need to obtain the "permission credential" issued by the model owner, and the system will authorize the model to decode the input and return the exact answer.
This method can achieve "behavior-based authorization call + belonging verification" without recryption costs.
Model rights confirmation and safe execution framework
Sentient currently uses Melange hybrid security: fingerprint authentication, TEE execution, and on-chain contract sharing. Among them, the fingerprint method is the main line of OML 1.0 implementation, emphasizing the idea of "Optimistic Security", that is, the default compliance and violations can be detected and punished.
The fingerprinting mechanism is a key implementation of OML, which allows the model to generate unique signatures during the training phase by embedding specific "question-answer" pairs. With these signatures, model owners can verify attribution, preventing unauthorized replication and commercialization. This mechanism not only protects the rights and interests of model developers, but also provides traceable on-chain records for the usage behavior of the model.
In addition, Sentient introduced the Enclave TEE compute framework, which leverages trusted execution environments such as AWS Nitro Enclaves to ensure that the model responds only to authorization requests and prevents unauthorized access and use. Although TEE relies on hardware and poses certain security risks, its high performance and real-time advantages make it the core technology of current model deployment.
In the future, Sentient plans to introduce zero-knowledge proof (ZK) and fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) technologies to further enhance privacy protection and verifiability and provide more mature solutions for the decentralized deployment of AI models.

OML proposes evaluation and comparison of five verifiability methods
2. Application layer
Currently, Sentient's products mainly include the decentralized chat platform Sentient Chat, the open source model Dobby series, and the AI Agent framework
Dobby series models
SentientAGI has released several "Dobby" series of models, mainly based on the Llama model, focusing on the values of freedom, decentralization and cryptocurrency support. Among them, the style of the leashed version is more constrained and rational, suitable for scenes with steady output; the unhinged version tends to be free and bold, with a richer dialogue style. The Dobby model has been integrated into multiple Web3 native projects, such as Firework AI and Olas, and users can also directly call these models in Sentient Chat for interaction. The Dobby 70B is the most decentralized model ever, with more than 600,000 owners (those who hold Dobby fingerprint NFTs are also co-owners of the model).
Sentient also plans to launch Open Deep Search, a search proxy system that attempts to surpass ChatGPT and Perplexity Pro. The system combines Sensient's search functions (such as query recaps, document processing) and inference agents to improve search quality through open source LLMs (such as Llama 3.1 and DeepSeek). On Frames Benchmark, its performance has surpassed other open source models and even approached some closed source models, showing strong potential.
Sentient Chat: Decentralized chat and on-chain AI Agent integration
Sentient Chat is a decentralized chat platform that combines open source large language models (such as the Dobby series) with an advanced inference proxy framework to support multi-agent integration and complex task execution. The platform-embedded inference agent can complete complex tasks such as search, calculation, and code execution, providing users with an efficient interactive experience. In addition, Sentient Chat also supports direct integration of on-chain agents, currently including Astrology Agent Astro247, Crypto Analysis Agent QuillCheck, Wallet Analysis Agent Pond Base Wallet Summary, and Spiritual Guide Agent ChiefRaiin. Users can choose different smart agents to interact according to their needs. Sentient Chat will be used as a distribution and coordination platform for the agent. User questions can be routed to any integrated model or proxy to provide optimal response results.
AI Agent Framework
Sentient provides two major AI Agent frameworks:
· Sentient Agent Framework: A lightweight open source framework focused on automating Web tasks (such as searching and playing videos) through natural language instructions. The framework supports the construction of a closed loop of agents with perception, planning, execution and feedback, suitable for lightweight development of off-chain Web tasks.
· Sentient Social Agent: An AI system developed for social platforms such as Twitter, Discord and Telegram, supports automated interaction and content generation. Through multi-agent collaboration, the framework can understand the social environment and provide users with a more intelligent social experience. It can also integrate with the Sentient Agent Framework to further expand its application scenarios.
Ecology and participation methods
The Sentient Builder Program currently has a $1 million funding program that encourages developers to use their development kits to build AI Agents that are accessible through the Sentient Agent API and can run within the Sentient Chat ecosystem. The Ecological Partners announced by Sentient's official website cover project teams in multiple fields of Crypto AI, as follows

Sentient Ecological Map
In addition, Sentient Chat is currently in the beta stage and needs to be entered into the whitelist through the invitation code before accessing it. Ordinary users can submit waitlist. According to official information, there have been more than 50,000 users and 1,000,000 query records. Sentient Chat has 2,000,000 users waiting to join.
Challenges and prospects
Starting from the model side, Sentient is committed to solving the core problems such as aberration and untrustworthiness faced by large-scale language models (LLMs). Through OML framework and blockchain technology, it provides a clear ownership structure, usage tracking and behavioral constraints for the model, which greatly promotes the development of decentralized open source models.
With the resource support from Polygon co-founder Sandeep Nailwal, and endorsement from top VCs and industry partners, Sentient leads in resource integration and market attention. However, in the context of the current market gradually disenchanting high-valuation projects, whether Sentient can deliver truly influential decentralized AI products will be an important test for whether it can become a decentralized AI ownership standard. These efforts not only concern Sentient's own success, but also have a profound impact on the reconstruction of trust and decentralized development of the entire industry.
Sahara AI: Creating a decentralized AI world where everyone participates
Project Overview
Sahara AI is a decentralized infrastructure born for the new AI × Web3 paradigm dedicated to building an open, equitable and collaborative AI economy. The project uses decentralized ledger technology to realize on-chain management and transactions of data sets, models and intelligent agents, ensuring the sovereignty and traceability of data and models. At the same time, Sahara AI introduces transparent and fair incentives so that all contributors, including data providers, annotators and model developers, can obtain an immutable return on revenue during the collaboration process. The platform also protects contributors' ownership and ownership of AI assets through a license-free "copyright" system, and encourages open sharing and innovation.
Sahara AI provides a one-stop solution for services ranging from data collection, annotation to model training, AI Agent creation, AI asset trading, etc., covering the entire AI life cycle and becoming a comprehensive ecological platform to meet the needs of AI development. Its product quality and technical capabilities have been highly recognized by top global companies and institutions such as Microsoft, Amazon, MIT, Motherson Group and Snap, demonstrating strong industry influence and wide applicability.
Sahara is not just a scientific research project, but a deep technology platform jointly promoted by front-line technology entrepreneurs and investors and has a land-oriented approach. Its core architecture may become a key fulcrum for the implementation of AI × Web3 applications. Sahara AI has received a total of US$43 million in investment support from leading institutions such as Pantera Capital, Binance Labs, and Sequoia China; it was co-founded by Sean Ren, tenured professor at the University of Southern California, Samsung Fellow of 2023, and Tyler Zhou, former investment director of Binance Labs. The core team members come from top institutions such as Stanford University, UC Berkeley, Microsoft, Google, and Binance, integrating the deep accumulation of academia and industry.
Design architecture

Sahara AI architecture diagram
1. Basic layer
The basic layers of Sahara AI are divided into: 1. The upper-chain layer is used for registration and monetization of AI assets, and 2. The lower-chain layer is used to run Agents and AI services. It is composed of on-chain systems and off-chain systems, which are responsible for the registration, rights confirmation, execution and profit distribution of AI assets, and support the trusted collaboration of the entire AI life cycle.
Sahara Blockchain and SIWA Test Network (on-chain infrastructure)
SIWA Test Network is the first public version of the Sahara blockchain. The Sahara Blockchain Protocol (SBP) is the core of the Sahara Blockchain. It is a smart contract system specially built for AI, which realizes on-chain ownership, traceability records and profit distribution of AI assets. The core modules include asset registration system, ownership agreement, contribution tracking, permission management, income distribution, execution proof, etc., to build an "on-chain operating system" for AI.
AI execution protocol (off-chain infrastructure)
In order to support the credibility of model operation and call, Sahara also built an off-chain AI execution protocol system, combining with a trusted execution environment (TEE), supporting Agent creation, deployment, operation and collaborative development. Each task execution automatically generates a verifiable record and uploads it to the chain to ensure that the entire process is traceable and verifiable. The on-chain system is responsible for registration, authorization and ownership records, while the off-chain AI execution protocol supports the real-time operation and service interaction of AI Agent. Because Sahara is cross-chain compatible, applications built on Sahara AI-based infrastructure can be deployed on any chain, or even off-chain.
2. Application layer
Sahara AI Data Service Platform (DSP)
The Data Service Platform (DSP) is the basic module of the Sahara application layer. Anyone can accept data tasks through Sahara ID, participate in data annotation, denoising and auditing, and receive on-chain points rewards (Sahara Points) as contribution certificates. This mechanism not only guarantees data traceability and ownership, but also promotes the formation of a closed loop of "contribution-reward-model optimization". The fourth season of the event is currently underway, which is also the main way for ordinary users to participate in the contribution.
On this basis, in order to encourage users to submit high-quality data and services, by introducing the dual incentive mechanism, you can not only receive rewards provided by Sahara, but also obtain additional returns from ecological partners, achieving one-time contribution and multi-party benefits. Take data contributors as an example. Once their data is repeatedly called by the model or used to generate new applications, they can continue to gain benefits and truly participate in the AI value chain. This mechanism not only extends the life cycle of data assets, but also injects strong momentum into collaboration and co-construction. For example, MyShell on BNB Chain generates customized data sets through DSP crowdsourcing to improve model performance, while users receive MyShell token incentives, forming a win-win closed loop.
AI enterprises can crowdsourcing custom data sets based on data service platforms, and quickly get responses from data annotators located around the world by publishing specialized data tasks. AI companies no longer rely solely on traditional centralized data suppliers, but can obtain high-quality labeled data on a large scale.
Sahara AI Developer Platform
Sahara AI Developer Platform is a one-stop AI construction and operation platform for developers and enterprises, providing full process support from data acquisition, model training to deployment execution and asset monetization. Users can directly call high-quality data resources in Sahara DSP and use them for model training and fine-tuning; the processed models can be combined, registered and put on the AI market within the platform, and ownership confirmation and flexible authorization can be achieved through the Sahara blockchain.
Studio also integrates decentralized computing capabilities, supports model training and deployment and operation of Agents, ensuring the security and verifiability of the computing process. Developers can also store key data and models, encrypted hosting and permission control, preventing unauthorized access. Through the Sahara AI AI Developer Platform, developers can build, deploy and commercialize AI applications without building their own infrastructure, and fully integrate into the on-chain AI economic system through protocol mechanisms.
AI Markerplace
Sahara AI Marketplace is a decentralized asset market for models, datasets and AI Agents. It not only supports the registration, transaction and authorization of assets, but also builds a transparent and traceable income distribution mechanism. Developers can register the models they built or collected data sets as on-chain assets, set flexible usage authorization and profit sharing ratios, and the system will automatically perform revenue settlement based on the call frequency. Data contributors can also continuously obtain profits due to repeated calls from their data, achieving "continuous monetization".
This market is deeply integrated with the Sahara blockchain protocol, and all asset transactions, calls, and profit distribution records will be verified on-chain to ensure that the asset ownership is clear and the returns are traceable. With this market, AI developers no longer rely on traditional API platforms or centralized model hosting services, but have an autonomous and programmable commercial path.
3. Ecological layer
The ecological layer of Sahara AI connects data providers, AI developers, consumers, corporate users and cross-chain partners. Whether you want to contribute information, develop applications, use products, or promote internal AI, you can play a role and find a profit model. Data markers, model development teams and computing power providers can register their resources as on-chain assets, authorize and share profits through Sahara AI's protocol mechanism, so that every resource used can automatically get returns. Developers can directly commercialize their results in AI Marketplace through a one-stop platform for connecting data, training models, and deploying agents.
Ordinary users can participate in data tasks, use AI Apps, collect or invest in assets on the chain, and become part of the AI economy without technical background. For enterprises, Sahara provides full process support from data crowdsourcing, model development to private deployment and profit monetization. In addition, Sahara supports cross-chain deployment. Any public chain ecosystem can use the protocols and tools provided by Sahara AI to build AI applications and access decentralized AI assets, so as to achieve compatibility and expansion with the multi-chain world. This makes Sahara AI not only a single platform, but also an underlying collaboration standard for the on-chain AI ecosystem.
Ecological progress
Since the project was launched, Sahara AI has not only provided a set of AI tools or computing power platforms, but also reconstructs the production and distribution order of AI on the chain and creates a decentralized collaboration network where everyone can participate, confirm rights, contribute and share. Because of this, Sahara chose to use blockchain as the underlying architecture to build a verifiable, traceable and allocable economic system for AI.
Around this core goal, the Sahara ecosystem has made significant progress. While still in the private testing stage, the platform has generated more than 3.2 million on-chain accounts in total, and the daily active accounts are stable at more than 1.4 million, showing user participation and network vitality. Among them, more than 200,000 users participated in data annotation, training and verification tasks through the Sahara data service platform and received on-chain incentive rewards. At the same time, millions of users are still waiting to be added to the whitelist, confirming the strong demand and consensus of the market for decentralized AI platforms.
In terms of enterprise cooperation, Sahara has established cooperation with leading global institutions such as Microsoft, Amazon, and MIT to provide them with customized data collection and labeling services. Enterprises can submit specific tasks through the platform, and efficiently execute a network composed of Sahara's global data annotators to achieve large-scale crowdsourcing, and the advantages of implementation efficiency, flexibility, and diversified demand support.

Sahara AI Ecological Map
How to participate
SIWA will be launched in four phases. The first stage is currently laying the foundation for on-chain data ownership, and contributors can register and tokenize their own data sets. Currently open to the public, no whitelist is required. It is necessary to ensure that data is uploaded useful to AI, and plagiarism or inappropriate content may be processed. The second stage realizes on-chain monetization of data sets and models. The third phase opens the test network and opens the source protocol. The fourth phase introduces AI data flow registration, traceability and contribution proof mechanisms.

SIWA Test Network
In addition to the SIWA test network, ordinary users can participate in Sahara Legends at this stage and understand the functions of Sahara AI through gamified tasks. After completing the task, harvest the Guardian fragments, and finally, a NFT can be synthesized to record the contribution to the network.
Or label data on the data service platform, contribute valuable data, and serve as an auditor. Sahara's follow-up plan and ecological partners jointly publish tasks, allowing participants to receive incentives from ecological partners in addition to Sahara's points. The first dual reward mission is held together with Myshell. Users can earn Sahara points and Myshell token rewards after completing the mission. According to the roadmap, Sahara is expected to launch its main network in Q3 2025, and it may also usher in TGE at that time.
Challenges and prospects
Sahara AI makes AI no longer limited to developers or large AI companies, making AI more open, inclusive and democratized. For ordinary users, participating in contributions and gaining benefits without programming knowledge, Sahara AI creates a decentralized AI world that everyone can participate in. For technical developers, Sahara AI opens up the Web2 and Web3 development paths, providing decentralized but flexible and powerful development tools and high-quality data sets.
For AI infrastructure providers, Sahara AI provides a new path to decentralized monetization of models, data, computing power and services. Sahara AI not only works on public chain infrastructure, but also takes the lead in core applications, using blockchain technology to promote the development of AI copyright systems. At this stage, Sahara AI has reached cooperation with several top AI institutions and has achieved initial success. Whether the subsequent success should be observed, the performance performance after the main network is launched, the development and adoption rate of ecological products, and whether the economic model can drive users to continue to contribute to the data set after TGE.
Ritual: Innovative design breaks through core AI problems such as
heterogeneous tasks
Project Overview
Ritual aims to solve the centralization, closure and trust problems existing in the current AI industry, providing AI with transparent verification mechanisms, fair computing resource allocation and flexible model adaptability; allowing any protocol, application or smart contract to integrate verifiable AI models in the form of several lines of code; and through its open architecture and modular design, it promotes the widespread application of AI on the chain and creates an open, secure and sustainable AI ecosystem.
Ritual completed a US$25 million Series A financing in November 2023, led by Archetype, participated by multiple institutions such as Accomplice and well-known angel investors, demonstrating market recognition and strong social capabilities of the team. Founders Niraj Pant and Akilesh Potti are both former partners at Polychain Capital. They have led investment in industry giants such as Offchain Labs and EigenLayer, showing profound insight and judgment. The team has rich experience in cryptography, distributed systems, AI and other fields. The consulting lineup includes project founders such as NEAR and EigenLayer, demonstrating its strong background and potential.
Design architecture
From the Internet to Ritual Chain
Ritual Chain is a second-generation product that naturally transitions from the Internet node network, representing Ritual's comprehensive upgrade on the decentralized AI computing network. Internet is the first phase of Ritual's launch and will be officially launched in 2023. This is a decentralized oracle network designed for heterogeneous computing tasks, aiming to solve the limitations of centralized APIs and allow developers to call transparent and open decentralized AI services more freely and stably.
Internet adopts a flexible and simple lightweight framework that quickly attracted more than 8,000 independent nodes after its launch due to its ease of use and efficiency. These nodes have diverse hardware capabilities, including GPUs and FPGAs, and provide powerful computing power for complex tasks such as AI inference and zero-knowledge proof generation. However, to keep the system simple, the Internet abandons some key features, such as through consensus coordinating points or integrating robust task routing mechanisms. These limitations make it difficult for the Internet to meet the needs of a wider range of Web2 and Web3 developers, prompting Ritual to launch a more comprehensive and powerful Ritual Chain.
Ritual Chain is the next generation Layer 1 blockchain designed for AI applications, aiming to make up for the limitations of the Internet and provide developers with a more robust and efficient development environment. Through Resonance technology, Ritual Chain provides the Internet network with a simple and reliable pricing and task routing mechanism, greatly optimizing resource allocation efficiency. In addition, Ritual Chain is based on the EVM++ framework, a backward compatible extension of Ethereum virtual machines (EVMs), with more powerful features including precompiled modules, scheduling, built-in account abstraction (AA), and a series of advanced Ethereum improvement proposals (EIPs). Together, these features create a powerful, flexible and efficient development environment, providing developers with new possibilities.

Ritual Chain Workflow Chart
Precompiled Sidecars
Compared with traditional precompilation, Ritual Chain's design improves the scalability and flexibility of the system, allowing developers to create custom functional modules in a containerized manner without modifying the underlying protocol. This architecture not only significantly reduces development costs, but also provides more powerful computing power for decentralized applications.
Specifically, Ritual Chain decouples complex computations from execution clients through a modular architecture and implements them in the form of standalone Sidecars. These precompiled modules can efficiently handle complex computing tasks, including AI inference, zero-knowledge proof generation, and trusted execution environment (TEE) operations.
Native Scheduling
Native scheduling solves the requirements of task timing triggering and conditional execution. Traditional blockchains usually rely on centralized third-party services (such as keeper) to trigger task execution, but this model has centralized risks and high costs. Ritual Chain completely gets rid of its dependence on centralized services through the built-in scheduler. Developers can directly set the entry point and callback frequency of smart contracts on the chain. Block producers maintain the pending calls to the mapping table, prioritizing these tasks when generating new blocks. Combined with Resonance's dynamic resource allocation mechanism, Ritual Chain can efficiently and reliably handle computing-intensive tasks, providing stable guarantees for decentralized AI applications.
Technological innovation
Ritual’s core technological innovations ensure its leading position in performance, verification, and scalability, providing strong support for on-chain AI applications.
1. Resonance: Optimize resource allocation
Resonance is a bilateral market mechanism that optimizes blockchain resource allocation to solve the complexity of heterogeneous transactions. As blockchain transactions evolve from simple transfers to diversified forms such as smart contracts and AI reasoning, existing fee mechanisms (such as EIP-1559) are difficult to efficiently match user needs and node resources. Resonance achieves the best matching between user transactions and node capabilities by introducing two core roles, Broker and Auctioneer:
Broker is responsible for analyzing the user's transaction fee intention and the node's resource cost function to achieve the best match between transactions and nodes and improve the utilization rate of computing resources. Auctioneer organizes transaction fee allocation through bilateral auction mechanisms to ensure fairness and transparency. The node selects the transaction type based on its own hardware capabilities, while the user can submit transaction requirements based on priority conditions such as speed or cost.
This mechanism significantly improves the network's resource utilization efficiency and user experience, and further enhances the transparency and openness of the system through the decentralized auction process.

Under the Resonance mechanism: Auctioneer assigns appropriate tasks to nodes according to Broker 's analysis
2. Symphony: Improve verification efficiency
Symphony 则专注于提升验证效率,解决传统区块链「重复执行」模式在处理和验证复杂计算任务时的低效问题。Symphony 基于「执行一次,多次验证」(EOVMT)的模型,通过将计算与验证流程分离,大幅减少重复计算带来的性能损耗。计算任务由指定节点执行一次,计算结果通过网络广播,验证节点利用非交互证明(succinct proofs)确认结果的正确性,而无需重复执行计算。
Symphony 支持分布式验证,将复杂任务分解为多个子任务,由不同的验证节点并行处理,从而进一步提升验证效率,并确保隐私保护和安全性。Symphony 对可信执行环境(TEE)和零知识证明(ZKP)等证明系统高度兼容,为快速确认交易和隐私敏感的计算任务提供灵活支持。这一架构不仅显著降低了重复计算带来的性能开销,还确保了验证过程的去中心化和安全性。

Symphony 将复杂任务分解为多个子任务,由不同的验证节点并行处理
3. vTune:可追踪的模型验证
vTune 是Ritual 提供的一种用于模型验证和来源追踪的工具,对模型性能几乎没有影响,同时具备良好的抗干扰能力,特别适用于保护开源模型的知识产权并促进公平分发。vTune 结合了水印技术和零知识证明,通过嵌入隐蔽的标记实现模型来源追踪和计算完整性保障:
· 水印技术: 通过权重空间水印、数据水印或函数空间水印嵌入标记,即使模型公开,其归属仍可以被验证。特别是函数空间水印能够在无需访问模型权重的情况下,通过模型输出验证归属,从而实现更强的隐私保护和鲁棒性。
· 零知识证明: 在模型微调过程中引入隐蔽数据,用于验证模型是否被篡改,同时保护模型创建者的权益。
这一工具不仅为去中心化AI 模型市场提供了可信的来源验证,还显著提升了模型的安全性和生态透明性。
生态发展
Ritual 目前处于私有测试网阶段,对于普通用户来说参与机会较少;开发者可以申请并参与官方推出的Altar 和Realm 激励计划,加入Ritual 的AI 生态建设,获得来自官方的全栈技术支持以及资金支持。
目前官方公布了一批来自Altar 计划的原生应用:
· Relic: 基于机器学习的自动做市商(AMM),通过Ritual 的基础设施动态调整流动性池参数,实现费用和底层池的优化;
· Anima: 专注于基于LLM 的链上交易自动化工具,为用户提供流畅自然的Web3 交互体验;
· Tithe: AI 驱动的借贷协议,通过动态优化借贷池和信用评分,支持更广泛的资产类型。
此外,Ritual 还与多个成熟项目展开了深度合作,推动去中心化AI 生态的发展。例如,与Arweave 的合作为模型、数据和零知识证明提供了去中心化的永久存储支持;通过与StarkWare 和Arbitrum 的集成,Ritual 为这些生态系统引入了原生的链上AI 能力;此外,EigenLayer 提供的再质押机制为Ritual 的证明市场增加了主动验证服务,进一步增强了网络的去中心化和安全性。
挑战和展望
Ritual 的设计从分配、激励、验证等关键环节入手,解决了去中心化AI 面临的核心问题,同时通过vTune 等工具实现了模型的可验证性,突破了模型开源与激励的矛盾,为去中心化模型市场的构建提供了技术支撑。
当下Ritual 处于早期阶段,主要针对模型的推理阶段,产品矩阵正在从基础设施扩展至模型市场、L2 即服务(L2aaS)以及Agent 框架等领域。由于当下区块链仍处于私有测试阶段,Ritual 提出的先进的技术设计方案仍有待大规模公开落地,需要持续关注。期待随着技术的不断完善和生态的逐步丰富,Ritual 能够成为去中心化AI 基础设施的重要组成部分。
Gensyn:解决去中心化模型训练的核心问题
Project Overview
在人工智能加速演进、算力资源愈发稀缺的时代背景下,Gensyn 正试图重塑整个AI 模型训练的底层范式。
传统AI 模型训练流程,算力几乎被垄断在少数几家云计算巨头手中,训练成本高昂、透明度低,阻碍了中小团队与独立研究者的创新步伐。而Gensyn 的愿景正是打破这一「中心化垄断」结构,它主张将训练任务「下沉」至全球范围内无数个具备基本计算能力的设备上——无论是MacBook、游戏级GPU,还是边缘设备、闲置服务器,都可接入网络、参与任务执行、获取报酬。
Gensyn 成立于2020 年,专注于构建去中心化AI 计算基础设施。早在2022 年,团队便首次提出了意图在技术和制度层面重新定义AI 模型的训练方式:不再依赖封闭的云平台或巨型服务器集群,而是将训练任务下沉至全球范围内的异构计算节点之中,构建一个无需信任的智能计算网络。
2023 年,Gensyn 对其愿景进行了进一步拓展:构建一个全球连接、开源自治、无许可门槛的AI 网络——任何具备基本计算能力的设备,都可成为这个网络中的一份子。其底层协议基于区块链架构设计,不仅具备激励机制与验证机制的可组合性。
Gensyn 自创立以来,累计获得5060 万美元支持,投资方涵盖a16z、CoinFund、Canonical、Protocol Labs、Distributed Global 等共计17 家机构。其中,2023 年6 月由a16z 领投的A 轮融资被广泛关注,标志着去中心化AI 领域开始进入主流Web3 风投的视野。
团队核心成员背景也颇具分量:联合创始人Ben Fielding 曾在牛津大学攻读理论计算机科学,具备深厚的技术研究背景;另一位联合创始人Harry Grieve 则长期参与去中心化协议的系统设计与经济建模,为Gensyn 的架构设计与激励机制提供了坚实支撑。
设计架构
当前去中心化人工智能系统的发展正面临三大核心技术瓶颈:执行(Execution)、验证(Verification)与通信(Communication)。这些瓶颈不仅限制了大模型训练能力的释放,也制约了全球算力资源的公平整合与高效利用。Gensyn 团队在系统性研究基础上,提出了三项具有代表性的创新机制——RL Swarm、Verde 以及SkipPipe,针对上述问题分别构建了解决路径,推动了去中心化AI 基础设施从概念走向落地。
一、执行挑战:如何让碎片化设备协同高效训练大模型?
当前,大语言模型的性能提升主要依赖于「堆规模」策略:更大的参数量、更广的数据集以及更长的训练周期。但这也显著推高了计算成本——超大模型的训练往往需要被拆分至成千上万个GPU 节点,这些节点之间还需进行高频的数据通信与梯度同步。在去中心化场景下,节点分布地域广泛、硬件异构、状态波动性高,传统的中心化调度策略难以奏效。
为应对这一挑战,Gensyn 提出RL Swarm,一种点对点的强化学习后训练系统。其核心思路是将训练过程转化为一个分布式协作博弈。该机制分为「共享—批判—决策」三阶段:首先,节点独立完成问题推理并公开共享结果;随后,各节点对同伴答案进行评价,从逻辑性与策略合理性等角度提出反馈;最后,节点基于群体意见修正自身输出,生成更稳健的答案。该机制有效融合个体计算与群体协同,尤其适用于数学与逻辑推理等需要高精度和可验证性的任务。实验显示,RL Swarm 不仅提升了效率,也显著降低了参与门槛,具备良好的扩展性和容错性。

RL Swarm 的「共享—批判—决策」三阶段强化学习训练系统
二、验证挑战:如何验证不可信供应者的计算结果是否正确?
在去中心化训练网络中,「任何人都可提供算力」是优势也是风险。问题在于:如何在无需信任的前提下验证这些计算是否真实有效?
传统方式如重计算或白名单审核存在明显局限——前者成本极高,不具可扩展性;后者又排除了「长尾」节点,损害网络开放性。Gensyn 为此设计了Verde,一套专为神经网络训练验证场景构建的轻量级仲裁协议。
Verde 的关键思想是「最小可信裁定」:当验证者怀疑供应者训练结果有误时,仲裁合约只需重算计算图中首个存在争议的操作节点,而无需重演整个训练过程。这大幅度降低了验证负担,同时确保了至少一方诚实时的结果正确性。为解决不同硬件间浮点非确定性问题,Verde 还配套开发了Reproducible Operators(可复现操作符库),强制对常见数学操作如矩阵乘法设置统一执行顺序,从而实现跨设备的位级一致输出。这一技术显著提升了分布式训练的安全性与工程可行性,是目前去信任验证体系中的重要突破。
整个机制建立在训练者记录关键中间状态(即检查点)的基础上,多个验证者被随机指派去复现这些训练步骤,从而判断输出的一致性。一旦有验证者复算结果与训练者存在分歧,系统不会粗暴地重跑整个模型,而是通过网络仲裁机制精确定位二者在计算图中首次发生分歧的操作,仅对该操作进行重放比对,从而以极低的开销实现争议裁决。通过这种方式,Verde 在无需信任训练节点的前提下,既保证了训练过程的完整性,又兼顾了效率与可扩展性,是为分布式AI 训练环境量身定制的验证框架。

Vader 的工作流程
三、通信挑战:如何减少节点间高频同步带来的网络瓶颈?
在传统的分布式训练中,模型要么被完整复制,要么被按层拆分(流水线并行),二者都要求节点间进行高频同步。特别是在流水线并行中,一个微批次必须严格按顺序经过每一层模型,导致只要某个节点延迟,就会阻塞整个训练流程。
Gensyn 针对这一问题提出SkipPipe:一种支持跳跃执行与动态路径调度的高容错流水线训练系统。SkipPipe 引入了「跳跃比例(skip ratio)」机制,允许某些微批数据在特定节点负载过高时跳过部分模型层,同时使用调度算法动态选择当前最优计算路径。实验显示,在地理分布广、硬件差异大、带宽受限的网络环境下,SkipPipe 训练时间可降低高达55%,并在高达50% 节点故障率时仍能维持仅7% 的损失,展现出极强的韧性和适应性。
How to participate
Gensyn 的公共测试网已于2025 年3 月31 日上线,目前仍处于其技术路线图中的初期阶段(Phase 0),其功能重心集中在RL Swarm 的部署与验证上。RL Swarm 是Gensyn 的第一个应用场景,围绕强化学习模型的协作训练进行设计。每一个参与节点都将其行为绑定至链上身份,贡献过程被完整记录,这为后续激励分配和可信计算模型提供了验证基础。

Gensyn 的节点排名
早期测试阶段的硬件门槛相对友好:Mac 用户使用M 系列芯片即可运行,Windows 用户则建议配备3090 或4090 等高性能GPU,以及16GB 以上内存,即可部署本地Swarm 节点。系统运行后通过网页登录邮箱(推荐Gmail)完成验证流程,并可选择是否绑定HuggingFace 的Access Token,以激活更完整的模型能力。
挑战和展望
目前Gensyn 项目最大的不确定性,在于其测试网尚未涵盖所承诺的完整技术栈。Verde 与SkipPipe 等关键模块仍处于待集成状态,这也使外界对其架构落地能力保持观望。官方给出的解释是:测试网将分阶段推进,每一阶段解锁新的协议能力,优先验证基础设施的稳定性与扩展性。首阶段以RL Swarm 为起点,未来将逐步拓展至预训练、推理等核心场景,最终过渡至支持真实经济交易的主网部署。
尽管测试网启动之初采用了相对保守的推进节奏,但值得关注的是,仅一个月后,Gensyn 即推出了支持更大规模模型与复杂数学任务的新Swarm 测试任务。此举在一定程度上回应了外界对其开发节奏的质疑,也展现出团队在局部模块推进上的执行效率。
然而,问题也随之而来:新版任务对硬件提出了极高门槛,推荐配置包括A100、H100 等顶级GPU(80GB 显存),这对于中小节点而言几乎不可达,也与Gensyn 所强调的「开放接入、去中心化训练」的初衷形成一定张力。算力的集中化趋势,若未得到有效引导,或将影响网络的公平性和去中心化治理的可持续性。
接下来,若Verde 与SkipPipe 能顺利集成,将有助于提升协议的完整性与协同效率。但Gensyn 能否在性能和去中心化之间找到真正的平衡,仍有待测试网更长时间、更广范围的实践检验。眼下,它已初步显现出潜力,也暴露出挑战,而这正是一个早期基础设施项目最真实的状态。
Bittensor:去中心化AI 网络的创新与发展
Project Overview
Bittensor 是一个结合区块链与人工智能的开创性项目,由Jacob Steeves 和Ala Shaabana 于2019 年创立,旨在构建「机器智能的市场经济」。两位创始人均具备人工智能和分布式系统的深厚背景。项目白皮书的署名作者Yuma Rao 被认为是团队核心技术顾问,为项目注入了密码学与共识算法方面的专业视角。
该项目旨在通过区块链协议整合全球算力资源,构建一个不断自我优化的分布式神经网络生态系统。这一愿景将计算、数据、存储和模型等数字资产转化为智能价值流,构建全新经济形态,确保AI 发展红利的公平分配。有别于OpenAI 等中心化平台,Bittensor 建立了三大核心价值支柱:
· 打破数据孤岛: 利用TAO 代币激励体系促进知识共享与模型贡献
· 市场驱动的质量评价: 引入博弈论机制筛选优质AI 模型,实现优胜劣汰
· 网络效应放大器: 参与者增长与网络价值呈指数级正相关,形成良性循环
在投资布局方面,Polychain Capital 自2019 年起孵化Bittensor,目前持有价值约2 亿美元的TAO 代币;Dao5 持有约价值5000 万美元的TAO,也是Bittensor 生态系统的早期支持者。2024 年,Pantera Capital 和Collab Currency 通过战略投资进一步加码。同年8 月,灰度集团将TAO 纳入其去中心化AI 基金,标志着机构投资者对项目价值的高度认可和长期看好。
设计架构与运行机制
网络架构
Bittensor 构建了一个由四个协同层级组成的精密网络架构:
· 区块链层: 基于Substrate 框架搭建,作为网络的信任基础,负责记录状态变化与代币发行。系统每12 秒生成新区块并按规则发行TAO 代币,确保网络共识与激励分配。
· 神经元层(Neuron): 作为网络的计算节点,神经元运行各类AI 模型提供智能服务。每个节点通过精心设计的配置文件明确声明其服务类型与接口规范,实现功能模块化和即插即用。
· 突触层(Synapse): 网络的通信桥梁,动态优化节点间连接权重,形成类神经网络结构,保障信息高效传递。突触还内置经济模型,神经元间的互动与服务调用需支付TAO 代币,形成价值流转闭环。
· 元图层(Metagraph): 作为系统的全局知识图谱,持续监测与评估各节点的贡献价值,为整个网络提供智能导向。元图通过精确计算确定突触权重,进而影响资源分配、奖励机制以及节点在网络中的影响力。

Bittensor 的网络框架
Yuma 共识机制
网络采用独特的Yuma 共识算法,每72 分钟完成一轮奖励分配。验证过程结合主观评价与客观度量:
· 人工评分: 验证者对矿工输出质量进行主观评价
· Fisher 信息矩阵: 客观量化节点对网络整体贡献
这种「主观+ 客观」的混合机制,有效平衡了专业判断与算法公正。
子网(Subnet)架构和dTAO 升级
每个子网专注于特定AI 服务领域,如文本生成、图像识别等,独立运行但与主区块链subtensor 保持连接,形成高度灵活的模块化扩展架构。2025 年2 月,Bittensor 完成了具有里程碑意义的dTAO(Dynamic TAO)升级,这一系统将每个子网转变为独立经济单元,通过市场需求信号智能调控资源分配。其核心创新是子网代币(Alpha 代币)机制:
· 运作原理: 参与者通过质押TAO 获取各子网发行的Alpha 代币,这些代币代表了对特定子网服务的市场认可与支持力度资源
· 分配逻辑: Alpha 代币的市场价格作为衡量子网需求强度的关键指标,初始状态下各子网Alpha 代币价格一致,每个流动性池内仅有1 个TAO 和1 个Alpha 代币。随着交易活跃度提升和流动性注入,Alpha 代币价格动态调整,TAO 的分配按子网代币价格占比智能分配,市场热度高的子网获得更多资源倾斜,实现真正的需求驱动型资源优化配置

Bittensor 子网代币排放分配
dTAO 升级显著提升了生态活力与资源利用效率,子网代币市场总市值已达5 亿美元,展现出强劲的增长动能。

Bittensor 子网alpha 代币价值
生态进展与应用案例
主网发展历程
Bittensor 网络经历了三个关键发展阶段:
· 2021 年1 月:主网正式启动,奠定基础架构
· 2023 年10 月:「Revolution」升级引入子网架构,实现功能模块化
· 2025 年2 月:完成dTAO 升级,建立市场驱动的资源分配机制
子网生态呈爆发式增长:截至2025 年6 月,已有119 个专业子网,预计年内可能突破200 个。

Bittensor 子网数量
生态项目类型多元化,覆盖AI 代理(如Tatsu)、预测市场(如Bettensor)、DeFi 协议(如TaoFi)等多个前沿领域,构成了AI 与金融深度融合的创新生态。
代表性子网生态项目
· TAOCAT: TAOCAT 是Bittensor 生态中的原生AI 代理,直接构建在子网上,为用户提供数据驱动的决策工具。利用Subnet 19 的大语言模型、Subnet 42 的实时数据以及Subnet 59 的Agent Arena,提供市场洞察和决策支持。获得DWF Labs 投资,纳入其2000 万美元AI 代理基金,并在binance alpha 上线。
· OpenKaito: 由Kaito 团队在Bittensor 上推出的子网,旨在构建去中心化的加密行业搜索引擎。目前已索引5 亿网页资源,展示了去中心化AI 处理海量数据的强大能力。与传统搜索引擎相比,其核心优势在于减少商业利益干扰,提供更透明、中立的数据处理服务,为Web3 时代信息获取提供新范式。
· Tensorplex Dojo: 由Tensorplex Labs 开发的52 号子网,专注于通过去中心化平台众包高质量人类生成数据集,鼓励用户通过数据标注赚取TAO 代币。2025 年3 月,YZi Labs(原Binance Labs)宣布投资Tensorplex Labs,支持Dojo 和Backprop Finance 的发展。
· CreatorBid: 运行在Subnet 6,是一个结合AI 和区块链的创作平台,与Olas 和其他GPU 网络(如io.net)集成,支持内容创作者和AI 模型开发。
技术与行业合作
Bittensor 在跨领域合作方面取得了突破性进展:
· 与Hugging Face 建立深度模型集成通道,实现50 个主流AI 模型的链上无缝部署
· 2024 年携手高性能AI 芯片制造商Cerebras 联合发布BTLM-3B 模型,累计下载量突破16 万次
· 2025 年3 月与DeFi 巨头Aave 达成战略合作,共同探索rsTAO 作为优质借贷抵押品的应用场景
How to participate
Bittensor 设计了多元化的生态参与路径,形成完整的价值创造与分配体系:
· 挖矿: 部署矿工节点生产高质量数字商品(如AI 模型服务),根据贡献质量获取TAO 奖励
· 验证: 运行验证者节点评估矿工工作成果,维护网络质量标准,获取相应TAO 激励
· 质押: 持有并质押TAO 支持优质验证者节点,根据验证者表现获取被动收益
· 开发: 利用Bittensor SDK 和CLI 工具构建创新应用、实用工具或全新子网,积极参与生态建设
· 使用服务: 通过友好的客户端应用界面使用网络提供的AI 服务,如文本生成或图像识别
· 交易: 参与子网资产化代币的市场交易,捕捉潜在价值增长机会

子网alpha 代币给参与者的分配
挑战和展望
Bittensor 尽管展现出卓越潜力,但作为前沿技术探索,仍面临多维度挑战。在技术层面,分布式AI 网络面临的安全威胁(如模型窃取与对抗攻击)比中心化系统更为复杂,需持续优化隐私计算与安全防护方案;经济模型方面,早期存在通胀压力,子网代币市场波动性较高,需警惕可能的投机泡沫;监管环境上,虽然SEC 已将TAO 归类为效用型代币,但全球各地区监管框架差异仍可能限制生态扩张;同时,面对资源雄厚的中心化AI 平台激烈竞争,去中心化解决方案需在用户体验和成本效益方面证明其长期竞争优势。
随着2025 年减半周期临近,Bittensor 发展将聚焦四大战略方向:进一步深化子网专业化分工,提升垂直领域应用的服务质量与性能;加速与DeFi 生态的深度整合,借助新引入的EVM 兼容性拓展智能合约应用边界;通过dTAO 机制在未来100 天内平稳将网络治理权重从TAO 逐步转向Alpha 代币,推动治理去中心化进程;同时积极拓展与其他主流公链的互操作性,扩大生态边界与应用场景。这些协同发展的战略举措将共同推动Bittensor 向「机器智能市场经济」的宏伟愿景稳步迈进。
0G:以存储为基础的模块化AI 生态系统
Project Overview
0G 是一个专为AI 应用设计的模块化Layer 1 公链,旨在为数据密集型和高计算需求场景提供高效、可靠的去中心化基础设施。通过模块化架构,0G 实现了共识、存储、计算和数据可用性等核心功能的独立优化,支持动态扩展,能够高效处理大规模AI 推理和训练任务。
创始团队由Michael Heinrich(CEO,曾创立融资超1 亿美元的Garten)、Ming Wu(CTO,微软研究员,Conflux 联合创始人)、Fan Long(Conflux 联合创始人)和Thomas Yao(CBO,Web3 投资者)组成,拥有8 名计算机科学博士,成员背景涵盖微软、苹果等,具备深厚的区块链和AI 技术经验。
融资方面,0G Labs 完成3500 万美元Pre-seed 轮和4000 万美元Seed 轮,总计7500 万美元,投资方包括Hack VC、Delphi Ventures 和Animoca Brands 等。此外,0G Foundation 获得2.5 亿美元代币购买承诺、3060 万美元公开节点销售和8888 万美元生态基金。
设计架构
1、0G Chain
0G Chain 的目标是打造最快的模块化AI 公链,其模块化架构支持对共识、执行和存储等关键组件进行独立优化,并集成了数据可用性网络、分布式存储网络和AI 计算网络。这种设计为系统在应对复杂的AI 应用场景时提供了卓越的性能和灵活性。以下是0G Chain 的三大核心特色:
模块化可扩展性(Modular Scalability for AI)
0G 采用横向可扩展的架构,能够高效处理大规模的数据工作流。其模块化设计将数据可用性层(DA 层)与数据存储层分离,为AI 任务(如大规模训练或推理)的数据访问和存储提供了更高的性能和效率。
0G 共识(0G Consensus)
0G 的共识机制由多个独立的共识网络组成,这些网络可以根据需求动态扩展。随着数据量的指数级增长,系统吞吐量也能同步提升,支持从1 个到数百甚至上千个



